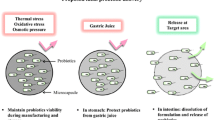
Abstract
Probiotics are living microorganisms that are beneficial to the host, enhancing the immune response by promoting antibody production, regulating cytokine secretion, and stimulating T cells. However, probiotics have limitations in that they require viability control and have a short shelf life. Recently, the use of paraprobiotics has gained attention. These include dead bacterial cells, bacterial fractions, and cell lysate that have health benefits and are stable and safe for use. Paraprobiotics comprise molecules of bacterial cell wall compounds, such as peptidoglycans, teichoic acids, polysaccharides, and cell surface proteins. Paraprobiotics are manufactured by a diverse range of techniques, including thermal treatments, high pressure, ultraviolet rays, sonication, ionizing radiation, and pH modification. Their beneficial health effects include immunomodulatory, intestinal balancing, anticancer, and antimicrobial activities. Therefore, this review summarizes and discusses the manufacturing methods and bioavailability of paraprobiotics and suggests their potential health advantages.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar-Toalá JE, Garcia-Varela R, Garcia HS, Mata-Haro V, González-Córdova AF, Vallejo-Cordoba B, Hernández-Mendoza A. Postbiotics: An evolving term within the functional foods field. Trends in Food Science and Technology. 75: 105-114 (2018)
Basavaprabhu HN, Sonu KS, Prabha R. Mechanistic insights into the action of probiotics against bacterial vaginosis and its mediated preterm birth: An overview. Microbial Pathogenesis. 141: 104029 (2020)
Baugher JL, Klaenhammer TR. Application of omics tools to understanding probiotic functionality. Journal of Dairy Science. 94: 4753-4765 (2011)
Bermudez-Brito M, Plaza- Díaz J, Muñoz-Quezada S, Gómez-Llorente C, Gil A. Probiotic mechanisms of action. Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism. 61: 160-174 (2012)
Birmpa A, Sfika V, Vantarakis A. Ultraviolet light and ultrasound as nonthermal treatments for the inactivation of microorganisms in fresh ready-to-eat foods. International Journal of Food Microbiology. 167: 96-102 (2013)
Bleau C, Monges A, Rashidan K, Laverdure JP, Lacroix M, Van Calsteren MR, Millette M, Savard R, Lamontagne L. Intermediate chains of exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus rhamnosus RW-9595 M increase IL-10 production by macrophages. Journal of Applied Microbiology. 108: 666-675 (2010)
Bosch M, Fuentes M, Audivert S, Bonachera MA, Peiro S, Cune J. Lactobacillus plantarum CECT 7527, 7528 and 7529: Probiotic candidates to reduce cholesterol levels. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 94: 803-809 (2014)
Bowland GB, Weyrich LS. The oral-microbiome-brain axis and neuropsychiatric disorders: An anthropological perspective. Frontiers in Psychiatry. 13: 800008 (2022)
Bull-Otterson L, Feng W, Kirpich I, Wang Y, Qin X, Liu Y, Gobejishvili L, Joshi-Barve S, Ayvaz T, Petrosino J, Kong M, Barker D, McClain C, Barve S. Metagenomic analysis of alcohol induced pathogenic alterations in the intestinal microbiome and the effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG treatment. PLoS One. 8: e53028 (2013)
Cebrián G, Condón S, Mañas P. Physiology of the inactivation of vegetative bacteria by thermal treatments: Mode of action, influence of environmental factors and inactivation kinetics. Foods. 6: 107 (2017)
Chen XY, Woodward A, Ziklstra RT, Gänzle MG. Exopolysaccharides synthesized by Lactobacillus reuteri protect against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in piglet. Applied Environmental Microbiology. 80: 5752-5760 (2014)
Cheon MJ, Lee NK, Paik HD. Neuroprotective effects of heat–killed Lactobacillus plantarum 200655 isolated from kimchi against oxidative stress. Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins. 13: 788-795 (2021)
Choi GH, Bock HJ, Lee NK, Paik HD. Soy yogurt using Lactobacillus plantarum 200655 and fructooligosaccharides: Neuroprotective effects against oxidative stress. Journal of Food Science and Technology. 59:4870-4879 (2022)
Ciandrini E, Campana R, Baffone W. Live and heat-killed Lactobacillus spp. interfere with Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus oralis during biofilm development on titanium surface. Archives of Oral Biology. 78: 48-57 (2017)
Deepak V, Sundar WA, Pandian SRK, Sivasubramaniam SD, Haihara N, Sundar K. Exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus acidophilus modulates the antioxidant status of 1,2-dimethy hydrazine-induced colon cancer rat model. 3 Biotech. 11: 225 (2021)
Del Toro-Barbosa M, Hurtado-Romero A, Garcia-Amezquita LE, García-cayuela T. Psychobiotics: Mechanisms of action, evaluation methods and effectiveness in applications with food products. Nutrients. 12: 3896 (2020)
Devlieghere F, Vermeiren L, Debvere J. New preservation technologies, possibilities and limitations-review. International Dairy Journal. 14: 273-285 (2004)
Di Stefano M, Miceli E, Mazzocchi S, Tana P, Moroni F, Corazza GR. Visceral hypersensitivity and intolerance symptoms in lactose malabsorption. Neurogastroenteology & Motility 19: 887-895 (2007)
Dinić M, Lukić J, Djokić J, Milenković M, Strahinić I, Golić N. Lactobacillus fermentum postbiotic-induced autophagy as potential approach for treatment of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Frontiers in Microbiology. 8: 594 (2017)
Dinić M, Pecikoza U, Djokić J, Stepanović -Petrović R, Milenković M, Stevanović M, Filipović N, Begović J, Golić N, Lukić J. Exopolysaccharide produced by probiotic strain Lactobacillus paraplantarum BGCG11 reduces inflammatory hyperalgesia in rats. Frontiers in Pharmacology. 9: 1 (2018)
Efaq AN, Rahman NNNA, Nagao H, Al-Gheethi AA, Shahadat M, Kadir MOA. Supercritical carbon dioxide as non-thermal alternative technology for safe handling of clinical wastes. Environmental Processes. 2: 797-822 (2015)
Evivie SE, Huo GC, Igene JO, Bian X. Some current applications, limitations and future perspectives of lactic acid bacteria as probiotics. Food & Nutrition Research. 61: 1318034 (2017)
FAO/WHO. Health and nutritional properties of probiotics in food including powder milk with live lactic acid bacteria. World Health Organization. (2001)
FAO/WHO. Health and nutritional properties of probiotics in food including powder milk with live lactic acid bacteria. Report of a Joint FAO/WHO expert consultation on evaluation of health and nutritional properties of probiotics in food including powder milk with live lactic acid bacteria. Accessed February 2, 2021. Untitled (fao.org). http://www.fao.org/3/a-a0512e.pdf
Farkas J, Mohácsi-Farkas C. History and future of food irradiation. Trends in Food Science and Technology. 22: 121-126 (2011)
Hong HJ, Kim E, Cho D, Kim TS. Differential suppression of heat-killed lactobacilli isolated from kimchi, a Korean traditional food, on airway hyper-responsiveness in mice. Journal of Clinical Immunology. 30: 449-458 (2010)
Hwang CH, Kim KT, Lee NK, Paik HD. Immune–enhancing effect of heat–treated Levilactobacillus brevis KU15159 in RAW264.7 cells. Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins. 30: 1-10 (2022a)
Hwang CH, Lee NK, Paik HD. The anti-cancer potential of heat-killed Lactobacillus brevis KU15176 upon AGS cell lines through intrinsic apoptosis pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 23: 4073 (2022b)
Hynönen U, Palva A. Lactobacillus surface layer proteins: structure, function and applications. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 97: 5225-5243 (2013)
Ibrahim HM. Prediction of meat and meat products by gamma rays, electron beams and X-ray irradiations-A review. International Journal of Agricultural Sciences. 3: 521-534 (2013)
Ishikawa H, Kutsukake E, Fukui T, Sato I, Shirai T, Kurihara T, Okada N, Danbara H, Toba M, Kohda N, Maeda Y, Matsumoto T. Oral administration of heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum strain b240 protected mice against Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry. 74: 1338-1342 (2010)
Itamura M, Sawada Y. Involvement of atopic dermatitis in the development of systemic inflammatory diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 23: 13445 (2022)
Jensen GS, Benson KF, Carter SG, Endres JR. GanedenBC30 cell wall and metabolites: Anti-inflammatory and immune modulating effects in vitro. BMC Immunology. 11: 15 (2010)
Jhun J, Min HK, Ryu J, Lee SY, Ryu JG, Choi JW, Na HS, Lee SY, Jung Y, Park SJ, Park MS, Kwon B, Ji GE, Cho MR, Park SH. Lactobacillus sakei suppresses collagen-induced arthritis and modulates the differentiation of T-helper 17 cells and regulatory B cells. Journal of Translational Medicine. 18: 317 (2020)
Kainulainen V, Loimaranta V, Pekkala A, Edelman S, Antikainen J, Kylväjä R, Laaksonen M, Laakkonen L, Finne J, Korhonen TK. Glutamine synthetase and glucose-6-phosphate isomerase are adhesive moonlighting proteins of Lactobacillus crispatus released by epithelial cathelicidin LL-37. Journal of Bacteriology. 194: 2509-2519 (2012)
Kawase M, He F, Miyazawa K, Kubota A, Yoda K, Hiramatsu M. Orally administered heat-killed Lactobacillus gasseri TMC0356 can upregulate cell-mediated immunity in senescence-accelerated mice. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 326: 125-130 (2012)
Kim JY, Park BK, Park HJ, Park YH, Kim BO, Pyo S. Atopic dermatitis-mitigating effects of new Lactobacillus strain, Lactobacillus sakei probio 65 isolated from Kimchi. Journal of Applied Microbiology. 115: 517-526 (2013)
Kimoto-Nira H, Aoki R, Sasaki K, Suzuki C, Mizumachi K. Oral intake of heat-killed cells of Lactococcus lactis strain H61 promotes skin health in women. Journal of Nutritional Science. 1: e18 (2012)
Lado BH, Yousef AE. Alternative food-preservation technologies: Efficacy and mechanisms. Microbes and Infection. 4: 433-440 (2002)
Lebeer S, Vanderleyden J, De Keersmaecker SCJ. Host interactions of probiotic bacterial surface molecules: Comparison with commensals and pathogens. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 8: 171-184 (2010)
Lebeer S, Claes I, Tytgat HLP, Verhoeven TLA, Marien E, von Ossowski I, Reunanen J, Palva A, de Vos W, de Keersmaecker SCJ, Vanderleyden J. Functional analysis of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG pili in relation to adhesion and immunomodulatory interactions with intestinal epithelial cells. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 78: 185-193 (2012)
Lee NK, Lim SM, Cheon MJ, Paik HD. Physicochemical analysis of yogurt produced by Leuconostoc mesenteroides H40 and its effects on oxidative stress in neuronal cells. Food Science of Animal Resources. 41: 261-273 (2021)
Li N, Russell WM, Douglas-Escobar M, Hauser N, Lopez M, Neu J. Live and heat-killed Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG: Effects on proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines/chemokines in gastrostomy-fed infant rats. Pediatric Research. 66: 203-207 (2009)
Liévin-Le Moal V. A gastrointestinal anti-infectious biotherapeutic agent: The heat-treated Lactobacillus LB. Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology. 9: 57-75 (2016)
Lim SM, Lee NK, Paik HD. Potential neuroprotective effects of heat-killed Lactococcus lactis KC24 using SH-SY5Y cells against oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide. Food Science and Biotechnology. 29: 1735-7340 (2020)
Lin WH, Yu B, Lin CK, Hwang WZ, Tsen HY. Immune effect of heat-killed multistrain of Lactobacillus acidophilus against Salmonella typhimurium invasion to mice. Journal of Applied Microbiology. 102: 22-31 (2007)
Llewellyn A, Foey A. Probiotic modulation of innate cell pathogen sensing and signaling events. Nutrients. 9: 1156 (2017)
Maehata H, Arai S, Iwasbuchi N, Abe F. Immuno-modulation by heat-killed Lacticaseibacillus paracasei MCC 1849 and its application to food products. International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology. 35: 1-9 (2021)
Malamud M, Carasi P, Freire T, de los Angels Serradell M. S-layer glycoprotein from Lactobacillus kefiri CIDCA 8348 enhances macrophages response to LPS in a Ca+ 2-dependent manner. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 495: 1227-1232 (2018)
Mañas P, Pagán R. Microbial inactivation by new technologies of food preservation. Journal of Applied Microbiology. 98: 1387-1399 (2005)
Martinelli M, Ummarino D, Giugliano FP, Sciorio E, Tortora C, Bruzzese D, de Giovanni D, Rutigliano I, Valenti S, Romano C, Campanozzi A, Miele E, Staiano A. Efficacy of a standardized extract of Matricariae chamomilla L., Melissa officinalis L. and tyndallized Lactobacillus acidophilus (HA122) in infantile colic: An open randomized controlled trial. Neurogastroenterology and Motility. 29: e13145 (2017)
Mendoza RM, Kim SH, Vasquez R, Hwang IC, Park YS, Paik HD, Moon GS, Kang DK. Bioinformatics and its role in the study of the evolution and probiotic potential of lactic acid bacteria. Food Science and Biotechnology. 32: 389-412 (2023)
Meng J, Zhu X, Gao SM, Zhang QX, Sun Z, Lu RR. Characterization of surface layer proteins and its role in probiotic properties of three Lactobacillus strains. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 65: 110-114 (2014)
Miyazawa K, He F, Kawase M, Kubota A, Yoda K, Hirmatsu M. Enhancement of Lactobacillus gasseri TMC0356 by heat treatment and culture medium. Letters in Applied Microbiology. 53: 210-216 (2011)
Moroi M, Uchi S, Nakamura K, Sato S, Shimizu N, Fujii M, Kumagai T, Saito M, Uchiyama K, Watanabe T, Yamaguchi H, Yamamoto T, Takeuchi S, Furue M. Beneficial effect of a diet containing heat-killed Lactobacillus paracasei K71 on adult type atopic dermatitis. The Journal of Dermatology. 38: 131-139 (2011)
Murata M, Kondo J, Iwabuchi N, Takahashi S, Yamauchi K, Abe F, Miura K. Effects of paraprobiotic Lactobacillus paracasei MCC1849 supplementation on symptoms of the common cold and mood states in healthy adults. Beneficial Microbes. 9: 855-864 (2018)
Nakamura S, Kuda T, An C, Kanno T, Takahasi H, Kimura B. Inhibitory effects ofL euconostoc mesenterodes 1RM3 isolated from narezushi, a fermented fish with rice, on Listeria monocytogenes infection to Caco-2 cells and A/J mice. Anaerobe. 18: 19-24 (2012)
Nakamura F, Ishida Y, Sawada D, Ashida N, Sugawara T, Sakai M, Fujiwara S. Fragmented lactic acid bacteria cells activate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and ameliorate dyslipidemia in obese mice. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 64: 2549-2559 (2016)
Nataraj BH, Ali SA, Behare PV, Yadav H. Postbiotics-parabiotics: the new horizons in microbial biotherapy and functional foods. Microbial Cell Factories. 19: 168 (2020)
O’Toole PW, Marchesi JR, Hill C. Next-generation probiotics: the spectrum from probiotics to live biotherapeutics. Nature Microbiology. 2: 1-6 (2017)
Ou CC, Ko JL, Lin MY. Antioxidative effects of intracellular extracts of yogurt bacteria on lipid peroxidation and intestine 407 cells. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis. 14: 304-310 (2006)
Ou CC, Lin SL, Tsai JJ, Lin MY. Heat-killed lactic acid bacteria enhance immunomodulatory potential by skewing the immune response toward Th1 polarization. Journal of Food Science. 76: M260-M267 (2011)
Paul AK, Pau A, Jahan R, Jannat K, Bondhon TA, Hasan A, Nissapatorn V, Pereira ML, Wilairatana P, Rahmatullah M. Probiotics and amelioration of Rheumatoid arthritis: Significant roles of Lactobacillus casei and Lactobacillus acidophilus. Microorganisms. 9: 1070 (2021)
Peng GC, Hsu CH. The efficacy and safety of heat-killed Lactobacillus paracasei for treatment of perennial allergic rhinitis induced by house-dust mite. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology. 16: 433-438 (2005)
Piqué N, Berlanga M, Miñana-Galbis D. Health benefits of heat-killed (tyndallized) probiotics: An overview. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 20: 2534 (2019)
Pramanik S, Venkatraman S, Karthik P A, Vaidyanathan VK. Systematic review on selection characterization and implementation of probiotics in human health. Food Science and Biotechnology. 32: 423-440 (2023)
Prapa I, Nikolaou A, Panas P, Tassou C, Kourkoutas Y. Develo** stable freeze-dried functional ingredients containing wild-type presumptive probiotic strains for food systems. Applied Sciences. 13: 630 (2023)
Puttarat N, Tangrongthog S, Kasemwong K, Kerdsup P, Tseweechotipatr M. Spray-drying microencapsulation using whey protein isolate and nano-crystalline starch for enhancing the survivability and stability of Lactobacillus reuteri TF-7. Food Science and Biotechnology. 30: 245-256 (2021)
Rafter J. Probiotics and colon cancer. Bailliere’s Best Practice and Research in Clinical Gastroenterology. 17: 849-859 (2003)
Rampengan NK, Manoppo J, Warouw SM. Comparison of efficacies between live and killed probiotics in children with lactose malabsorption. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health. 41: 474-481 (2010)
Reunanen J, von Ossowski I, Hendrickx APA, Palva A, de Vosa WM. Characterization of the SpaCBA pilus fibers in the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 78: 2337-2344 (2012)
Saad N, Urdaci M, Vignoles C, Chaignepain S, Tallon R, Schmitter JM, Bressollier P. Lactobacillus plantarum 299v surface-bound GAPDH: A new insight into enzyme cell walls location. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology. 19: 1635-1643 (2009)
Sang LX, Chang B, Dai C, Gao N, Liu WX, Jiang M. Heat-killed VSL# 3 ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced acute experimental colitis in rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 15: 15-28 (2014)
Segawa S, Wakita Y, Hirata H, Watari J. Oral administration of heat-killed Lactobacillus brevis SBC8803 ameliorates alcoholic liver disease in ethanol-containing diet-fed C57BL/6 N mice. International Journal of Food Microbiology. 128: 371-377 (2008)
Sehrawat R, Kaur BP, Nema PK, Tewari S, Kumar L. Microbial inactivation by high pressure processing: Principle, mechanism and factors responsible. Food Science and Biotechnology. 30: 19-35 (2021)
Sharma N, Kang DK, Paik, HD. Park YS. Beyond probiotics: a narrative review on an era of revolution. Food Science and Biotechnology. 32: 413-421 (2023)
Shin HS, Park SY, Lee DK, Kim SA, An HM, Kim JR, Kim MJ, Cha MG, Lee SW, Kim KJ, Lee KO, Ha NJ. Hypocholesterolemia effect of sonication-killed Bifidobacterium longum isolated from healthy adult Koreans in high cholesterol fed rats. Archives of Pharmacal Research. 33: 1425-1431 (2010)
Shin J, Noh JR, Choe D, Lee N, Song Y, Cho S, Kang EJ, Go MJ, Ha SK, Chang DH, Kim JH, Kim YH, Kim KS, Jung H, Kim MH, Sung BH, Lee SG, Lee DH, Kim BC, Lee CH, Cho BK. Ageing and rejuvenation models reveal changes in key microbial communities associated with healthy ageing. Microbiome. 9: 240 (2021)
Siciliano RA, Reale A, Mazzeo MF, Morandi S, Silvetti T, Brasca M. Parabiotics: A new perspective for functional foods and nutraceuticals. Nutrients. 13: 1225 (2021)
Teame T, Wang A, **e M, Zhang Z, Yang Y, Ding Q, Gao C, Olsen RE, Ran C, Zhou Z. Paraprobiotics and postbiotics of probiotic Lactobacilli, their positive effects on the host and action mechanisms: A review. Fronters in Nutrition. 7: 570344 (2020)
Troge A, Scheppach W, Schroeder BO, Rund SA, Heuner K, Wehkamp J, Stange EF, Oelschlaeger TA. More than a marine propeller-the flagellum of the probiotic Escherichia coli strain Nissle 1917 is the major adhesin mediating binding to human mucus. International Journal of Medical Microbiology. 302: 304-314 (2012)
Ueno N, Fujiya M, Segawa S, Nata T, Moriichi K, Tanabe H, Mizukami Y, Kobayashi N, Ito K, Kohgo Y. Heat-killed body of Lactobacillus brevis SBC8803 ameliorates intestinal injury in a murine model of colitis by enhancing the intestinal barrier. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. 17: 2235-5220 (2011)
Wang Y, Liu Y, Sidhu A, Ma Z, McClain C, Feng W. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG culture supernatant ameliorates acute alcohol-induced intestinal permeability and liver injury. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology. 303: G32-G41 (2012)
Wang Y, **e J, Wang N, Li Y, Sun X, Zhang Y, Zhang H. Lactobacillus casei Zhang modulate cytokine and toll-like receptor expression and beneficially regulate poly I: C-induced immune responses in RAW264.7 macrophages. Microbiology and Immunology. 57: 54-62 (2013)
Weidniger S, Novak N. Atopic dermatitis. The Lancet. 387: 12-18 (2016)
Wollenberg A, Thomsen SF, Lacour JP, Jaumont X, Lazarewicz S. Targeting immunoglobulin E in atopic dermatitis: A review of existing evidence. World Allergy Organization Journal. 14: 100519 (2021)
Yuk HG, Geveke DJ. Nonthermal inactivation and sublethal injury of Lactobacillus plantarum in apple cider by a pilot plant scale continuous supercritical carbon dioxide system. Food Microbiology. 28: 377-383 (2011)
Yunes RA, Poluektova EU, Belkina TV, Danilenko VN. Lactobacilli: Legal regulation and prospects for new generation drugs. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology. 58: 652-664 (2022)
Zeng J, Jiang J, Zhu W, Chu Y. Heat-killed yogurt-containing lactic acid bacteria prevent cytokine-induced barrier disruption in human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Annals of Microbiology. 66: 171-179 (2016)
Zhang YZ, Li YY. Inflammatory bowel disease: Pathogenesis. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 20: 91-99 (2014)
Zhang YC, Zhang LW, Tuo YF, Guo CF, Yi HX, Li JY, Han X, Du M. Inhibition of Shigella sonnei adherence to HT-29 cells by Lactobacilli from Chinese fermented food and preliminary characterization of S-layer protein involvement. Research in Microbiology. 161: 667-672 (2010)
Zhu L, Shimada T, Chen R, Lu R, Zhang Q, Lu W, Yin M, Enomoto T, Cheng L. Effects of lysed Enterococcus faecalis FK-23 on experimental allergic rhinitis in a murine model. The Journal of Biomedical Research. 26: 226-234 (2012)
Zong M, Chang C, Anjum R, **u H, Gou Y, Pan D, Wu Z. Multifunctional LPxTG-motif surface protein derived from Limosilactobacillus reuteri SH 23 in DSS-induced ulcerative colitis of mice. The FASEB Journal. 37: e22895 (2023)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, and Forestry (IPET) through the High Value-Added Food Technology Development Program, funded by the Ministry of Agriculture, Food, and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (#321035-5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors confirmed that they do not have conflicts of interest to disclose in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, N., Park, YS., Kang, DK. et al. Paraprobiotics: definition, manufacturing methods, and functionality. Food Sci Biotechnol 32, 1981–1991 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-023-01378-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-023-01378-y