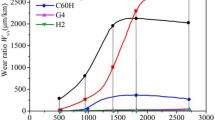
Abstract
When earth pressure balance tunnel boring machines (EPB-TBMs) tunnelling in abrasive sandy ground, soil additives are critical for promoting excavation surface stability, reducing residual soil permeability, decreasing screw conveyor torque, avoiding mud cake siltation and preventing excessive tool wear. However, the existing studies mainly focus on the first four aspects. The influence mechanism of soil additives on cutting tool wear is still unclear due to the lack of reliable test methods. In the present study, a newly developed WHU-SAT tester (Soil Abrasion Tester developed by Wuhan University) was used to evaluate the influence of conditioning additives (foam additives and bentonite slurry) on soil abrasivity. Scraper wear in additive-conditioned sand has been compared with that in water-conditioned sand to reveal the mechanism of foam additive and bentonite slurry. The soil additive parameters (solution concentration and injection ratio) were optimized to reduce scraper wear in abrasive sandy ground. The results indicate that the mitigation effect of the foam additive on scraper wear is related to the lubrication of the active agent and the cushioning of the air bubbles. The optimized foam solution concentration and foam injection ratio for the quartz sand samples are FSC = [5%, 10%] and FIR = [22.5%, 25.0%], respectively. The aggravation in scraper wear caused by bentonite slurry is related to the improvement of particle gradation and the increase of sand cohesion. The bentonite slurry parameters should be selected to keep the water content of the conditioned sand away from the peak water content to decrease scraper wear.



























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
- Foam solution concentration FSC :
-
The mass ratio of the foam addictive to the diluted solution.
- Foam injection ratio FIR :
-
The mass ratio of the foam addictive to the sand sample.
- Bentonite slurry concentration BSC :
-
The mass ratio of the bentonite powder to the bentonite slurry.
- Bentonite injection ratio BIR :
-
The mass ratio of the bentonite slurry to the sand sample.
- Water content ω :
-
The mass ratio of the water to the sand sample.
- Scraper wear δ :
-
The weight loss of scraper before and after wear.
References
Alavi Gharahbagh E, Rostami J, Talebi K (2014) Experimental study of the effect of conditioning on abrasive wear and torque requirement of full face tunneling machines. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 41:127–136
Barzegari G, Uromeihy A, Zhao J (2013) A newly developed soil abrasion testing method for tunnelling using shield machines. Quart J Eng Geol Hydrol 46(1):63–74
Barzegari G, Uromeihy A, Zhao J (2014) EPB tunneling challenges in bouldery ground: a new experience on the Tabriz metro line 1. Iran Bull Eng Geol Environ 73:429–440
Barzegari G, Uromeihy A, Zhao J (2015) Parametric study of soil abrasivity for predicting wear issue in TBM tunneling projects. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 48:43–57
Bosio F, Bassini E, Salazar CGO, Ugues D, Peila D (2018) The influence of microstructure on abrasive wear resistance of selected cemented carbide grades operating as cutting tools in dry and foam conditioned soil. J Wear 394:203–216
Carigi A, Luciani A, Todaro C, Martinelli D, Peila D (2020) Influence of conditioning on the behaviour of alluvial soils with cobbles. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 96:103225
de Oliveira DG, Thewes M, Diederichs MS (2019) Clogging and flow assessment of cohesive soils for EPB tunnelling: proposed laboratory tests for soil characterisation. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 94:103110
El Souwaissi N, Djeran-Maigre I, Boulange L, Trottin JL (2023) Effects of the physical characteristics of foams on conditioned soil’s flow behavior: a case study. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 137:105111
Farrokh E (2021) Primary and secondary tools’ life evaluation for soft ground TBMs. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80:4909–4927
Filho LCEF, Hartwig ME, Moreira CA (2022) EPB excavation in transitional mixed face: Line 5—Lilac (São Paulo Metro, Brazil). Bull Eng Geol Environ 81(5):196
Galli M, Thewes M (2019) Rheological characterisation of foam-conditioned sands in EPB tunneling. Int J Civ Eng 17(1):145–160
Goh ATC, Zhang W, Zhang Y, **ao Y, **ang Y (2018) Determination of earth pressure balance tunnel-related maximum surface settlement: a multivariate adaptive regression splines approach. Bull Eng Geol Environ 77:489–500
Hamzaban MT, Mohammadi NRS, Jakobsen PD (2020) The effect of the particle size distribution curve on the abrasivity of non-cohesive soils in LCPC test. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 105:103573
Hu W, Rostami J (2020) A new method to quantify rheology of conditioned soil for application in EPB TBM tunneling. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 96:103192
Hu W, Rostami J (2021) Evaluating rheology of conditioned soil using commercially available surfactants (foam) for simulation of material flow through EPB machine. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 112:103881
Huang S, Wang SY, Xu CJ, Shi YF, Ye F (2019a) Effect of grain gradation on the permeability characteristics of coarse-grained soil conditioned with foam for EPB shield tunneling. KSCE J Civ Eng 23(11):4662–4674
Huang ZQ, Wang C, Dong JY, Zhou JY, Yang JH, Li YW (2019b) Conditioning experiment on sand and cobble soil for shield tunneling. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 87:187–194
Langmaack L, Lee KF (2016) Difficult ground conditions? Use the right chemicals! Chances–limits–requirements. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 57:112–121
Lee H, Kwak J, Choi J, Hwang B, Choi H (2022) A lab-scale experimental approach to evaluate rheological properties of foam-conditioned soil for EPB shield tunnelling. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 128:104667
Liu XX, Shen SL, Zhou A, Xu YS (2019) Evaluation of foam conditioning effect on groundwater inflow at tunnel cutting face. Int J Numer Anal Meth Geomech 43(2):463–481
Mori L, Mooney M, Cha M (2018) Characterizing the influence of stress on foam conditioned sand for EPB tunneling. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 71:454–465
Peila D, Martinelli D, Todaro C, Luciani A (2019) Soil conditioning in EPB shield tunnelling–an overview of laboratory tests. Geomech Tunnel 12(5):491–498
Tang SH, Zhang XP, Liu QS, Chen P, Sun XT, Sun L, Dai Y, Chen ST (2020) Prediction and analysis of replaceable scraper wear of slurry shield TBM in dense sandy ground: a case study of Sutong GIL Yangtze River Crossing Cable Tunnel. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 95:103090
Tang SH, Zhang XP, Liu QS, **e WQ, Yang XM, Chen P, Tu XB (2021a) Analysis on the excavation management system of slurry shield TBM in permeable sandy ground. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 113:103935
Tang SH, Zhang XP, Liu QS, **e WQ, Wu XL, Chen P, Qian YH (2021b) Control and prevention of gas explosion in soft ground tunneling using slurry shield TBM. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 113:103963
Tang SH, Zhang XP, Liu QS, **e WQ, Wang HJ, Li XF, Zhang XY (2022) New soil abrasion testing method for evaluating the influence of geological parameters of abrasive sandy ground on scraper wear in TBM tunneling. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 128:104604
Tang SH, Zhang XP, **e WQ, Liu QS, Wu J, Chen P (2023) A new evaluation method to quantify the wear failure of irregular cutting tool during shield TBM tunneling in abrasive sandy ground. Eng Fail Anal 146:107011
Tang SH, Zhang XP, Liu QS, Zhang Q, Li XF, Wang HJ (2024) Experimental study on the influences of cutter geometry and material on scraper wear during shield TBM tunnelling in abrasive sandy ground. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 16:410–425
Vinai R, Oggeri C, Peila D (2008) Soil conditioning of sand for EPB applications: a laboratory research. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 23(3):308–317
Wang G, Zhang XW, Liu XY, Gao HD, An R, Yin S (2023) Experimental assessment of clayey layers for clogging potential in TBM tunnel driving and the influence of compositional factors. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 137:105113
Wei YJ, Yang YY, Tao MJ (2018) Effects of gravel content and particle size on abrasivity of sandy gravel mixtures. Eng Geo 243:26–35
Wei YJ, Yang YY, Tao MJ, Wang DL, Jie YX (2020) Earth pressure balance shield tunneling in sandy gravel deposits: a case study of application of soil conditioning. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79:5013–5030
Wei YJ, Yang YY, Qiu T (2021) Effects of soil conditioning on tool wear for earth pressure balance shield tunneling in sandy gravel based on laboratory test. J Test Eval 49(4):2692–2706
Wei YJ (2019) Study on mechanism and evaluation method of shield tool wear in Bei**g waterless sand-pebble stratum. (Doctoral dissertation, Doctor’s thesis, China University of Geosciences) (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.27493/d.cnki.gzdzy.2019.000040
Wu J (2020) Study on the mechanical interaction and wear between shield cutting tools and rock or soil. (Doctoral dissertation, Doctor’s thesis, Bei**g Jiaotong University) (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.26944/d.cnki.gbfju.2020.003832
Yu HJ, Mooney M, Bezuijen A (2020) A simplified excavation chamber pressure model for EPBM tunneling. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 103:103457
Zhang XP, Tang SH, Liu QS, Tu XB, Chen P, Li FY (2021) An experimental study on cutting tool hardness optimization for shield TBMs during dense fine silty sand ground tunneling. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80(9):6813–6826
Zhang XP, Tang SH, Liu QS, Wang HJ, Li XF, Chen P, Liu H (2023) Key technology for the construction and inspection of long-distance underwater tunnel for 1000 kV gas-insulated transmission line. Bull Eng Geol Environ 82(1):7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02991-7
Zhao BY, Liu DY, Jiang B (2018) Soil conditioning of waterless sand–pebble stratum in EPB tunnel construction. Geotech Geol Eng 36(4):2495–2504
Zheng DZ, Bezuijen A, Thewes M (2021) An experimental study on foam infiltration into saturated sand and its consequence for EPB shield tunneling. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 111:103878
Zhou X (2020) Development and experimental research on new soil conditioner materials for sandy pebble stratum (Doctoral dissertation, Doctor's thesis, China University of Geosciences) (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.27493/d.cnki.gzdzy.2020.000072
Zumsteg R, Langmaack L (2017) Mechanized tunneling in soft soils: choice of excavation mode and application of soil-conditioning additives in glacial deposits. Eng 3(6):863–870
Acknowledgements
The support provided by National Natural Science Foundation of Youth Fund Project of China (Grant No. 52308415), China postdoctoral Science Foundation on the 74th grant program (Grant No.2023M742713), Fellowship of China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2022TQ0241), Key Research and Development Program of Hubei Province (Grant No. 2021BCA154) and Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (Grant No. 2021CFA081) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, SH., Zhang, XP., Liu, QS. et al. Experimental study on the influence mechanism of soil additives on scraper wear during EPB-TBM tunnelling in abrasive sandy ground. Bull Eng Geol Environ 83, 202 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-024-03648-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-024-03648-3