Abstract
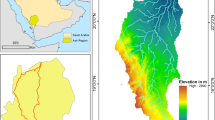
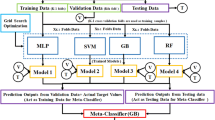
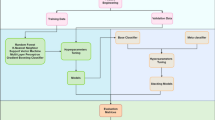
This study introduces an intelligent method for regional subsurface prediction using a Stacking ensemble learning approach, which incorporates K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Decision Tree (DT), Random Forest (RF), Gradient Boosted Decision Trees (GBDT), and Xgboost as base classifiers, with Logistic Regression (LR) serving as the meta-classifier. Leveraging data from 1119 boreholes in Zigong City, China, this method achieves a prediction accuracy of 93%, and notably improves the prediction of weak layers, with accuracy rates ranging from 71.4% to 81.5%. This enhancement is particularly significant in areas with a random distribution of excavation and backfill. Furthermore, this study employs the SHAP method (SHapley Additive explanations) to interpret the Stacking ensemble learning model, revealing that the outputs of the base classifiers enhance the feature set for the meta-classifier, effectively addressing the insensitivity of the spatial coordinates x, y, and z as input features for lithology prediction. The findings demonstrate that the expansion of effective feature dimensions is key to the superior performance of the Stacking ensemble learning method in regional subsurface lithology prediction.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anemangely M, Ramezanzadeh A, Amiri H, Hoseinpour S-A (2019b) Machine learning technique for the prediction of shear wave velocity using petrophysical logs. J Pet Sci Eng 174:306–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2018.11.032
Anemangely M, Ramezanzadeh A, Behboud MM (2019a) Geomechanical parameter estimation from mechanical specific energy using artificial intelligence. J Pet Sci Eng 175:407–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2018.12.054
Anemangely M, Ramezanzadeh A, Tokhmechi B, Molaghab A, Mohammadian A (2018) Development of a new rock drillability index for oil and gas reservoir rocks using punch penetration test. J Pet Sci Eng 166:131–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2018.03.024
Bai J, Wang S, Xu Q et al (2023) Intelligent real-time predicting method for rock characterization based on multi-source information integration while drilling. Bull Eng Geol Environ 82(4):150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03182-8
Chen Z, Lin T, **a X, Xu H, Ding S (2018) A synthetic neighborhood generation-based ensemble learning for the imbalanced data classification. Appl Intell 48(8):2441–2457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-017-1088-8
Gao Z, Wang L, Soroushmehr R, Wood A, Gryak J, Nallamothu B et al (2022) Vessel segmentation for X-ray coronary angiography using ensemble methods with deep learning and filter-based features. BMC Med Imaging 22(1):10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12880-022-00734-4
Gladchenko ES, Gubanova AE, Orlov DM, Koroteev DA (2023) Kriging-boosted CR modeling for prompt infill drilling optimization. Petroleum. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2023.02.014
Gonçalves ÍG, Guadagnin F, Cordova DP (2022) Learning spatial patterns with variational Gaussian processes: Regression. Comput Geosci 161:105056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2022.105056
Guo J, Wang X, Wang J, Dai X, Wu L, Li C et al (2021) Three-dimensional geological modeling and spatial analysis from geotechnical borehole data using an implicit surface and marching tetrahedra algorithm. Eng Geol 284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106047
He Y, Zhang H, Dong Y, Wang C, Ma P (2024) Residential net load interval prediction based on stacking ensemble learning. Energy 296:131134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2024.131134
Hou H, Liu C, Wei R, He H, Wang L, Li W (2023) Outage duration prediction under typhoon disaster with stacking ensemble learning. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 237:109398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2023.109398
Huang S, Wang Y, Wong EYC, Yu L (2024) Ensemble learning with soft-prompted pretrained language models for fact checking. Nat Lang Process 7:100067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlp.2024.100067
Jesell M, Guo J, Li Y, Lindsay M, Scalzo R, Giraud J et al (2022) Into the Noddyverse: a massive data store of 3D geological models for machine learning and inversion applications. Earth Syst Sci Data 14(1):381–392. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-14-381-2022
Jesu Godwin D, Varuvel EG, Leenus Jesu Martin M (2023) Prediction of combustion, performance, and emission parameters of ethanol-powered spark ignition engine using ensemble Least Squares boosting machine learning algorithms. J Clean Prod 421:138401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.138401
Kadkhodaei HR, Moghadam AME, Dehghan M (2020) HBoost: A heterogeneous ensemble classifier based on the Boosting method and entropy measurement. Expert Syst Appl 157:113482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113482
Krishna TB, Kokil P (2024) Standard fetal ultrasound plane classification based on stacked ensemble of deep learning models. Expert Syst Appl 238:122153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.122153
Lawal AI, Kwon S (2021) Application of artificial intelligence to rock mechanics: An overview. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 13(1):248–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2020.05.010
Li S, Liu B, Xu X, Nie L, Liu Z, Song J, Sun H, Chen L, Fan K (2017) An overview of ahead geological prospecting in tunneling. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 63:69–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2016.12.011
Li X, Huang F, Yang Z (2024) Multisource monitoring data-driven slope stability prediction using ensemble learning techniques. Comput Geotech 169:106255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2024.106255
Luo Z, Qi X, Sun C, Dong Q, Gu J, Gao X (2024) Investigation of influential variations among variables in daylighting glare metrics using machine learning and SHAP. Build Environ 254:111394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2024.111394
Maciąg PS, Bembenik R, Piekarzewicz A, Del Ser J, Lobo JL, Kasabov NK (2023) Effective air pollution prediction by combining time series decomposition with Stacking and bagging ensembles of evolving spiking neural networks. Environ Model Softw 170:105851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2023.105851
Madsen RB, Høyer A-S, Andersen LT, Møller I, Hansen TM (2022) Geology-driven modeling: a new probabilistic approach for incorporating uncertain geological interpretations in 3D geological modeling. Eng Geol 309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106833
Miao C, Wang Y (2024) Interpolation of non-stationary geo-data using Kriging with sparse representation of covariance function. Comput Geotech 169:106183
Mo R, Chen L, Chen Y, **ong C, Zhang C, Chen Z, Lin E (2024) Prediction and correlations estimation of seismic capacities of pier columns: extended Gaussian process regression models. Struct Saf 109:102457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strusafe.2024.102457
Özbayrak F, Foster JT, Pyrcz MJ (2024) Spatial bagging to integrate spatial correlation into ensemble machine learning. Comput Geosci 186:105558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2024.105558
Pavlyshenko, B. (2018). Using stacking approaches for machine learning models. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Data Stream Mining and Processing, DSMP 2018 (pp. 255-258). https://doi.org/10.1109/DSMP.2018.8478522.
Pelegrina GD, Duarte LT, Grabisch M (2023) A k-additive Choquet integral-based approach to approximate the SHAP values for local interpretability in machine learning. Artif Intell 325:104014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artint.2023.104014
Qi X, Wang H, Pan X, Chu J, Chiam K (2021) Prediction of interfaces of geological formations using the multivariate adaptive regression spline method. Undergr Space 6(3):252–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.undsp.2020.02.006
Sesmero MP, Iglesias JA, Magán E, Ledezma A, Sanchis A (2021) Impact of the learners diversity and combination method on the generation of heterogeneous classifier ensembles. Appl Soft Comput 111:107689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107689
Shi C, Wang Y (2022) Data-driven construction of Three-dimensional subsurface geological models from limited Site-specific boreholes and prior geological knowledge for underground digital twin. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 126:104493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2022.104493
Wang N, Zhang H, Dahal A, Cheng W, Zhao M, Lombardo L (2024) On the use of explainable AI for susceptibility modeling: examining the spatial pattern of SHAP values. Geosci Front 15(4):101800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2024.101800
Wu R-j, **a J, Chen K-y, Chen J-j, Liu Q-f, ** W-l (2023) Spatiotemporal interpolation of surface chloride content for marine RC structures based on non-uniform spatiotemporal Kriging interpolation method. Struct Saf 103:102329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strusafe.2023.102329
Ye M, Li L, Yoo D-Y, Li H, Zhou C, Shao X (2023) Prediction of shear strength in UHPC beams using machine learning-based models and SHAP interpretation. Constr Build Mater 408:133752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.133752
Zhang L, Cheng Y, Zhang J, Chen H, Cheng H, Gou W (2023) Refrigerant charge fault diagnosis strategy for VRF systems based on stacking ensemble learning. Build Environ 234:110209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2023.110209
Zhang W, Han L, Gu X, Wang L, Chen F, Liu H (2022) Tunneling and deep excavations in spatially variable soil and rock masses: a short review. Undergr Space (China) 7(3):380–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.undsp.2020.03.003
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Zhang C, Qiao X, Ge Y, Li X, Peng T, Nazir MS (2024) State-of-health estimation for lithium-ion battery via an evolutionary Stacking ensemble learning paradigm of random vector functional link and active-state-tracking long–short-term memory neural network. Appl Energy 356:122417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2023.122417
Acknowledgments
This paper has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42072339, 41702388, U19A2097), the State Key Laboratory of Geohazard Prevention and Geoenvironment Protection (Grant No. SKLGP2022Z006), and Everest Technology Research Proposal of Chengdu University of Technology (Grant No. 80000-2020ZF11411).
Code availability
GeoStackingPredictor Contact: 2021010113@stu.cdut.edu.cn. Program language: Python. The source codes in this paper are available for download at the link: https://github.com/Lukacdut/GeoStackingPredictor.git.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, J., Wang, S., Xu, Q. et al. Intelligent regional subsurface prediction based on limited borehole data and interpretability stacking technique of ensemble learning. Bull Eng Geol Environ 83, 272 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-024-03758-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-024-03758-y