Abstract:
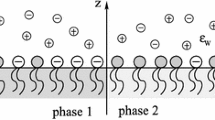
We propose a Poisson-Boltzmann electrostatic theory for DNA/cationic lipid complexes modeled as a stack of aligned DNA chains intercalated with lipid bilayers, a structure suggested by the recent X-ray synchrotron studies of Radler et al. Poisson-Boltzmann theory is shown to predict that the isoelectric point - where the DNA and cationic lipid charges are in balance - is unstable against absorption of extra DNA or lipid material. The instability is caused by the entropy gain obtained following the release of small ions inside the complex and is manifested by singular behavior of the rod-rod spacing near the isoelectric point. We apply the theory to a discussion of the results of Radler et al.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 21 July 1997 / Received in final form: 19 January 1998 /Accepted: 5 March 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruinsma, R. Electrostatics of DNA-cationic lipid complexes: isoelectric instability. Eur. Phys. J. B 4, 75–88 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100510050353
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s100510050353