Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of telitacicept in SLE patients specifically with hematological involvement.
Method
A total of 22 patients with SLE and hematological involvement were included in this study. These patients received telitacicept in addition to standard therapy. We compared their demographic characteristics, clinical manifestations, and laboratory indicators before and after the administration of telitacicept.
Results
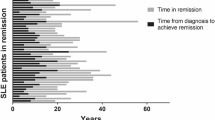
A total of 22 patients received telitacicept treatment for a median duration of 10.4 months (ranging from 6 to 19 months). Following telitacicept therapy, significant improvements were observed in various parameters compared to baseline. Specifically, white blood cell count increased from (3.98 ± 1.80) 109/L to (6.70 ± 2.47) 109/L, (P = 0.002), hemoglobin levels increased from (100 ± 19) g/L to (125 ± 22) g/L, (P < 0.001), and platelet count increased from (83 ± 60) 109/L to (161 ± 81) 109/L, (P = 0.004). SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) scores decreased from 12(5,15) to 0(0,4), (P < 0.001). Additionally, C3 and C4 levels showed improvement. Telitacicept treatment also resulted in a significant reduction in serum IgG levels and daily prednisone dosage. Only one adverse event (4.5%) was reported during the treatment, which was a urinary tract infection.
Conclusion
The combination of telitacicept and standard treatment demonstrated significant improvements in anemia, as well as increased leukocyte and platelet levels in patients with SLE and hematological involvement. Importantly, the observed adverse events were manageable and controllable.
Key Points • Telitacicept effectively improves anemia, clinical outcomes, and increases leukocyte and platelet counts. • Treatment with telitacicept leads to decreased levels of lgG, IgA, anti-dsDNA, and SLEDAI scores, while serum complement C3 and C4 returned to normal. • During the follow-up period there were observed changes in individual parameters, clinical symptoms, and organ involvement, all without significant adverse events. |


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available upon reasonable request, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
References
Pan L, Lu MP, Wang JH, Xu M, Yang SR (2020) Immunological pathogenesis and treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. World J Pediatr 16:19–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-019-00229-3
Rekvig OP (2020) Autoimmunity and SLE: factual and semantic evidence-based critical analyses of definitions, etiology, and pathogenesis. Front Immunol 11:569234. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.569234
Justiz VA, Goyal A, Varacallo M (2023) Systemic lupus erythematosus. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan
Alarcón GS, Mcgwin GJ, Roseman JM, Uribe A, Fessler BJ, Bastian HM, Friedman AW, Baethge B, Vilá LM, Reveille JD (2004) Systemic lupus erythematosus in three ethnic groups. XIX. Natural history of the accrual of the American College of Rheumatology criteria prior to the occurrence of criteria diagnosis. Arthritis Rheum 51:609–615. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.20548
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40:1725. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780400928
Petri M, Orbai AM, Alarcón GS, Gordon C, Merrill JT, Fortin PR, Bruce IN, Isenberg D, Wallace DJ, Nived O, Sturfelt G, Ramsey-Goldman R, Bae SC, Hanly JG, Sánchez-Guerrero J, Clarke A, Aranow C, Manzi S, Urowitz M, Gladman D, Kalunian K, Costner M, Werth VP, Zoma A, Bernatsky S, Ruiz-Irastorza G, Khamashta MA, Jacobsen S, Buyon JP, Maddison P, Dooley MA, van Vollenhoven RF, Ginzler E, Stoll T, Peschken C, Jorizzo JL, Callen JP, Lim SS, Fessler BJ, Inanc M, Kamen DL, Rahman A, Steinsson K, Franks AJ, Sigler L, Hameed S, Fang H, Pham N, Brey R, Weisman MH, Mcgwin GJ, Magder LS (2012) Derivation and validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 64:2677–2686. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.34473
Basta F, Fasola F, Triantafyllias K, Schwarting A (2020) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) therapy: the old and the new. Rheumatol Ther 7:433–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40744-020-00212-9
Judd LL, Schettler PJ, Brown ES, Wolkowitz OM, Sternberg EM, Bender BG, Bulloch K, Cidlowski JA, de Kloet ER, Fardet L, Joëls M, Leung DY, Mcewen BS, Roozendaal B, Van Rossum EF, Ahn J, Brown DW, Plitt A, Singh G (2014) Adverse consequences of glucocorticoid medication: psychological, cognitive, and behavioral effects. Am J Psychiatry 171:1045–1051. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2014.13091264
Durcan L, O’Dwyer T, Petri M (2019) Management strategies and future directions for systemic lupus erythematosus in adults. Lancet 393:2332–2343. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30237-5
Harvey PR, Gordon C (2013) B-cell targeted therapies in systemic lupus erythematosus: successes and challenges. BioDrugs 27:85–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40259-013-0015-8
Sakai J, Akkoyunlu M (2017) The role of BAFF system molecules in host response to pathogens. Clin Microbiol Rev 30:991–1014. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00046-17
Salazar-Camarena DC, Ortiz-Lazareno PC, Cruz A, Oregon-Romero E, Machado-Contreras JR, Muñoz-Valle JF, Orozco-López M, Marín-Rosales M, Palafox-Sánchez CA (2016) Association of BAFF, APRIL serum levels, BAFF-R, TACI and BCMA expression on peripheral B-cell subsets with clinical manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 25:582–592. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203315608254
Gordon C, Wofsy D, Wax S, Li Y, Pena Rossi C, Isenberg D (2016) Post hoc analysis of the phase II/III APRIL-SLE study: association between response to atacicept and serum biomarkers including BLyS and APRIL. Arthritis Rheumatol 69:122–130. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.39809
Salzer U, Grimbacher B (2021) TACI deficiency - a complex system out of balance. Curr Opin Immunol 71:81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2021.06.004
Garcia-Carmona Y, Cols M, Ting AT, Radigan L, Yuk FJ, Zhang L, Cerutti A, Cunningham-Rundles C (2015) Differential induction of plasma cells by isoforms of human TACI. Blood 1749–1758. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-05
Cornelis R, Chang HD, Radbruch A (2021) Kee** up with the stress of antibody production: BAFF and APRIL maintain memory plasma cells. Curr Opin Immunol 71:97–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2021.06.012
Katsenelson N, Kanswal S, Puig M, Mostowski H, Verthelyi D, Akkoyunlu M (2007) Synthetic CpG oligodeoxynucleotides augment BAFF- and APRIL-mediated immunoglobulin secretion. Eur J Immunol 37:1785–1795. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.200636800
Chen X, Hou Y, Jiang J, Zhao Q, Zhong W, Wang W, Yao X, Li L, Fang J, Zhang F, Hu P (2014) Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and tolerability of single ascending doses of RCT-18 in Chinese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Pharmacokinet 53:1033–1044. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-014-0175-9
Zhao Q, Chen X, Hou Y, Jiang J, Zhong W, Yao X, Wang W, Li L, Fang J, Zhang F, Hu P (2016) Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, and clinical activity of multiple doses of RCT-18 in Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Pharmacol 56:948–959. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcph.686
Font J, Cervera R (1993) 1982 revised criteria for classification of systemic lupus erythematosus–ten years later. Lupus 2(339–341):343. https://doi.org/10.1177/096120339300200512
WHO (2011) Haemoglobin concentrations for the diagnosis of anaemia and assessment of severity. World Health Organization, Geneva, 11
Ceccarelli F, Perricone C, Massaro L, Cipriano E, Alessandri C, Spinelli FR, Valesini G, Conti F (2015) Assessment of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus: lights and shadows. Autoimmun Rev 14:601–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2015.02.008
Jiang W, He D, Hu J et al (2020) Observation on the efficacy and safety of Taitaxipu in the treatment of moderate to severe active systemic lupus erythematosus. Jiangxi Med J 55:1637–1641. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-2238.2020.11.029. 1671, (in Chinese)
Lipp E, von Felten A, Sax H, Müller D, Berchtold P (1998) Antibodies against platelet glycoproteins and antiphospholipid antibodies in autoimmune thrombocytopenia. Eur J Haematol 60:283–288. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0609.1998.tb01041.x
Michel M, Lee K, Piette JC, Fromont P, Schaeffer A, Bierling P, Godeau B (2002) Platelet autoantibodies and lupus-associated thrombocytopenia. Br J Haematol 119:354–358. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2141.2002.03817.x
Ziakas PD, Routsias JG, Giannouli S, Tasidou A, Tzioufas AG, Voulgarelis M (2006) Suspects in the tale of lupus-associated thrombocytopenia. Clin Exp Immunol 145:71–80. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03122.x
Newman K, Owlia MB, El-Hemaidi I, Akhtari M (2013) Management of immune cytopenias in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus — old and new. Autoimmun Rev 12:784–791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2013.02.001
Möckel T, Basta F, Weinmann-Menke J, Schwarting A (2021) B cell activating factor (BAFF): structure, functions, autoimmunity and clinical implications in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Autoimmun Rev 20:102736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102736
Kwon OC, Kim Y, Park JH, Park M (2020) Seroconversion to antinuclear antibody negativity and its association with disease flare in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 29:697–704. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203320917748
Bayer G, Agier M, Lioger B, Lepelley M, Zenut M, Lanoue M, Maillot F, Jonville-Bera A (2019) Rituximab-induced serum sickness is more frequent in autoimmune diseases as compared to hematological malignancies: a French nationwide study. Eur J Intern Med 67:59–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2019.06.009
Kaegi C, Wuest B, Schreiner J, Steiner UC, Vultaggio A, Matucci A, Crowley C, Boyman O (2019) Systematic review of safety and efficacy of rituximab in treating immune-mediated disorders. Front Immunol 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01990
Wallace DJ, Stohl W, Furie RA, Lisse JR, Mckay JD, Merrill JT, Petri MA, Ginzler EM, Chatham WW, Mccune WJ, Fernandez V, Chevrier MR, Zhong ZJ, Freimuth WW (2009) A phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study of belimumab in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 61:1168–1178. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.24699
Sultan SM (2003) Prevalence, patterns of disease and outcome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus who develop severe haematological problems. Rheumatology 42:230–234. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keg069
Fanouriakis A, Kostopoulou M, Alunno A, Aringer M, Bajema I, Boletis JN, Cervera R, Doria A, Gordon C, Govoni M, Houssiau F, Jayne D, Kouloumas M, Kuhn A, Larsen JL, Lerstrøm K, Moroni G, Mosca M, Schneider M, Smolen JS, Svenungsson E, Tesar V, Tincani A, Troldborg A, van Vollenhoven R, Wenzel J, Bertsias G, Boumpas DT (2019) update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 78(2019):736–745. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215089
Petri M, Bechtel B, Dennis G, Shah M, Mclaughlin T, Kan H, Molta C (2014) Burden of corticosteroid use in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: results from a Delphi panel. Lupus 23:1006–1013. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203314532699
Shah M, Chaudhari S, Mclaughlin TP, Kan HJ, Bechtel B, Dennis GJ, Molta CT (2013) Cumulative burden of oral corticosteroid adverse effects and the economic implications of corticosteroid use in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Ther 35:486–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2013.03.001
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all patients and study site personnel for participating in this study.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFE0131700, 2022YFC3602000), Bei**g sci-Tech Program (Z191100006619114), National Natural Science Foundation of China (82071813 and 8227183).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JC, YP collected data, made the data analysis, drafted the manuscript and contributed equally to this work. QW, Qian W, XL, DM help to collect data. JH and GY designed this study and they were the corresponding authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Medical Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College (2023ER180-1).
Patient and public involvement
Patients and/or the public were not involved in the design, or conduct, or reporting, or dissemination plans of this research.
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, J., Peng, Y., Wu, Q. et al. Efficacy and safety of telitacicept therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus with hematological involvement. Clin Rheumatol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-024-06992-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-024-06992-7