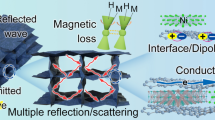
Abstract
A variety of electromagnetic wave absorption materials (EMWAs) have been reported, but the integration of powder materials and multifunctional devices should be investigated in-depth to adapt to practical demands. Herein, carbon-coated cobalt composites were prepared by adsorbing magnetic metal cations into an anionic crystalline framework through an electrostatic encapsulate process. Excellent reflection loss (RLmin) of −40.49 dB and effective absorption bandwidth (EAB) of 5.36 GHz (RL<−10 dB, 10.4–15.76 GHz) was achieved with an optimal radar cross section (RCS) reduction of 34.9 dB·m2 for the sample tested. For commercial applications, Co@CN-4 was integrated into sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) aerogel to create an ultra-lightweight composite aerogel that is compressive resistant and heat-holding while also having photothermal conversion capabilities.The hydrophobic modification makes it more widely useful. This study provides a new strategy for EWAMs to integrate versatility and improve their application prospects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
Data requiring special software tools to open: The related data (DOI: https://doi.org/10.57760/sciencedb.16402; CSTR: 31253.11.Sciencedb.16402) of this paper can be accessed in the Science Date Bank database https://www.scidb.cn/s/VrIzQ3, and the software for opening the data is Origin 2021.
References
Hou, Y.; Liu, K.; Chen, J.; Wang, B.; He, X.; Li, D.; Wei, S.; Li, B.; Han, Q. Bimetallic MOFs/MXene derived CoNi@C@Ti3C2Tx/TiO2 nanocomposites for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 2024, 216, 118587.
Liu, L.; Wen, B. A bead-string Co/C@BNNT nanocomposite: preparation and tunable electromagnetic wave absorption performance. CrystEngComm 2023, 25, 1657–1668.
Gao, Z.; Lan, D.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H. Simultaneous manipulation of interfacial and defects polarization toward Zn/Co phase and ion hybrids for electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2106677.
Su, J.; Nie, Z.; Feng, Y.; Hu, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, Z.; Zan, S.; Qi, S. Hollow core–shell structure Co/C@MoSe2 composites for high-performance microwave absorption. Compos. Part A: Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 162, 107140.
Ren, X.; Song, Y.; Gao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Jia, Z.; Wu, G. Rational manipulation of composition and construction toward Zn/Co bimetal hybrids for electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 134, 254–261.
Yang, Y.; Qian, C.; Hu, P.; Yang, W.; He, Z.; Dong, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, Y. Nitrogen-doped core-shell Fe/Fe3C@C nanocomposites for electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 1847.
Liu, P.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; He, W.; Huang, W.; Luo, J. Carbon nanocages with N-doped carbon inner shell and Co/N-doped carbon outer shell as electromagnetic wave absorption materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122653.
Ban, Q.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Kong, J. Polymer self-assembly guided heterogeneous structure engineering towards high-performance low-frequency electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 650, 1434–1445.
Ban, Q.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Zhou, D.; Zheng, Y.; Qin, Y.; **ng, R.; Kong, J. Polymerization-induced assembly-etching engineering to hollow Co@N-doped carbon microcages for superior electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 2023, 215, 118506.
Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.; Gong, C. Biomass-derived heterogeneous RGO/Ni/C composite with hollow structure for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption. Mater. Today Phys. 2023, 31, 100966.
Wang, Y.; Hui, Z.; Hao, G.; Zhang, S.; Ke, X.; Yan, H. Structural and component optimization of conventional magnetic material Co to synthesis dendritic-like FeCo and rose-like CoNi toward high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 418–430.
Yang, G.; Wen, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X.; Ding, S. In situ construction of ZIF-67 derived Mo2C@cobalt/carbon composites toward excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Nanotechnology 2023, 34, 185704.
Chen, H.; Chu, F; Zhuang, H; Wang, L.; Ye, Z.; Dong, W.; **e, Z.; **e, A. Hyper-crosslinked conjugated microporous polymers with increased micropores promotes confining polymerization for electromagnetic absorption application. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 41, 1305–1316.
Han, Y.; He, M.; Hu, J.; Liu, P.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Z.; Ju, W.; Gu, J., Hierarchical design of FeCo-based microchains for enhanced microwave absorption in C band. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 1773–1778.
Yu, G.; Ye, M.; Han, A.; Liu, Q.; Su, Y.; Chen, C. Optimization of electromagnetic wave absorption properties of CoNi/MoSe2 composites with 3D flower-like by controlling the Co/Ni molar ratio. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 939, 168592.
Shu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Abdul, J.; Li, X.; Yang, L.; Luo, F. High-efficient electromagnetic wave absorption of coral-like Co/CoO/RGO hybrid aerogels with good hydrophobic and thermal insulation properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144535.
Jiang, C.; Wen, B. Electromagnetic wave absorption performance and mechanism of Co/C composites derived from different cobalt source ZIF-67: a comparative study. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 5730–5749.
Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, R.; Chen, S.; He, Q.; Wu, G. Self-assembly of submillimeter porous structure on metal-organic framework to construct heterogeneous interface for controlling microwave absorption. Mater. Today Phys. 2023, 35, 101126.
Lin, J.; Qiao, J.; Tian, H.; Li, L.; Liu, W.; Wu, L.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Z. Ultralight, hierarchical metal-organic framework derivative/graphene hybrid aerogel for electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2023, 6, 177.
Zeng, X.; Xu, L.; Deng, T.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhang, W. Anionic MOFs embedded in anion-exchange membranes for the separation of lithium/magnesium cations ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 12877–12887
Ouyang, Y.; Gong, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Guo, S.; **ao, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, C.; Sun, X.; Wang, C.; Huang, S. Bilayer zwitterionic metalorganic framework for selective all-solid-state superionic conduction in lithium metal batteries. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2304685
More, Y. D.; Mollick, S.; Saurabh, S.; Fajal, S.; Tricarico, M.; Dutta, S.; Shirolkar, M. M.; Mandal, W.; Tan, J.C.; Ghosh, S. K. Nanotrap grafted anionic MOF for superior uranium extraction from seawater. Small 2024, 20, 2302014.
Li, K.; Han, L.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, J. Metal-organic framework derived multidimensional carbon/multifluorination epoxy nanocomposite with electromagnetic wave absorption, environmentally adaptive, and blue energy harvesting. Small Struct. 2023, 4, 2300210.
Rehman, S. U.; Xu, S.; Li, Z.; Tao, T.; Zhang, J.; **a, H.; Xu, H.; Ma, K.; Wang, J. Hierarchical-bioinspired MOFs enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. Small 2024, 20, 2306466.
Zhang, X.; Tian, X.L.; Qin, Y.; Qiao, J.; Pan, F.; Wu, N.; Wang, C.; Zhao, S.; Liu, W.; Cui, J.; Qian, Z.; Zhao, M.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Z. Conductive metal-organic frameworks with tunable dielectric properties for boosting electromagnetic wave absorption. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 12510–12518.
Chen, C.; Shan, Z.; Tao, S.; **e, A.; Yang, H.; Su, J.; Horke, S.; Kitagawa, S.; Zhang, G. Atomic tuning in electrically conducting bimetallic organic frameworks for controllable electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2305082.
Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, Z.; Jia, C.; Lu, F.; Jia, Z.; Wu, G. MXene@Co hollow spheres structure boosts interfacial polarization for broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 176, 167–175.
Xu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Han, X.; Chai, C.; Ma, H. Facile synthesis of Co/La-MOF/Ti3C2Tx nanocomposite for electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 960, 170829.
Liu, Z.; Wu, C.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; **an, G.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Kong, L. Self-assembled Co nanosheet/Ti3C2Tx composites with tunable electromagnetic wave absorption. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 1339–1346.
Yang, J.; Chan, K.; Venkatesan, H.; Kim, E.; Adegun, M. H.; Lee, J. H.; Shen, X.; Kim, J. K. Superinsulating BNNS/PVA composite aerogels with high solar reflectance for energy-efficient buildings. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 54.
Wang, L.; Ma, Z.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Gu, J. Significantly enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding performances of epoxy nanocomposites with long-range aligned lamellar structures. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 224.
Rao, L.; Wang, L.; Yang, C.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, J.; Liang, C.; Che, R. Confined diffusion strategy for customizing magnetic coupling spaces to enhance low-frequency electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2213258.
Yu, M.; Li, J.; Wang, L., KOH-activated carbon aerogels derived from sodium carboxymethyl cellulose for high-performance supercapacitors and dye adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 310, 300–306.
Ren, J.; **, F.; Bao, Y.; Yu, J.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, F. Microcapsule preparation of melamine and orange peel charcoal encapsulated by sodium alginate and its effect on combustion performance of epoxy resins. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2023, 148, 9489–9500.
Jia, L.; Huang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wen, S.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Z. Ultra-light polylactic acid/combination composite foam: a fully biodegradable flame retardant material. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 220, 754–765.
Long, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, K.; Wang, C.; Zeng, N.; Gao, B.; Tang, X.; Qi, X.; Fan, R. Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance of hematite@carbon nanotubes/polyacrylamide hydrogel composites with good flexibility and biocompatibility. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2023, 6, 173.
Sun, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J. Synthesis of anionic metal-organic zeolites for selective gas adsorption and ion exchange. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 4076–4079.
Yan, M.; Cheng, X.; Gong, L.; Lun, Z.; He, P.; Shi, L.; Liu, C.; Pan, Y. Growth mechanism and structure regulation of super-elastic SiC aerogels for thermal insulation and electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 475, 146417.
Cheng, Y.; Hu, L.; Zhang, K.; Fan, J. Facile synthesis of hollow SiC/C nanospheres for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 2023, 215, 118391.
Wang, W.; Wen, J.; Hou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, W.; Wang, S.; Zhao, R.; Xue, W. Enhanced microwave absorption of superlattice C-CuS/MXene composites with rich heterogeneous interfaces and conductive network synergies. Mater. Today Phys. 2023, 35, 101108.
Cai, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, K.; Yun, M.; Wang, X.; Tong, Z.; Wang, M.; Suhr, J.; **ao, L.; Jia, S.; Chen, X. Ti3C2Tx MXene/graphene oxide/Co3O4 nanorods aerogels with tunable and broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 462, 142042.
Gu, W.; Sheng, J.; Huang, Q.; Wang, G.; Chen, J.; Ji, G. Environmentally friendly and multifunctional shaddock peel-based carbon aerogel for thermal-insulation and microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 102.
Liu, Q., Cao, Q., Bi, H., Liang, C., Yuan, K., She, W., Yang, Y., Che, R. CoNi@SiO2@TiO2 and CoNi@Air@TiO2 microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 486–490.
Ye, W.; Wang, S.; Hou, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Xue, W. Construction of Bi2S3/rGO heterointerfaces for enhanced and tunetable electromagnetic wave absorption. Compos. Commun. 2023, 37, 101433.
Wu, L.; Gao, H.; Guo, R.; Li, W.; Wu, F.; Tao, S.; Zhu, X.; **e, A. MnO2 intercalation-guided impedance tuning of carbon/polypyrrole double conductive layers for electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 460, 141749.
Wu, Z.; Pei, K.; **ng, L.; Yu, X.; You, W. B.; Che, R. Enhanced microwave absorption performance from magnetic coupling of magnetic nanoparticles suspended within hierarchically tubular composite. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901448.
Li, F.; Bi, Z.; Kimura, H.; Li, H.; Liu, L.; **e, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Ma, Z.; Du, W.; Hou, C. Energy- and cost-efficient salt-assisted synthesis of nitrogen-doped porous carbon matrix decorated with nickel nanoparticles for superior electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2023, 6, 133.
Ge, C.; Xu, D.; Du, H.; Zhang, X.; Song, Z.; Zhao, H.; Chen, Z.; Song, B.; Shen, Z.; Gao, C.; Yan, G.; Xu, W.; Fang, J. All-in-one evaporators for efficient solar-driven simultaneous collection of water and electricity. Small Methods 2023, 7, 2300227.
Shao, C.; Guo, B.; Lu, B.; Yu, J.; Kong, H.; Wang, B.; Ding, M.; Li, C. PDI-based organic small molecule regulated by inter/intramolecular interactions for efficient solar vapor generation. Small 2023, 19, 2305856.
Li, Y., Shi, Y., Wang, H., Liu, T., Zheng, X., Gao, S., Lu, J. Recent advances in carbon-based materials for solar-driven interfacial photothermal conversion water evaporation: assemblies, structures, applications, and prospective. Carbon Energy 2023, 5, e331.
Tang, L.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Y.; Kong, J.; Zhou, K.; Gu, J. High-strength super-hydrophobic double-layered PBO nanofiber-polytetrafluoroethylene nanocomposite paper for high-performance wave-transparent applications. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 2196–2207.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 22001156 and 22301239), the Youth Talent Fund of University Association for Science and Technology in Shaanxi, China (No. 20210602), International Cooperation Key Project of Science and Technology Department of Shaanxi, China (No. 2022KWZ-06), the research project of Science and Technology Department of Shaanxi Province (No. 2021JQ-533), the Research Program of the Shaanxi Provincial Department of Education (No. 23JK0596), the open Foundation of **’an Key Laboratory of Functional Supramolecular Structure and Materials (No. CFZKFKT23003) and Shaanxi Provincial Department of Education service local special project, industrialization cultivation project (No. 23JC007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no interest conflict.
Electronic Supplementary Information
10118_2024_3111_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Electrostatic Encapsulation of Cobalt Ions into Crystalline Framework Derived Polymer Aerogel: Ultra-light, Pressure Resistant, Hydrophobic, Photothermal Conversion, Heat Insulation and Infrared Stealth
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, YF., Tang, JL., Song, M. et al. Electrostatic Encapsulation of Cobalt Ions into Crystalline Framework Derived Polymer Aerogel: Ultra-light, Pressure Resistant, Hydrophobic, Photothermal Conversion, Heat Insulation and Infrared Stealth. Chin J Polym Sci (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-024-3111-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-024-3111-y