Abstract
Context
The article explores and compares the electronic structure and magnetic properties of transition metal phosphate materials, namely FePS3, CoPS3, and NiPS3.
Research findings
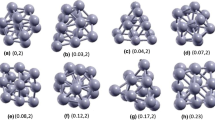
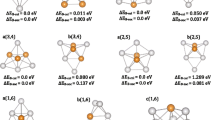
Analysis of the optimized configuration reveals significant insights into the electronic properties of MnPS3 clusters. Electrons within the cluster exhibit a flow from the metal atom M and the non-metal atom P to the non-metal atom S. The S atom serves as the primary site for electrophilic reactions within the cluster, while the metal atom hosts the main site for nucleophilic reactions. Configurations 2a(2), 2b(2), 3a(4), 3b(3), and 3c(2) exhibit enhanced electron mobility and optimal electronic properties. Moreover, the analysis of the magnetic properties of the optimized configurations demonstrates that the magnetic behavior of MnPS3 clusters is influenced by the spin motion of α electrons in the p orbital. Metal atoms make a relatively significant contribution to the magnetic properties of MnPS3 clusters. Configurations 1b(3), 2c(4), and 3a(4) exhibit comparatively higher magnetic properties compared to other configurations of the same size. This study identifies the optimal configuration for the magnetic and electronic properties of transition metal phosphorothioate materials. It also elucidates the trends in magnetic and electronic properties as the number of metal atoms varies, thereby providing valuable theoretical support for the application of these materials in the fields of magnetic materials and electronic devices.
Methods
In this study, the Fe-based transition elements, namely Fe, Co, and Ni, are selected as the metal atoms M. The cluster MPS3 is used to simulate the local structure of the material, allowing for an investigation into the influence of the metal atoms on its electronic and magnetic properties. By increasing the number of metal atoms and expanding the cluster size, the variations in these properties are explored. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations are performed using the B3LYP functional within the Gaussian09 software package. The MnPS3 cluster is subjected to optimal calculations and vibrational analysis at the def2-tzvp quantization level, resulting in optimized configurations with different spin multiplet degrees. Quantum chemistry software GaussView, wave function analysis software Multiwfn, and plotting software Origin are utilized for data characterization and graphical representation of the magnetic and electronic properties of the optimized configurations. Through the employment of these computational tools, valuable insights into the magnetic and electronic properties of the MnPS3 cluster and its dependency on different metal atoms are obtained.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Novoselov KS, Geim AK, Morozov SV, Jiang DE, Zhang Y, Dubonos SV, Firsov AA (2004) Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 306(5696):666–669
Akinwande D, Brennan CJ, Bunch JS, Egberts P, Felts JR, Gao H, Zhu Y (2017) A review on mechanics and mechanical properties of 2D materials—graphene and beyond. Extreme Mech Lett 13:42–77
Gibertini M, Koperski M, Morpurgo AF, Novoselov K (2019) Magnetic 2D materials and heterostructures. Nat Nanotechnol 14(5):408–419
Kim SJ, Choi K, Lee B, Kim Y, Hong BH (2015) Materials for flexible, stretchable electronics: graphene and 2D materials. Annu Rev Mater Res 45:63–84
Zheng XX, Fang ZG, Qin Y, Hou QQ, Wu TH, Mao ZL (2021) Electronic properties of cluster Fe3Ni3. J Guizhou Univ 38(05):7–12+19
Anichini C, Czepa W, Pakulski D, Aliprandi A, Ciesielski A, Samorì P (2018) Chemical sensing with 2D materials. Chem Soc Rev 47(13):4860–4908
Yamashita S (2019) Nonlinear optics in carbon nanotube, graphene, and related 2D materials. Apl Photonics 4(3):034301
Mao ZL, Fang ZG, Hou QQ, Wang Q, Xu Y, Song JL (2022) The predictive analysis of cluster Co3FeP spectra. J Jiangxi Norm Univ 46(01):81–86
Kanahashi K, Pu J, Takenobu T (2020) 2D materials for large-area flexible thermoelectric devices. Adv Energy Mater 10(11):1902842
FlemG Le, Brec R, Ouvard G, Louisy A, Segransan P (1982) Magnetic interactions in the layer compounds MPX3 (M= Mn, Fe, Ni; X= S, Se). J Phys Chem Solids 43(5):455–461
Lançon D, Walker HC, Ressouche E, Ouladdiaf B, Rule KC, McIntyre GJ, Wildes AR (2016) Magnetic structure and magnon dynamics of the quasi-two-dimensional antiferromagnet FePS3. Phys Rev B 94(21):214407
Zollner K, Fabian J (2022) Proximity effects in graphene on monolayers of transition-metal phosphorus trichalcogenides MPX3 (M: Mn, Fe, Ni Co, and X: S, Se). Phys Rev B 106(3):035137
Zheng Y, Jiang X, Xue X, Dai J, Feng Y (2019) Ab initio study of pressure-driven phase transition in FePS3 and FePSe3. Phys Rev B 100(17):174102
Wang S, ** of FePS3 promotes intrinsic active sites for the efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. Nanoscale 12(27):14459–14464
Wildes AR, Lançon D, Chan MK, Weickert F, Harrison N, Simonet V, Rønnow HM (2020) High field magnetization of FePS3. Phys Rev B 101(2):024415
Coak MJ, Jarvis DM, Hamidov H, Wildes AR, Paddison JAM, Liu C, Saxena SS (2021) Emergent magnetic phases in pressure-tuned van der Waals antiferromagnet FePS3. Phys Rev X 11(1):011024
Ghosh A, Palit M, Maity S, Dwij V, Rana S, Datta S (2021) Spin-phonon coupling and magnon scattering in few-layer antiferromagnetic FePS3. Phys Rev B 103(6):064431
Lee JU, Lee S, Ryoo JH, Kang S, Kim TY, Kim P, Cheong H (2016) Ising-type magnetic ordering in atomically thin FePS3. Nano Lett 16(12):7433–7438
Wildes AR, Simonet V, Ressouche E, Ballou R, McIntyre GJ (2017) The magnetic properties and structure of the quasi-two-dimensional antiferromagnet CoPS3. J Phys: Condens Matter 29(45):455801
Gu Y, Zhang S, Zou X (2020) Tunable magnetism in layered CoPS3 by pressure and carrier do**. Sci China Mater 64(3):673–682
Oliveira FM, Paštika J, Mazánek V, Melle-Franco M, Sofer Z, Gusmão R (2021) Cobalt phosphorous trisulfide as a high-performance electrocatalyst for the oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13(20):23638–23646
Li X, Fang Y, Wang J, Wei B, Qi K, Hoh HY, Su C (2019) High-yield electrochemical production of large-sized and thinly layered NiPS3 flakes for overall water splitting. Small 15(30):1902427
Kim SY, Kim TY, Sandilands LJ, Sinn S, Lee MC, Son J (2018) Charge-spin correlation in van der Waals antiferromagnet NiPS3. Phys Rev Lett 120(13):136402
Chu J, Wang F, Yin L, Lei L, Yan C, Wang F, He J (2017) High-performance ultraviolet photodetector based on a few-layered 2D NiPS3 nanosheet. Adv Func Mater 27(32):1701342
Pen L, Wu SY, Guo JX, Zhong SY, Chen XH (2018) Theoretical investigations on the structural, electronic and spectral properties of VFn (n= 1–7) clusters. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung A 73(12):1091–1104
Wu TH, Fang ZG, Wang ZY, Song J, Song JL, Liu LE (2023) The stable polarizability of cluster Co2Mo2P3 structure. J Jiangxi Norm Univ 47(02):148–153
Li HX, Cheng KG, Wang JC, Liu ZP, He H, Zhao YR (2023) Probing the structural evolution, electronic and vibrational properties of anionic sodium-doped magnesium clusters. Comp Mater Sci 226:112212
Car R, Parrinello M (1985) Unified approach for molecular dynamics and density-functional theory. Phys Rev Lett 55(22):2471–2474
Zhang XY, Zhao YR, Li HX, Cheng KG, Liu ZR, Liu ZP, He H (2023) Probing the effects of lithium do** on structures, properties, and stabilities of magnesium cluster anions. Chinese Phys B 32:066102
Qin Y, Fang ZG, Zhang W, Li LH, Liao Q (2020) The study on the catalytic properties of cluster Co3NiB in the hydrogen evolution reaction. J Jiangxi Norm Univ 44(01):56–62
Saloni S, Ranjan P, Chakraborty T (2023) A computational study of CuCrX2 (X= S, Se, Te) for intermediate band solar cell: conceptual density functional theory approach. J Mol Graph Model 124:108534
Fang ZG, Xu Y, Wang ZY, Mao ZL, Zheng XX, Zeng XY, Wu TH (2022) The study on hydrogen evolution reaction of cluster Co4P amorphous alloy based on quantum chemistry. J Jiangxi Norm Univ 46(3):221–226
Lou Z, Cheng C, Cui Y, Tian H (2022) Interfacial interaction-driven rheological properties of quartz nanofluids from molecular dynamics simulations and density functional theory calculations. J Mol Model 28(7):189
Fang ZG, Wang ZY, Zheng XX, Qin Y, Mao ZL, Zeng XY, Zhu YW, Wang Q (2022) Study on the polarizability, dipole moment and density of states of cluster Co3NiB2. J Guizhou Univ 39(1):17–24
Haines CRS, Coak MJ, Wildes AR, Lampronti GI, Liu C, Nahai-Williamson P, Saxena SS (2018) Pressure-induced electronic and structural phase evolution in the van der Waals compound FePS3. Phys Rev Lett 121(26):266801
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR (2010) Gaussian 09, Revision D.01[CP]. Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT
Evarestov RA, Kuzmin A (2020) Origin of pressure-induced insulator-to-metal transition in the van der Waals compound FePS3 from first-principles calculations. J Comput Chem 41(14):1337–1344
Liu Q, Wang L, Fu Y, Zhang X, Huang L, Su H, Dai J-F (2021) Magnetic order in XY-type antiferromagnetic monolayer CoPS3 revealed by Raman spectroscopy. Phys Rev B 103(23):235411
Kuo C-T, Neumann M, Balamurugan K, Park HJ, Kang S, Shiu HW, Park J-G (2016) Exfoliation and Raman spectroscopic fingerprint of few-layer NiPS3 van der Waals crystals. Sci Rep 6(1):1–10
Zhang J, Lu T (2021) Efficient evaluation of electrostatic potential with computerized optimized code. Phys Chem Chem Phys 23(36):20323–20328
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China Key Project (51634004); National Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (202210146008, 202110146027); and Liaoning Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program Projects (202210146021, 202210146020, 202110146052, 202110146049, 202110146049).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
**gli Song was mainly responsible for data analysis and writing the first draft. Zhigang Fang is the corresponding author of the article and is responsible for the guidance of the writing work. Li’e Liu, Daixia Wei, and Lin Yuan were responsible for data calculation and collection. All the authors revised the draft manuscript and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, J., Fang, Z., Liu, L. et al. Application of density functional theory to study the electronic structure and magnetic behavior of clusters MnPS3 (M = Fe, Co, Ni; n = 0 ~ 3). J Mol Model 29, 240 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-023-05642-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-023-05642-0