Abstract
Background
The role of pembrolizumab in the treatment of poor performance status (PS) patients remains unclear.
Patients and methods
We conducted a phase II trial to investigate the efficacy and safety of pembrolizumab as first-line therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with PSs of 2–3 and programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression ≥ 50%. The primary endpoint of this study was the objective response rate (ORR).
Results
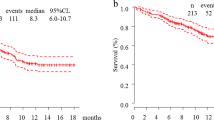
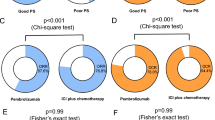
Fourteen patients treated at eight institutions were enrolled. Most patients had PS 2 (12/14; 86%) and others had PS 3 (2/14; 14%). The ORR was 57.1% (95% confidence interval 28.9–82.3%), which met the primary endpoint. The median progression-free survival (PFS) and 1-year PFS rates were 5.8 months and 20.0%, respectively. At the time of data cut-off, one patient had received treatment for more than 1 year; another patient had received treatment for more than 2 years. Nine patients had improved PS with treatment (Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p = 0.003). Two patients had immune-related adverse events ≥ grade 3: grades 5 and 3 elevation in alanine and aspartate aminotransferases. Two PS 3-stage patients were diagnosed with clinically progressive disease prior to initial computed tomography; both died within 2 months.
Conclusion
Pembrolizumab was effective for the treatment of NSCLC patients with a poor PS and PD-L1 level ≥ 50%. However, given the poor outcomes of the PS 3 patients, the drug is not indicated for such patients. Adverse events, including liver dysfunction, should be carefully monitored.
Registration ID
UMIN000030955.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed in this report are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Gandhi L, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Gadgeel S et al (2018) Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 378:2078–2092. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1801005
Reck M, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG et al (2016) Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 375:1823–1833. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1606774
Gridelli C, Ardizzoni A, Le Chevalier T et al (2004) Treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients with ECOG performance status 2: results of an European Experts Panel. Ann Oncol Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol 15:419–426. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdh087
Lilenbaum RC, Herndon JE, List MA et al (2005) Single-agent versus combination chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: the cancer and leukemia group B (study 9730). J Clin Oncol 23:190–196. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2005.07.172
Langer CJ, Li S, Schiller J et al (2007) Randomized phase II trial of paclitaxel plus carboplatin or gemcitabine plus cisplatin in Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status 2 non-small-cell lung cancer patients: ECOG 1599. J Clin Oncol 25:418–423. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2005.04.9452
Zukin M, Barrios CH, Pereira JR et al (2013) Randomized phase III trial of single-agent pemetrexed versus carboplatin and pemetrexed in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 2. J Clin Oncol 31:2849–2853. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2012.48.1911
Ahn B-C, Pyo K-H, **n C-F et al (2019) Comprehensive analysis of the characteristics and treatment outcomes of patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with anti-PD-1 therapy in real-world practice. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 145:1613–1623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-02899-y
Kano H, Ichihara E, Harada D et al (2020) Utility of immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with poor performance status. Cancer Sci 111:3739–3746. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.14590
Middleton G, Brock K, Savage J et al (2020) Pembrolizumab in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer of performance status 2 (PePS2): a single arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Respir Med 8:895–904. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30033-3
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Masafumi Fujii of the Kawasaki College of Allied Health Professions (a member of the Safety Review Committee). We also thank all investigators at the participating institutions. All authors contributed to study coordination among the various hospitals. We received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sector.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
E. Ichihara has received honoraria from Eli Lilly Japanand research funds from MSD, Ono Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., and Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K. T. Kubo has received honoraria from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. T. Kozuki has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly Japan, and Ono Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., and research funds from MSD, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Taiho Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Daiichi-Sankyo Co. Ltd and Merck. S. Kuyama has received honoraria from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. K. Hotta received honoraria from Pfizer, AZ, Chugai, Lilly, Takeda, MSD, BMS, Ono, Taiho, and Boehringer-Ingelheim, and research funds from MSD, AZ, Chugai, Lilly, BMS, and Abbvie outside the submitted work. A. Bessho has received research funds from Ono Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., AstraZeneca, MSD, and Chugai Pharmaceutical CO. Ltd. Y. Maeda has received honoraria from Novartis and research funds from Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Eisai, MSD, Asahi Kasei Pharma, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Nippon Shinyaku Co. Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Kyowa Kirin, Astellas, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., and Mundipharma K.K. K. Kiura has received honoraria from MSD and research funds from Nippon Kayaku Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Ono Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Bristol Myers Squibb, Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Taiho Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Shionogi Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Boehringer Ingelheim, and MSD.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Hosokawa, S., Ichihara, E., Harada, D. et al. Pembrolizumab in advanced NSCLC patients with poor performance status and high PD-L1 expression: OLCSG 1801. Int J Clin Oncol 27, 1139–1144 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-022-02164-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-022-02164-2