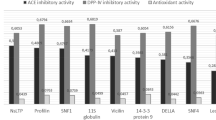
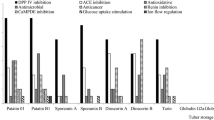
Abstract
In this study, the potential of oilseed proteins from soybean, peanut, sesame, sunflower seed and flaxseed as antimicrobial peptide (AMP) precursors was assessed using the bioinformatics method. Thirty-four novel potential AMPs were obtained by in silico hydrolysis of 12 oilseed protein sequences, and 11 of them were positive in all four algorithm tests in CAMPR3. Among the six proteases analyzed, trypsin cleaved soybean, peanut, sesame and sunflower seed proteins most effectively to generate AMPs, with three, four, two and two AMPs obtained, respectively. Subtilisin was most effective for flaxseed AMPs release, obtaining three AMPs. More than 85% of AMPs were predicted to be cationic peptides, and some AMPs were hydrophobic. These potential AMPs were classified as non-toxic peptides, and 15 peptides were non‐allergenic. All the AMPs were unstable to digestive enzymes according to in silico simulated digestion. The results of this study provide a theoretical basis for further development of AMPs using oilseed proteins.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Brogden KA (2005) Antimicrobial peptides: pore formers or metabolic inhibitors in bacteria? Nat Rev Microbiol 3(3):238–250. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1098
Browne K, Chakraborty S, Chen RX, Willcox MDP, Black DS, Walsh WR, Kumar N (2020) A new era of antibiotics: the clinical potential of antimicrobial peptides. Int J Mol Sci 21(19):7047. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197047
Cherkasov A, Hilpert K, Jenssen H, Fjell CD, Waldbrook M, Mullaly SC, Volkmer R, Hancock REW (2009) Use of artificial intelligence in the design of small peptide antibiotics effective against a broad spectrum of highly antibiotic-resistant superbugs. ACS Chem Biol 4(1):65–74. https://doi.org/10.1021/cb800240j
Das R, Dutta A, Bhattacharjee C (2012) Preparation of sesame peptide and evaluation of antibacterial activity on typical pathogens. Food Chem 131(4):1504–1509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.09.136
Dimitrov I, Naneva L, Doytchinova I, Bangov I (2014) AllergenFP: allergenicity prediction by descriptor fingerprints. Bioinformatics 30(6):846–851. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt619
dos Santos-Silva CA, Zupin L, Oliveira-Lima M, Vilela LMB, Bezerra-Neto JP, Ferreira-Neto JR, Ferreira JDC, de Oliveira-Silva RL, de Pires CJ, Aburjaile FF, de Oliveira MF, Kido EA, Crovella S, Benko-Iseppon AM (2020) Plant antimicrobial peptides: state of the art, in silico prediction and perspectives in the omics era. Bioinf Biol Insights 14:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1177/1177932220952
Duan XJ, Zhang M, Chen FS (2021) Prediction and analysis of antimicrobial peptides from rapeseed protein using in silico approach. J Food Biochem 45(4):e13598. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.13598
Dziuba B, Dziuba M (2014) New milk protein-derived peptides with potential antimicrobial activity: an approach based on bioinformatic studies. Int J Mol Sci 15(8):14531–14545. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150814531
Freitas CS, Vericimo MA, da Silva ML, da Costa GCV, Pereira PR, Paschoalin VMF, Del Aguila EM (2019) Encrypted antimicrobial and antitumoral peptides recovered from a protein-rich soybean (Glycine max) by-product. J Funct Foods 54:187–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2019.01.024
Gasteiger E, Hoogland C, Gattiker A, Duvaud S, Wilkins MR, Appel RD, Bairoch A (2005) Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In: The proteomics protocols handbook. Humana Press, pp 571–607
Geourjon C, Deléage G (1995) SOPMA: significant improvements in protein secondary structure prediction by consensus prediction from multiple alignments. Bioinformatics 11(6):681–684. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/11.6.681
Gomaa AI, Martinent C, Hammami R, Fliss I, Subirade M (2017) Dual coating of liposomes as encapsulating matrix of antimicrobial peptides: development and characterization. Front Chem 5:103. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2017.00103
Gonzalez-Perez S, Vereijken JM (2007) Sunflower proteins: overview of their physicochemical, structural and functional properties. J Sci Food Agric 87(12):2173–2191. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.2971
Goto C, Hirano M, Hayashi K, Kikuchi Y, Hara-Kudo Y, Misawa T, Demizu Y (2019) Development of amphipathic antimicrobial peptide foldamers based on magainin 2 sequence. ChemMedChem 14(22):1911–1916. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201900460
Gu YC, Majumder K, Wu JP (2011) QSAR-aided in silico approach in evaluation of food proteins as precursors of ACE inhibitory peptides. Food Res Int 44(8):2465–2474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2011.01.051
Gupta S, Kapoor P, Chaudhary K, Gautam A, Kumar R, Raghava GPS (2013) In silico approach for predicting toxicity of peptides and proteins. PLoS ONE 8(9):e73957. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0073957
Han RX, Maycock J, Murray BS, Boesch C (2019) Identification of angiotensin converting enzyme and dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory peptides derived from oilseed proteins using two integrated bioinformatic approaches. Food Res Int 115:283–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2018.12.015
Han RX, Alvarez AJH, Maycock J, Murray BS, Boesch C (2021) Comparison of alcalase- and pepsin-treated oilseed protein hydrolysates—experimental validation of predicted antioxidant, antihypertensive and antidiabetic properties. Curr Res Food Sci 4:141–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crfs.2021.03.001
Houyvet B, Zanuttini B, Corre E, Le Corguillé G, Henry J, Zatylny-Gaudin C (2018) Design of antimicrobial peptides from a cuttlefish database. Amino Acids 50(11):1573–1582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-018-2633-4
Hwang CF, Chen YA, Luo C, Chiang WD (2016) Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of peptide fractions from flaxseed protein hydrolysed by protease from Bacillus altitudinis HK02. Int J Food Sci Technol 51(3):681–689. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.13030
Ibrahim MA, Bester MJ, Neitz AW, Gaspar ARM (2019) Tuber storage proteins as potential precursors of bioactive peptides: an in silico analysis. Int J Pep Res Therapeu 25(2):437–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-018-9688-7
Ji DW, Udenigwe CC, Agyei D (2019) Antioxidant peptides encrypted in flaxseed proteome: an in silico assessment. Food Sci Hum Well 8(3):306–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2019.08.002
Jimsheena VK, Gowda LR (2011) Angiotensin 1-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides derived from arachin by simulated gastric digestion. Food Chem 125(2):561–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.09.048
Kalmykova SD, Arapidi GP, Urban AS, Osetrova MS, Gordeeva VD, Ivanov VT, Govorum VM (2018) In silico analysis of peptide potential biological functions. Russ J Bioorg Chem 44(4):367–385. https://doi.org/10.1134/S106816201804009X
Kong XZ, Zhang LN, Song WG, Zhang CM, Hua YF, Chen YM, Li XF (2021) Separation, identification and molecular binding mechanism of dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory peptides derived from walnut (Juglans regia L.) protein. Food Chem 347:129062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129062
Kotecka-Majchrzak K, Sumara A, Fornal E, Montowsk M (2020) Oilseed proteins—properties and application as a food ingredient. Trends Food Sci Technol 106:160–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.10.004
Macesic N, Polubriaginof F, Tatonetti NP (2017) Machine learning: novel bioinformatics approaches for combating antimicrobial resistance. Curr Opin Infect Dis 30(6):511–517. https://doi.org/10.1097/QCO.0000000000000406
Minkiewicz P, Iwaniak A, Darewicz M (2019) BIOPEP-UWM database of bioactive peptides: current opportunities. Int J Mol Sci 20:5978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20235978
Moretta A, Scieuzo C, Petrone AM, Salvia R, Manniello MD, Franco A, Lucchetti D, Vassallo A, Vogel H, Sgambato A, Falabella P (2021) Antimicrobial peptides: a new hope in biomedical and pharmaceutical fields. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 11:668632. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2021.668632
Nath A, Szecsi G, Csehi B, Mednyánszky Z, Kiskó G, Bányai É, Dernovics M, Koris A (2017) Production of hypoallergenic antibacterial peptides from defatted soybean meal in membrane bioreactor: a bioprocess engineering study with comprehensive product characterization. Food Technol Biotechnol 55(3):308–324. https://doi.org/10.17113/ftb.55.03.17.5040
Nath A, Kailo GG, Mednyánszky Z, Kiskó G, Csehi B, Pásztorne-Huszár K, Gerencsér-Berta R, Galambos I, Pozsgai E, Bánvölgyi S, Vatai G (2020) Antioxidant and antibacterial peptides from soybean milk through enzymatic- and membrane-based technologies. Bioengineering 7(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7010005
Orruno E, Morgan MRA (2007) Purification and characterisation of the 7S globulin storage protein from sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Food Chem 100(3):926–934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.10.051
Taheri B, Mohammadi M, Nabipour I, Momenzadeh N, Roozbehani M (2018) Identification of novel antimicrobial peptide from Asian sea bass (Lates calcarifer) by in silico and activity characterization. PLoS ONE 13(10):e0206578. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0206578
Tan YN, Ayob MK, Yaacob WAW (2013) Purification and characterisation of antibacterial peptide-containing compound derived from palm kernel cake. Food Chem 136(1):279–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.08.012
Thanh VH, Shibasaki K (1976) Major proteins of soybean seeds. A straightforward fractionation and their characterization. J Agric Food Chem 24(6):1117–1121. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf60208a030
Thomas S, Karnik S, Barai RS, Jayaraman VK, Idicula-Thomas S (2010) CAMP: a useful resource for research on antimicrobial peptides. Nucleic Acids Res 38:D774–D780. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp1021
Tkaczewska J (2020) Peptides and protein hydrolysates as food preservatives and bioactive components of edible films and coatings—a review. Trends Food Sci Technol 106:298–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.10.022
Torres MDT, Sothiselvam S, Lu TK, de la Fuente-Nunez C (2019) Peptide design principles for antimicrobial applications. J Mol Biol 431(18):3547–3567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2018.12.015
Tu ML, Cheng SZ, Lu WH, Du M (2018) Advancement and prospects of bioinformatics analysis for studying bioactive peptides from food-derived protein: sequence, structure, and functions. Trends Anal Chem 105:7–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.04.005
Udenigwe CC (2014) Bioinformatics approaches, prospects and challenges of food bioactive peptide research. Trends Food Sci Technol 36(2):137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2014.02.004
Waghu FH, Gopi L, Barai RS, Ramteke P, Nizami B, Idicula-Thomas S (2014) CAMP: collection of sequences and structures of antimicrobial peptides. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D1154–D1158. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1157
Waghu FH, Barai RS, Gurung P, Idicula-Thomas S (2016) CAMPR3: a database on sequences, structures and signatures of antimicrobial peptides. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D1094–D1097. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1051
Wang GS, Li X, Wang Z (2016) APD3: the antimicrobial peptide database as a tool for research and education. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D1087–D1093. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1278
Wang JJ, Dou XJ, Song J, Lyu YF, Zhu X, Xu L, Li WZ, Shan AS (2019) Antimicrobial peptides: promising alternatives in the post feeding antibiotic era. Med Res Rev 39(3):831–859. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.21542
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U21A20270), the Science and Technology Project of Henan Province (212102110323), the Scientific Research Starting Foundation Project for High-level Talents of Henan University of Technology (2018BS078) and the Innovative Funds Plan of Henan University of Technology (2021ZKCJ03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XD and YL contributed to the study conception and design. XD, YL, MZ and ZL performed data collection and analysis. XD and YL wrote the main manuscript text. XD and FC contributed to the revision of the manuscript and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This study did not involve human or animals participants.
Additional information
Handling editor: S. Albrecht.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, X., Leng, Y., Chen, F. et al. Evaluation of oilseed proteins as precursors of antimicrobial peptides using bioinformatics method. Amino Acids 55, 359–370 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-023-03234-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-023-03234-z