Abstract
The quest for efficient dehumidification solutions in modern industries emphasizes the need for advancements in measuring the cleanliness of products and processes, particularly in the context of environmental sustainability. This research explores the potential of natural waste fiber desiccant paper coated with biopolymeric materials. These emerging materials in the field of dehumidification technology offer an attractive blend of cost-effectiveness and eco-friendliness. This initiative not only provides a practical solution for moisture control but also contributes to the reuse of materials, echoing global efforts in sustainable development. The research introduces the fabrication and evaluation of desiccant paper, assessing its morphological structure and moisture reduction capabilities using scanning electron microscope (SEM), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX), wettability, and moisture evaluation tests. SEM analysis highlighted surface morphologies and porosity showing that the desiccant exhibits a porous structure suitable for moisture absorption. FTIR analysis revealed the presence of hydroxyl groups on desiccant samples with broad peaks around 3200–3500 cm−1 indicating that moisture has been absorbed. EDX analysis showed a high carbon content in desiccant sample with presence of calcium and chloride. Wettability tests indicated that the coated polymeric material contributes to maintaining the structure of the desiccant, preventing fiber separation, and swelling. The moisture evaluation test demonstrated a significant decrease in relative humidity, from 92 to 48% with a notable reduction in humidity ratio from 0.0183 to 0.0096 kgkg−1. These findings underscore the effectiveness of desiccant in their moisture absorbing properties, porosity, and eco-friendly advantages over conventional materials.
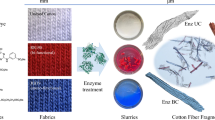
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data have been used is confidential.
References
Abu Hassan NA, Ahmad S, Chen RS, Natarajan V (2022) Synergistically enhanced mechanical, combustion and acoustic properties of biopolymer composite foams reinforcement by kenaf fibre. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 155:106826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2022.106826
Abu Hassan NA, Haafiz MK, Weerasooriya PRD et al (2023) Regenerated cellulose fabricated from oil palm biomass integrated with bismuth ferrite for methyl orange degradation. Polym Int. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.6580
Ahmad A, Omar KM, Alahmadi AA et al (2024) Bioadsorbent nanocellulose aerogel efficiency impregnated with spent coffee grounds. Int J Biol Macromol 258:128746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.128746
Aleem M, Hussain G, Sultan M et al (2020) Experimental investigation of desiccant dehumidification cooling system for climatic conditions of Multan (Pakistan). Energies (basel) 13(21):5530
Almasarani A, Ahmad IK, El-Amin MF, Brahimi T (2022) Experimental investigations and modeling of atmospheric water generation using a desiccant material. Energies (basel) 15(18):6834
An H, Chen Y, Wang Y et al (2023) High-performance solar-driven water harvesting from air with a cheap and scalable hygroscopic salt modified metal–organic framework. Chem Eng J 461:141955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.141955
Anatoly C, Pavel Z, Tatiana C et al (2020) Water vapor permeability through porous polymeric membranes with various hydrophilicity as synthetic and natural barriers. Polymers (basel) 12(2):282
ASTM D7334-08 (2013) Standard practice for surface wettability of coatings, substrates and pigments by advancing contact angle measurement
ASTM D4442-16 (2016) Standard test methods for direct moisture content measurement of wood and wood-base materials. Annu Book ASTM Stand 4:1–6
Bachchan AA, Das PP, Chaudhary V (2022) Effect of moisture absorption on the properties of natural fiber reinforced polymer composites: a review. Mater Today Proc 49:3403–3408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.02.812
Baiju V, Abhishek P, Priya KL, Mohammed SPA (2022) Performance investigation of silica gel based consolidated composite adsorbents effective for adsorption desalination systems. Mater Today Commun 32:104015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.104015
Bhabhor KK, Jani DB (2022) Progressive development in solid desiccant cooling: a review. Int J Ambient Energy 43:992–1015. https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2019.1681293
Bharathi ALK, Hussain SI, Kalaiselvam S (2023) Performance evaluation of various fiber paper matrix desiccant wheels coated with nano-adsorbent for energy efficient dehumidification. Int J Refrig 146:416–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2022.12.002
Boon JG, Hashim R, Danish M, Nadhari WNAW (2019) Physical and mechanical properties of binderless particleboard made from steam-pretreated oil palm trunk particles. J Compos Sci 3:46
Budaev ZB, Livanova AV, Meshcheryakov EP et al (2019) Influence of the composition of the adsorbent “hygroscopic salt/aluminum oxide” on its physicochemical properties. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/597/1/012025
De Antonellis S, Bramanti E, Calabrese L et al (2022) A novel desiccant compound for air humidification and dehumidification. Appl Therm Eng 214:118857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2022.118857
Fahad FG, Al-Humairi ST, Al-Ezzi AT et al (2023) Advancements in liquid desiccant technologies: a comprehensive review of materials, systems, and applications. Sustainability 15(18):14021
Horikawa Y, Hirano S, Mihashi A et al (2019) Prediction of lignin contents from infrared spectroscopy: chemical digestion and lignin/biomass ratios of Cryptomeria japonica. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-02965-8
Huang S-M, Liu S-M, Tseng H-Y, Chen W-C (2023) Effect of citric acid on swelling resistance and physicochemical properties of post-crosslinked electrospun polyvinyl alcohol fibrous membrane. Polymers (basel) 15(7):1738
Jafarpour AM, Fazelpour F, Mousavi SA (2020) Performance optimization of polymeric porous membrane-based liquid desiccant air dehumidifier used in air conditioning system. Int J Energy Environ Eng 11:55–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40095-019-00324-1
Jani DB, Mishra M, Sahoo PK (2016) Solid desiccant air conditioning—a state of the art review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 60:1451–1469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.03.031
Lazim AM, Azfaralariff A, Azman I et al (2020) Improving wood durability against G. Trabeum and C. versicolor using starch based antifungal coating from Dioscorea hispida sp. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 115:242–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2020.10.002
Liu H, Sundarrajan S, Kumar GV, Ramakrishna S (2023) Review on polymer materials for solid desiccant cooling system. Macromol Mater Eng 308:2300176. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.202300176
Mahmud NA, Osman N, Jani AMM (2018) Characterization of acid treated activated carbon from oil palm empty fruit bunches (EFB). J Phys Conf Ser 1083:12049. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1083/1/012049
Muhamad Damanhuri AA (2016) Comparison for humidity absorption using various silica gel in experimental chamber
Philipp M, Zimmer B, Ostermeyer M, Krüger JK (2019) Polymerization-induced shrinkage and dynamic thermal expansion behavior during network formation of polyurethanes. Thermochim Acta 677:144–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2019.01.012
VivekhChua PKJon (2021) Advances in desiccant dehumidification : from fundamentals to applications. Springer, Cham
Ramli NK, Yusup Y, Lin CLP et al (2021) Performance of calcium chloride and silica gel as solid desiccant dehumidifiers for indoor air quality. J Adv Res Fluid Mech Therm Sci 88:57–70. https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.88.3.5770
Rezk A, Gediz Ilis G, Demir H (2022) Experimental study on silica gel/ethanol adsorption characteristics for low-grade thermal driven adsorption refrigeration systems. Therm Sci Eng Prog 34:101429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsep.2022.101429
Shakir MA, Ahmad MI, Mansur FZ et al (2024) Processing of waste biomass: production of composite thermal insulation panels from empty fruit bunch and spent mushroom substrates. Waste Biomass Valorization. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-024-02453-z
Shakir MA, Ahmad MI, Ramli NK et al (2023a) Review on the influencing factors towards improving properties of composite insulation panel made of natural waste fibers for building application. J Ind Text 53:1–33. https://doi.org/10.1177/15280837231151440
Shakir MA, Ahmad MI, Yusup Y, Rafatullah M (2023b) From waste to wealth: converting rubber wood sawdust into green mycelium-based composite. Biomass Convers Biorefin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-05113-9
Shakir MA, Yhaya MF, Ahmad MI (2017a) Physical effects of pre-hydrolysis and alkali treatment of empty fruit bunch (EFB) fibers. Int J Chem Eng Appl 8:387–391. https://doi.org/10.18178/ijcea.2017.8.6.689
Shakir MA, Yhaya MF, Ahmad MI (2017b) The effect of crosslinking fibers with polyvinyl alcohol using citric acid. Imp J Interdiscip Res (IJIR) 3:758–764
Sultan M, Miyazaki T, Koyama S, Khan ZM (2017) Performance evaluation of hydrophilic organic polymer sorbents for desiccant air-conditioning applications. Adsorpt Sci Technol 36:311–326. https://doi.org/10.1177/0263617417692338
Tan X, Rodrigue D (2019) A review on porous polymeric membrane preparation. Part I: production techniques with polysulfone and poly (vinylidene fluoride). Polymers (basel) 11(7):1160
Tkachenko Y, Niedzielski P (2022) FTIR as a method for qualitative assessment of solid samples in geochemical research: a review. Molecules 27(24):8846
Vivekh P, Islam MR, Chua KJ (2020) Experimental performance evaluation of a composite superabsorbent polymer coated heat exchanger based air dehumidification system. Appl Energy 260:114256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.114256
Wang L, Liu X, Qu M et al (2022) An experimental study on dehumidification and regeneration performance of a new nonporous membrane-based heat and mass exchanger using an ionic liquid desiccant. Energy Build 254:111592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2021.111592
Windiastuti E, Suprihatin BY, Hasanudin U (2022) Identification of potential application of oil palm empty fruit bunches (EFB): a review. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/1063/1/012024
Wohlert M, Benselfelt T, Wågberg L et al (2022) Cellulose and the role of hydrogen bonds: not in charge of everything. Cellulose 29:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04325-4
Yang K-S, Wang J-S, Wu S-K et al (2017) Performance evaluation of a desiccant dehumidifier with a heat recovery unit. Energies (basel) 10(12):2006
Yu L, Hsu W-L, Shamim JA, Daiguji H (2022) Pore network modeling of a solid desiccant for dehumidification applications. Int J Heat Mass Transf 186:122456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2021.122456
Zhang P, Li Q, Wang J et al (2019) Effect of PVA fiber on durability of cementitious composite containing nano-SiO2. Nanotechnol Rev 8:116–127. https://doi.org/10.1515/ntrev-2019-0011
Zheng X, Ge Ts, Wang RZ (2014) Recent progress on desiccant materials for solid desiccant cooling systems. Energy 74:280–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2014.07.027
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Universiti Sains Malaysia for the Research University Grant Scheme with Project Code, 1001/PTEKIND/8014124.
Funding
This funding was supported by Universiti Sains Malaysia (Grant No. 1001/PTEKIND/8014124).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mohammad Aliff Shakir contributed to the conceptualization and was involved in writing the original draft preparation. Nur Kamila Ramli assisted in methodology, participated in writing the original draft, and was responsible for funding acquisition. Mardiana Idayu Ahmad was involved in conceptualization, methodology, validation, writing—review, supervision and managed project administration. Yusri Yusup, Sheikh Ahmad Zaki, and Abdul Khalil H.P.S. contributed to the validation of the work and were involved in writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shakir, M.A., Ramli, N.K., Ahmad, M.I. et al. Development of natural waste fiber desiccant paper coated with biopolymeric material for energy efficient dehumidification. Clean Techn Environ Policy (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-024-02848-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-024-02848-5