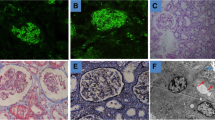
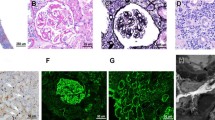
Abstract
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is still an underestimated disorder which affects multiple organs, and its recognition as a distinct clinical disease has been only proved in the recent decades. The renal involvement has been documented in approximately 15% of patients with IgG4-RD, and the typical manifestation is a tubulo-interstitial nephritis. The main histological findings in IgG4-RD are typically a dense tissue infiltration of IgG4-positive plasma cells, storiform fibrosis, obliterative phlebitis, and frequently elevated IgG4 serum levels. Herein we report our atypical and peculiar clinical presentation of an IgG4-related nephropathy (IgG4-RN) and the remarkable response to rituximab (RTX) treatment at the renal imaging with computerized tomography assessment. The current nephrological evidences support the renal function recovery after steroids or steroids plus RTX therapy, even if the renal imaging data are not always shown. In a complex and enigmatic clinical scenario such as the IgG4-RN, both the renal biopsy and the renal imaging before and after the immunosuppressive therapy become mandatory tools to thoroughly define the diagnosis, the management and the response to the immunological therapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stone JH, Khosroshahi A, Deshpande V, et al. Recommendations for the nomenclature of IgG4-related disease and its individual organ system manifestations. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(10):3061–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.34593.
Bledsoe JR, Della-Torre E, Rovati L, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease: review of the histopathologic features, differential diagnosis, and therapeutic approach. APMIS. 2018;126(6):459–76. https://doi.org/10.1111/apm.12845.
Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. Introduction Semin Diagn Pathol. 2012;29(4):175–6. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.semdp.2012.07.006.
Sarles H, Sarles JC, Muratore R, Guien C. Chronic inflammatory sclerosis of the pancreas–an autonomous pancreatic disease? Am J Dig Dis. 1961;6:688–98.
Aoki S, Nakazawa T, Ohara H, et al. Immunohistochemical study of autoimmune pancreatitis using anti-IgG4 antibody and patients’ sera. Histopathology. 2005;47(2):147–58.
Deshpande V, Mino-Kenudson M, Brugge W, Lauwers GY. Autoimmune pancreatitis: more than just a pancreatic disease? A contemporary review of its pathology. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2005;129(9):1148–54.
Igarashi H, Ito T, Oono T, Nakamura T, et al. Relationship between pancreatic and/or extrapancreatic lesions and serum IgG and IgG4 levels in IgG4-related diseases. J Dig Dis. 2012;13(5):274–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-2980.2012.00583.x.
Raissian Y, Nasr SH, Larsen CP, et al. Diagnosis of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22(7):1343–52. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2011010062.
Saeki T, Nishi S, Imai N, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of patients with IgG4-related tubulointerstitialnephritis. Kidney Int. 2010;78(10):1016–23. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2010.271.
Cortazar FB, Stone JH. IgG4-related disease and the kidney. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015;11(10):599–609. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2015.95.
Pradhan D, Pattnaik N, Silowash R, Mohanty SK. IgG4-related kidney disease–A review. Pathol Res Pract. 2015;211(10):707–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2015.03.004.
Zhang P, Cornell LD. IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2017;24(2):94–100. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ackd.2016.12.001.
Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2012;25(9):1181–92. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2012.72.
Salvadori M, Tsalouchos A. Immunoglobulin G4-related kidney diseases: an updated review. Word J Nephrol. 2018;7(19):29–40.
Hara S, Kawano M, Mizushima I, et al. Distribution and components of interstitial inflammation and fibrosis in IgG4-related kidney disease: analysis of autopsy specimens. Hum Pathol. 2016;55:164–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2016.05.010.
Raissian Y, Nasr SH, Larsen CP, et al. Diagnosis of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2011010062.
Kawano M, Saeki T. IgG4-related kidney disease–an update. Curr Op in Nephrol Hypertens. 2015;24(2):193–201. https://doi.org/10.1097/MNH.0000000000000102.
Vaglio A, Salvarani C, Buzio C. Retroperitoneal fibrosis. Lancet. 2006;367(9506):241–51.
Quattrocchio G, Roccatello D. IgG4-related nephropathy. J Nephrol. 2016;29(4):487–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-016-0279-4.
Wallace ZS, Deshpande V, Mattoo H, et al. IgG4-related disease: clinical and laboratory features in one hundred twenty-five patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(9):2466–75. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.39205.
Kawano M, Saeki T, Nakashima H, et al. Proposal for diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2011;15(5):615–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-011-0521-2.
Kim B, Kim JH, Byun JH, et al. IgG4-related kidney disease: MRI findings with emphasis on the usefulness of diffusion-weighted imaging. Eur J Radiol. 2014;83(7):1057–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2014.03.033.
Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(6):539–51. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1104650.
Kamisawa T, Okazaki K. Diagnosis and Treatment of IgG4-Related Disease. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017;401:19–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/82_2016_36.
Khosroshahi A, Wallace ZS. Crowe JL et al International Consensus Guidance Statement on the Management and Treatment of IgG4-Related Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(7):1688–99. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.39132.
Masaki Y, Shimizu H, Sato Nakamura T, et al. IgG4-related disease: diagnostic methods and therapeutic strategies in Japan. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2014;54(2):95–101.
Kamisawa T, Shimosegawa T, Okazaki K, et al. Standard steroid treatment for autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut. 2009;58:1504–7.
Ghazale A, Chari ST. Optimising corticosteroid treatment for autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut. 2007;56:1650–2.
Ghazale A, Chari ST, Zhang L, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis: clinical profile and response to therapy. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:706–15.
Raina A, Yadav D, Krasinskas AM, et al. Evaluation and management of autoimmune pancreatitis: experience at a large US center. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:2295–306.
Kamisawa T, Okazaki K, Kawa S, et al. Amendment of the Japanese Consensus Guidelines for Autoimmune Pancreatitis, 2013. III. Treatment and prognosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 2014;49:961–70.
Mizushima I, Yamada K, Fujii H, et al. Clinical and histological changes associated with corticosteroid therapy in IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2012;22(6):859–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-011-0589-2.
Mise N, Tomizawa Y, Fujii A, Yamaguchi Y, Sugimoto T. A case of tubulointerstitial nephritis in IgG4-related systemic disease with markedly enlarged kidneys. NDT Plus. 2009;2(3):233–5. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndtplus/sfp023.
Carruthers MN, Topazian MD, Khosroshahi A, et al. Rituximab for IgG4-related disease: a prospective, open-label trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(6):1171–7. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206605.
Yamamoto M, Awakawa T, Takahashi H. Is rituximab effective for IgG4-related disease in the long term? Experience of cases treated with rituximab for 4 years. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(8):e46.
Khosroshahi A, Carruthers MN, Deshpande V, Unizony S, Bloch DB, Stone JH. Rituximab for the treatment of IgG4-related disease: lessons from 10 consecutive patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2012;91(1):57–66. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0b013e3182431ef6.
Roccatello D, Sciascia S, Rossi D, Alpa M, Naretto C, Baldovino S. Intensive short-term treatment with rituximab, cyclophosphamide and methylprednisolone pulses induces remission in severe cases of SLE with nephritis and avoids further immunosuppressive maintenance therapy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26(12):3987–92. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfr109.
Hart PA, Topazian MD, Witzig TE, et al. Treatment of relapsing autoimmune pancreatitis with immunomodulators and rituximab: the Mayo Clinic experience. Gut. 2013;62:1607–15.
Khosroshahi A, Carruthers MN, Deshpande V, et al. Rituximab for the treatment of IgG4-related disease: lessons from 10 consecutive patients with IgG4-related disease. Medicine (Baltimore). 2012;91:57–66.
Soh SB, Pham A, O’Hehir RE, et al. Novel use of rituximab in a case of Riedel’s thyroiditis refractory to glucocorticoids and tamoxifen. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98:3543–9.
Funding
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose, and no funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
The patient has consented to the submission of the case report to the journal.
Ethical approval
Approved by the Local Ethical Committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spatola, L., Ravera, F., Sghirlanzoni, M.C. et al. An enigmatic case of IgG4-related nephropathy and an updated review of the literature. Clin Exp Med 21, 493–500 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-021-00696-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-021-00696-x