Abstract
The aim of this paper is to provide insight into research and activities of in situ remediation to remove petroleum hydrocarbon pollutants from a contaminated aquifer’s sediment, located near two radial collector wells of a water supply system. It was decided that the most appropriate method for remediation of this aquifer’s sediment is in situ bioremediation because it is clean, efficient and sustainable technology. Before the start of the bioremediation process, it was necessary to isolate and cultivate the microorganisms present at the contamination site, so they could be later applied in the bioremediation process. The samples before and after the bioremediation were studied using both GC and GC × GC–MS to determine how the concentrations of contaminants changed over time. Additionally, in this paper, a spatiotemporal representation of the change in hydrocarbon content by depth within the zone of the highest contamination over time is shown. After 12 months of bioremediation, the hydrocarbon content in the samples decreased by 82.0%, and based on GCxGC-MS analysis, the order of degradation of various hydrocarbon groups was as follows: steranes (99.6%), isoprenoids (98.4%), benzene derivatives (98.4%), alkanes (97.2%), and terpenes (49.3%). The exponential decay model showed the greatest decomposition rate of hydrocarbons occurred at depths of 8–10 m, with an average decay constant of 0.227, independent of the initial concentration of hydrocarbons. To the best of our knowledge, to date, the described approach has not been applied to an aquifer (the simultaneous treatment of groundwater and its associated sediment layers).
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Amiri F, Yaghmaei S, Samiei S (2007) Application of bioaugmentation technology to improve the activated sludge treatment process in removal of aromatic compounds. Iran J Chem Eng 4:43–53
APHA (2018) 9020 Quality assurance/Quality control In: Standard Methods For the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd. Lipps WC, Baxter TE, Braun-Howland E (eds.) Washington DC: APHA Press. https://doi.org/10.2105/SMWW.2882.180
Atlas RM (2010) Handbook of Microbiological Media, 4th ed. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Washington, D.C.
Avdalović J, Đurić A, Miletić S, Ilić M, Milić J, Vrvić MM (2016) Treatment of a mud pit by bioremediation. Waste Manag Res 34:734–739. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X16652961
Avdalović J, Miletić S, Božović O, Šolevic-Knudsen T, Stanković D, Lugonja N, Spasić S, Joksimović K, Dragičević I, Vrvić MM (2021) Study on the assessment of humification processes during biodegradation of heavy residual fuel oil. Sci Total Environ 797:149099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149099
Bedient PB, Rifai HS, Newell CJ (1999) Ground water contamination: transport and remediation, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Beškoski VP, Gojgić-Cvijović G, Milić J, Ilić M, Miletić S, Šolević T, Vrvić MM (2011) Ex situ bioremediation of a soil contaminated by mazut (heavy residual fuel oil) – a field experiment. Chemosphere 83:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.01.020
Bulatović S, Marić N, Šolević-Knudsen T, Avdalović J, Ilić M, Jovančićević B, Vrvić MM (2020) Bioremediation of groundwater contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbons applied at a site in Belgrade (Serbia). J Serbian Chem Soc 85:1067–1081. https://doi.org/10.2298/JSC191023003B
Chen W, Kong Y, Li J, Sun Y, Min J, Hu X (2020) Enhanced biodegradation of crude oil by constructed bacterial consortium comprising salt-tolerant petroleum degraders and biosurfactant producers. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 154:105047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2020.105047
Collins CH, Lyne PM, Grange JM, Falkinham JO (2004) Collins and Lyne’s microbiological methods, 8th edn. Arnold, London
Das N, Chandran P (2011) Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminants: an overview. Biotechnol Res Int 2011:1–13. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/941810
Desai AM, Autenrieth RL, Dimitriou-Christidis P, McDonald TJ (2008) Biodegradation kinetics of select polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) mixtures by Sphingomonas paucimobilis EPA505. Biodegradation 19:223–233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-007-9129-3
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1985.tb00420.x
Garbisu C, Garaiyurrebaso O, Epelde L, Grohmann E, Alkorta I (2017) Plasmid-mediated bioaugmentation for the bioremediation of contaminated soils. Front Microbiol 8:1966. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01966
European Commission, Directorate-General for Environment (2009) Groundwater protection in Europe: the new Groundwater Directive: consolidating the EU regulatory framework, Publications Office. https://data.europa.eu/doi/https://doi.org/10.2779/84304. Accessed 15 Jun 2022
Hammershøj R, Birch H, Redman AD, Mayer P (2019) Mixture effects on biodegradation kinetics of hydrocarbons in surface water: increasing concentrations inhibited degradation whereas multiple substrates did not. Environ Sci Technol 53:3087–3094. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b00638
Hatzinger PB, Whittier MC, Arkins MD, Bryan CW, Guarini WJ (2002) In-Situ and ex-situ bioremediation options for treating perchlorate in groundwater. Remediat J 12:69–86. https://doi.org/10.1002/rem.10026
ISO 16703 (2004) Soil quality - Determination of content of hydrocarbon in the range C10 to C40 by gas chromatography
Jaiswal S, Shukla P (2020) Alternative strategies for microbial remediation of pollutants via synthetic biology. Front Microbiol 11:808. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.00808
Kehew AE, Lynch PM (2011) Concentration trends and water-level fluctuations at underground storage tank sites. Environ Earth Sci 62:985–998. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0583-6
Knightes CD, Peters CA (2006) Multisubstrate biodegradation kinetics for binary and complex mixtures of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:1746–1756. https://doi.org/10.1897/05-483R.1
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Lama SMG, Pampel J, Fellinger TP, Beškoski VP, Slavković-Beškoski L, Antonietti M, Molinari V (2017) Efficiency of Ni nanoparticles supported on hierarchical porous nitrogen-doped carbon for hydrogenolysis of Kraft lignin in flow and batch systems. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:2415–2420. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02761
Łebkowska M, Zborowska E, Karwowska E, Miaśkiewicz-Pęska E, Muszyński A, Tabernacka A, Naumczyk J, Jęczalik M (2011) Bioremediation of soil polluted with fuels by sequential multiple injection of native microorganisms: field-scale processes in Poland. Ecol Eng 37:1895–1900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2011.06.047
Liu H, Tan X, Guo J, Liang X, **e Q, Chen S (2020) Bioremediation of oil-contaminated soil by combination of soil conditioner and microorganism. J Soil Sediment 20:2121–2129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02591-6
Logeshwaran P, Megharaj M, Chadalavada S, Bowman M, Naidu R (2018) Petroleum hydrocarbons (PH) in groundwater aquifers: an overview of environmental fate, toxicity, microbial degradation and risk-based remediation approaches. Environ Technol Innov 10:175–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2018.02.001
Löser C, Seidel H, Zehnsdorf A, Stottmeister U (1998) Microbial degradation of hydrocarbons in soil during aerobic/anaerobic changes and under purely aerobic conditions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 49:631–636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051225
Lyon DY, Vogel TM (2013) Bioaugmentation for groundwater remediation: an overview. In: Stroo H, Leeson A, Ward C (eds) Bioaugmentation for Groundwater Remediation. Springer, New York, pp 1–37
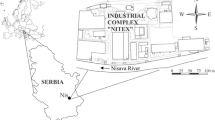
Marić N, Ilić M, Miletić S, Gojgić-Cvijović G, Beškoski V, Vrvić MM, Papić P (2015) Enhanced in situ bioremediation of groundwater contaminated by petroleum hydrocarbons at the location of the Nitex textiles, Serbia. Environ Earth Sci 74:5211–5219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4531-3
Milić J, Avdalović J, Šolević-Knudsen T, Gojgić-Cvijović G, Jednak T, Vrvić MM (2016) Initial microbial degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Chem Ind Chem Eng Q 22:293–299. https://doi.org/10.2298/CICEQ150606043M
Nur Zaida Z, Piakong MT (2018) Bioaugmentation of petroleum hydrocarbon in contaminated soil: a review. In: Kumar V, Kumar M, Prasad R (eds) Microbial Action on Hydrocarbons. Springer, Singapore, pp 415–439
Official Gazette of the Republic of Serbia (2010) The regulation on the programme for the systematic monitoring of soil quality, soil degradation risk assessment indicators and methodology for the development of remediation programmes, Serbia, Nov 23. (In Serbian)
Ossai IC, Ahmed A, Hassan A, Hamid FS (2020) Remediation of soil and water contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbon: a review. Environ Technol Innov 17:100526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2019.100526
Poi G, Shahsavari E, Aburto-Medina A, Mok PC, Ball AS (2018) Large scale treatment of total petroleum-hydrocarbon contaminated groundwater using bioaugmentation. J Environ Manage 214:157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.02.079
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Sayara T, Sánchez A (2020) Bioremediation of PAH-contaminated soils: process enhancement through composting/compost. Appl Sci 10:3684. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113684
Shahsavari E, Poi G, Aburto-Medina A, Haleyur N, Bal AS (2017) Bioremediation approaches for petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated environments. In: Anjum NA, Gill SS, Tuteja N (eds) Enhancing Cleanup of Environmental Pollutants, vol 1. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 21–41
Tamura K, Nei M (1993) Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol Biol Evol 10:512–526. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040023
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y, Seo H, Chun J (2017) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001755
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia (Grant no. 451-03-47/2023-01/200026 and Grant no. 451-03-47/2023-01/200168).
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation and analysis were performed by ML, JA, MI, GGC and AŽ Data collection and modeling were performed by SMK and SM The first draft of the manuscript was written by ML All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. Supervision was performed by JA, VB and MMV. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lukić, M., Avdalović, J., Gojgić-Cvijović, G. et al. Industrial-scale bioremediation of a hydrocarbon-contaminated aquifer’s sediment at the location of a heating plant, Belgrade, Serbia. Clean Techn Environ Policy 26, 1785–1798 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-023-02724-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-023-02724-8