Abstract
Introduction
Our aim is to study the correlation between vitamin D metabolites and osteoporosis in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC–MS/MS). At the same time, other influencing factors and serum biomarkers of osteoporosis in patients with RA were studied.
Materials and methods
Patients with RA admitted from January 2020 to December 2020 were selected at our hospital. The subjects were divided into the normal bone mineral density (BMD), osteopenia, and osteoporosis groups. The differences of vitamin D (VD) metabolites among groups were compared. The Pearson correlation coefficient was used to analyze the relationship between BMD and various parameters. The relationship between BMD and influencing factors was studied by a multiple linear regression equation.
Results
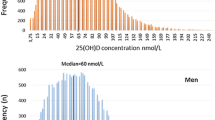
A total of 287 patients with RA were included. RA patients with 25-hydroxy vitamin D [25(OH)D] deficiency accounted for 43.63% and 25(OH)D insufficient levels accounted for 31.37%. There were 31 cases (10.80%) in the normal BMD group, 161 cases (56.10%) in the osteopenia group, and 95 cases (33.10%) in the osteoporosis group. The BMD of L1-4 (T- score) was negatively correlated with age (P < 0.05), course of disease (P < 0.05), and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) (P < 0.05), and positively correlated with 25(OH)D3 (P < 0.05). The multiple linear regression model results showed that age and 25(OH)D3 were independent predictors of BMD; this explained 22.11% of the total variation.
Conclusions
VD deficiency and insufficient are common in RA patients. RA patients can be appropriately supplemented with VD. VD3 may be a better choice.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, McInnes IB (2016) Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 388:2023–2038
Haugeberg G, Uhlig T, Falch JA, Halse JI, Kvien TK (2000) Bone mineral density and frequency of osteoporosis in female patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results from 394 patients in the Oslo County rheumatoid arthritis register. Arthritis Rheum 43:522–530
Calabresi E, Petrelli F, Bonifacio AF, Puxeddu I, Alunno A (2018) One year in review 2018: pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 36:175–184
Mori Y, Kuwahara Y, Chiba S, Kogre A, Baba K, Kamimura M, Itoi E (2017) Bone mineral density of postmenopausal women with rheumatoid arthritis depends on disease duration regardless of treatment. J Bone Miner Metab 35:52–57
Hauser B, Riches PL, Wilson JF, Horne AE, Ralston SH (2014) Prevalence and clinical prediction of osteoporosis in a contemporary cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Oxf Engl 53:1759–1766
Zerbini CAF, Clark P, Mendez-Sanchez L, Pereira RMR, Messina OD, Uña CR, Adachi JD, Lems WF, Cooper C, Lane NE, IOF Chronic Inflammation and Bone Structure (CIBS) Working Group (2017) Biologic therapies and bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoporos Int 28:429–446
Kang EH, Ha YJ, Lee YJ (2020) Autoantibody biomarkers in rheumatic diseases. Int J Mol Sci 21:1382
Fujita T, Matsui T, Nakao Y, Shiozawa S, Imai Y (1990) Cytokines and osteoporosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 587:371–375
Yong W, Hongbin L, **g W, **g Z, Ning T, Lijie B (2020) Associations of changes in serum inflammatory factors, MMP-3, 25(OH)D and intestinal flora with osteoporosis and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Lab. https://doi.org/10.7754/Clin.Lab.2020.200242
Tan LM, Long TT, Guan XL, Wu SF, Zheng W, Fu HY, Wang QH, Meng YM, Wu Y, Zeng TT, Tian YJ, Yu JL, Chen JJ, Li H, Cao LP (2018) Diagnostic value of vitamin D status and bone turnover markers in rheumatoid arthritis complicated by osteoporosis. Ann Clin Lab Sci 48:197–204
Lips P, van Schoor NM (2011) The effect of vitamin D on bone and osteoporosis. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 25:585–591
Despotović M, Jevtović Stoimenov T, Stojanović S, Bašić J, Kundalić J, Đorđević B, Ranđelović M, Pavlović D (2021) Association of vitamin D receptor genetic variants with bone mineral density and inflammatory markers in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Biochem 87:26–31
Sirbu E, Buleu F, Tudor A, Dragan S (2020) Vitamin D and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a retrospective study in a Romanian cohort. Acta Biochim Pol 67:267–272
Herly M, Stengaard-Pedersen K, Vestergaard P, Christensen R, Möller S, Østergaard M, Junker P, Hetland ML, Hørslev-Petersen K, Ellingsen T (2020) Impact of season on the association between vitamin D levels at diagnosis and one-year remission in early rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Rep 10:7371
Jelsness-Jørgensen LP, Grøvle L, Julsrud HA (2020) Association between vitamin D and fatigue in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 10:e034935
Lodder MC, de Jong Z, Kostense PJ, Molenaar ET, Staal K, Voskuyl AE, Hazes JM, Dijkmans BA, Lems WF (2004) Bone mineral density in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: relation between disease severity and low bone mineral density. Ann Rheum Dis 63:1576–1580
Saenger AK, Laha TJ, Bremner DE, Sadrzadeh SM (2006) Quantification of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D(2) and D(3) using HPLC-tandem mass spectrometry and examination of reference intervals for diagnosis of vitamin D deficiency. Am J Clin Pathol 125:914–920
Meng J, Li Y, Yuan X, Lu Y (2017) Evaluating osteoporotic fracture risk with the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool in Chinese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Medicine (Baltimore) 96:e6677
Nakamura T (2004) WHO diagnostic criteria for osteoporosis and trends in Europe and USA. Nihon Rinsho 62:235–239
Li YM, Feng Q, Jiang WQ, Wu BT, Feng JF (2021) Evaluation of vitamin D storage in patients with chronic kidney disease: detection of serum vitamin D components using high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 210:105860
Bauer D, Krege J, Lane N, Leary E, Libanati C, Miller P, Myers G, Silverman S, Vesper HW, Lee D, Payette M, Randall S (2012) National bone health alliance bone turnover marker project: current practices and the need for US harmonization, standardization, and common reference ranges. Osteoporos Int 23:2425–2433
Sukharani N, Dev K, Rahul F, Bai P, Ali A, Avinash F, Kammawal Y, Kumar N, Rizwan A (2021) Association between rheumatoid arthritis and serum vitamin D levels. Cureus 13:e18255
Ramu R, Arya V, Chitkara A, Taneja RS, Ali M (2018) Serum 25 hydroxy vitamin D levels in newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis and their correlation with disease activity. J Assoc Physicians India 66:38–41
Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Dawson-Hughes B, Orav EJ, Staehelin HB, Meyer OW, Theiler R, Dick W, Willett WC, Egli A (2016) Monthly high-dose vitamin D treatment for the prevention of functional decline: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med 176:175–183
Cranney A, Horsley T, O’Donnell S, Weiler H, Puil L, Ooi D, Atkinson S, Ward L, Moher D, Hanley D, Fang M, Yazdi F, Garritty C, Sampson M, Barrowman N, Tsertsvadze A, Mamaladze V (2007) Effectiveness and safety of vitamin D in relation to bone health. Evid Rep Technol Assess 158:1–235
Zhang SW, Jian W, Sullivan S, Sankaran B, Edom RW, Weng N, Sharkey D (2014) Development and validation of an LC–MS/MS based method for quantification of 25 hydroxyvitamin D2 and 25 hydroxyvitamin D3 in human serum and plasma. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 961:62–70
van den Ouweland JM, Beijers AM, van Daal H (2014) Overestimation of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 by increased ionisation efficiency of 3-epi-25-hydroxyvitamin D3 in LC–MS/MS methods not separating both components as determined by an LC–MS/MS method for separate quantification of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3, 3-epi-25-hydroxyvitamin D3 and 25-hydroxyvitamin D2 in human serum. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 967:195–202
Auréal M, Machuca-Gayet I, Coury F (2020) Rheumatoid arthritis in the view of osteoimmunology. Biomolecules 11:48
Wen H, Liu Y, Li J, Wei D, Liu D, Zhao F (2018) Inhibitory effect and mechanism of 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3 on RANKL expression in fibroblast-like synoviocytes and osteoclast-like cell formation induced by IL-22 in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 36:798–805
Luo J, Wen H, Guo H, Cai Q, Li S, Li X (2013) 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits the RANKL pathway and impacts on the production of pathway-associated cytokines in early rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed Res Int 2013:101805
Harrison SR, Jutley G, Li D, Sahbudin I, Filer A, Hewison M, Raza K (2020) Vitamin D and early rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Rheumatol 4:38
Mosaad YM, Hammad EM, Fawzy Z, Abdal Aal IA, Youssef HM, ElSaid TO, Monir R, El-Deek BS (2014) Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism as possible risk factor in rheumatoid arthritis and rheumatoid related osteoporosis. Hum Immunol 75:452–461
Hussien YM, Shehata A, Karam RA, Alzahrani SS, Magdy H, El-Shafey AM (2013) Polymorphism in vitamin D receptor and osteoprotegerin genes in Egyptian rheumatoid arthritis patients with and without osteoporosis. Mol Biol Rep 40:3675–3680
Raterman HG, Lems WF (2019) Pharmacological management of osteoporosis in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a review of the literature and practical guide. Drugs Aging 36:1061–1072
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to all those who helped us during the writing of this manuscript.
Funding
Science and Technology Program of Sichuan Province (2017SZ0148).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: JZ and LZ. Administrative support: JY, SL and YZ. Provision of study materials or patients: JZ, LZ. Collection and assembly of data: JL, ML and LT. Data analysis and interpretation: YR and JD. Manuscript writing: JZ and LZ. Manuscript revision: JF. Final approval of manuscript: all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All of the authors had no any personal, financial, commercial, or academic conflicts of interest separately.
Ethics approval
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. This study was conducted with approval from the Ethics Committee of our Hospital No.S2016051.
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, J., Zhu, L., Yang, J. et al. Correlation between vitamin D metabolites and rheumatoid arthritis with osteoporosis by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC–MS/MS). J Bone Miner Metab 40, 696–703 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-022-01337-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-022-01337-3