Abstract
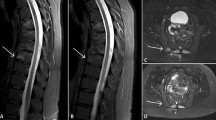
We describe the case of a 63-year-old female who presented with severe inflammatory spondylitis, refractory to various antibiotics. Mycobacterial and fungal osteomyelitis were unlikely. Although asymptomatic, she also had osteomyelitis in the sternocostoclavicular region, and was suspected of having synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis (SAPHO) syndrome, against which minocycline showed marked efficacy. The presence of severe inflammatory SAPHO, albeit rare, together with the marked efficacy of tetracycline, should be noted.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chamot AM, Benhamou CL, Kahn MF, Beraneck L, Kaplan G, Prost A. Acne-pustulosis-hyperostosis-osteitis syndrome. Results of a national survey. 85 cases. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic. 1987;54:187–96.
Kahn MF, Khan MA. The SAPHO syndrome. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol. 1994;8:333–62.
Vittecoq O, Said LA, Michot C, Mejjad O, Thomine JM, Mitrofanoff P, et al. Evolution of chronic multifocal osteitis toward spondyloarthropathy over the long term. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:109–19.
Hayem G, Bouchaud-Chabot A, Benali K, Roux S, Palazzo E, Silbermann-Hoffman O, et al. SAPHO syndrome: a long-term follow-up of 120 cases. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1999;29:159–71.
Rohekar G, Inman RD. Conundrums in nosology: synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis syndrome and spondylarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;55:665–9.
Hurtado-Nedelec M, Cholett-Martin S, Nicaise-Roland P, Grootenboer-Mignot S, Ruimy R, Meyer O, et al. Characterization of the immune response in the synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis (SAPHO) syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008;47:1160–7.
Rozin AP. SAPHO syndrome: is a range of pathogen-associated rheumatic diseases extended? Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11:131.
Assmann G, Kueck O, Kirchhoff T, Rosenthal H, Voswinkel J, Pfreundschuh M, et al. Efficacy of antibiotic therapy for SAPHO syndrome is lost after its discontinuation: an interventional study. Arthitis Res Ther. 2009;11:R140.
Colina M, Lo Monaco A, Khodeir M, Trotta F. Propionibacterium acnes and SAPHO syndrome: a case report and literature review. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007;25:457–60.
Kalke S, Perera SD, Patel ND, Gordon TE, Dasgupta B. The sternoclavicular syndrome: experience from a district general hospital and results of a national postal survey. Rheumatology. 2001;40:170–7.
Jansson A, Renner ED, Ramser J, Mayer A, Haban M, Meindl A, et al. Classification of non-bacterial osteitis: retrospective study of clinical, immunological and genetic aspects in 89 patients. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007;46:154–60.
Ferguson PJ, Sandu M. Current understanding of the pathogenesis and management of chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2012;14:130–41.
Takigawa T, Tanaka M, Nakanishi K, Misawa H, Sugimoto Y, Takahata T, et al. SAPHO syndrome associated spondylitis. Eur Spine J. 2008;17:1391–7.
Schaeverbeke T, Lequen L, de Barbeyrac B, Labbé L, Bébéar CM, Morrier Y, et al. Propionibacterium acnes isolated from synovial tissue and fluid in a patient with oligoarthritis associated with acne and pustulosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41:1889–93.
Ballara SC, Siraj QH, Maini RN, Venables PJ. Sustained response to doxycycline therapy in two patients with SAPHO syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42:819–21.
Perry A, Lambert P. Propionibacterium acnes: infection beyond the skin. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2011;9:1149–56.
Colina M, Govoni M, Orzincolo C, Trotta F. Clinical and radiologic evolution of synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis syndrome: a single center study of a cohort of 71 subjects. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;61:813–21.
Griffin MO, Ceballos G, Villarreal FJ. Tetracycline compounds with non-antimicrobial organ protective properties: possible mechanisms of action. Pharm Res. 2011;63:102–7.
Pang T, Wang J, Benicky J, Saavedra JM. Minocycline ameliorates LPS-induced inflammation in human monocytes by novel mechanisms including LOX-1, Nur77 and LITAF inhibition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1820:503–10.
Zhao Z, Li Y, Li Y, Zhao H, Li H. Synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis and osteitis (SAPHO) syndrome with review of the relevant published work. J Dermatol. 2011;38:155–9.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Takizawa, Y., Murota, A., Setoguchi, K. et al. Severe inflammation associated with synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis (SAPHO) syndrome was markedly ameliorated by single use of minocycline. Mod Rheumatol (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-013-0843-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-013-0843-x