Abstract
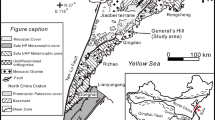
**angshan volcanic-related uranium ore field, as the historic largest uranium producer in China, is characterized by a large volcanic-intrusive complex and a number of uranium deposits. In most of the deposits, various types of dikes are spatially associated with the uranium ore bodies, although there have been no systematic attempts to integrate the geochronology and petrogenesis of these dykes and their link with uranium mineralization. In this study, whole-rock major and trace elements, zircon U–Pb dating and zircon Hf–O isotopic analysis were carried out on the **agnshan felsic-intermediate dikes, including granitic porphyry, quartz monzonitic porphyry and dioritic porphyry. These felsic-intermediate dikes have the similar geochemical characteristics with the major ore-hosting volcanic rocks, such as enrichment in large lithophile elements (i.e., Rb and Th) and some high-field strength elements (i.e., Zr, Y), but relative depletion in Sr, Ba, P and Ti. These dikes also exhibit zircon εHf(t) values concentrating from -9 to -4 and zircon δ18O values ranging from 7.6 to 10.0 ‰. Geochemical and isotopic data suggest that these dikes were predominantly derived from partial melting of crustal materials and possibly mingled with different proportions of mantle-derived materials during the formation of melts. SIMS and SHRIMP U–Pb dating of zircon grains from these felsic-intermediate dikes yield high-precision ages ranging from 136 to 131 Ma. Combined with previously reported age data indicates a rapid and concentrated dike emplacement event, although a few mafic-felsic dikes were sporadically emplaced at 126 -122 Ma. Such a relatively concentrated dike emplacement in the Early Cretaceous were most likely caused by the back-arc extension or intra-arc rift due to progressive rollback of the Paleo-Pacific Plate. Previous metallogenetic studies supported that the late-stage dikes at **angshan were temporally and spatially closely related to uranium mineralization. However, our new geochronological data and field observations indicate that the two episodes of uranium mineralization were not synchronous with the majority of dikes intrusions, indicating that they probably have no direct relationship in origin and that spatial coexistence were more likely due to multistage activities of faults. Rather, these dikes might act as a relatively reduced environment, and thus could facilitate the precipitation of uranium. In addition, all of these dikes can be considered favorable prospecting indicators in the **angshan ore field.












Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data presented in the text of the article are fully available without restriction from authors upon request. Code availability is not applicable.
References
Amelin Y, Lee DC, Halliday AN, Pidgeon RT (1999) Nature of the Earth’s earliest crust from hafnium isotopes in single detrital zircons. Nature 399:252–255
Black LP, Kamo SL, Allen CM, Aleinikoff JN, Davis DW, Korsch RJ, Foudoulis C (2003) TEMORA 1: a new zircon standard for Phanerozoic U-Pb geochronology. Chem Geol 200:155–170
Blichert-Toft J (2008) The Hf isotopic composition of zircon reference material 91500. Chem Geol 253:0–257
Bolhar R, Weaver SD, Whitehouse MJ, Palin JM, Woodhead JD, Cole JW (2008) Sources and evolution of arc magmas inferred from coupled O and Hf isotope systematics of plutonic zircons from the Cretaceous Separation Point Suite (New Zealand). Earth Planet Sc Lett 268:312–324
Bonnetti C, Liu X, Mercadier J, Cuney M, Deloule E, Villeneuve J, Liu W (2018) The genesis of granite-related hydrothermal uranium deposits in the **azhuang and Zhuguang ore fields, North Guangdong Province, SE China: Insights from mineralogical, trace elements and U-Pb isotopes signatures of the U mineralisation. Ore Geol Rev 92:588–612
Bonnetti C, Liu XD, Cuney M, Mercadier J, Riegler T, Yu C (2020) Evolution of the uranium mineralisation in the Zoujiashan deposit, **angshan ore field: Implications for the genesis of volcanic-related hydrothermal U deposits in South China. Ore Geol Rev 122:103514
Boynton WV (1984) Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: meteorite studies. Rare Earth Elem Geochem 93:63–114
Cai YQ, Zhang JD, Li ZY, Guo QY, Song JY, Fan HH, Liu HX, Qi FC, Zhang ML (2015) Outline of uranium resources characteristics and metallogenetic regularity in China. Acta Geol Sin-Engl 89:1051–1069 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen XM, Wang RC, Liu CS, Hu H, Zhang WL, Gao JF (2002) Isotopic bating and genesis for Fogang Biotite granites of Conghua Area. Guangdong Province Geol J China U 8(3):293–307 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen ZL, Wang YL, Zhou YG, Han FB, Wang PA, Gong HL, Shao F, Tang XS, Xu JS (2013) SHRIMP U-Pb dating of zircons from volcanic–intrusive complexes in the **angshan uranium ore field, Jiangxi Province, and Its Geological Implications. Geol China 40(1):217–228 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen YH, Chen ZY, Cai YQ, Shi ZH, Feng QH, Fu J (1997) The spatial–Temporal evolution of Meso-Cenozoic extensional structures and distribution of uranium deposits in Southeastern China. Uranium Geol 13:129–146 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen YW, Bi XW, Hu RZ, Dong SH (2012) Element geochemistry, mineralogy, geochronology and zircon Hf isotope of the Luxi and **azhuang granites in Guangdong province, China: implications for U mineralization. Lithos 150:119–134
Chesner CA, Ettlinger AD (1989) Composition of volcanic allanite from the Toba Tuffs, Sumatra, Indonesia. Am Mineral 74:750–758
Dahlkamp JF (2009) Uranium deposits of the World. Berlin Heidelberg, Springer–Verlag, pp 86–157
Deng P, Shen WZ, Lin HF, Ye HM, Wang XC, Pu W, Tan ZZ (2003) Uranium mineralization relation related to mantle fluid: a case study of the **anshi deposit in the **azhuang uranium ore field. Geochimica 32:520–528 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Fan HH, Ling HF, Shen WZ, Wang DZ, Liu CS, Jiang YH (2001a) Nd–Sr–Pb isotope geochemistry of the volcanic–intrusive complex at **angshan. Jiangxi Province Acta Petrol Sin 17(3):395–402 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Fan HH, Ling HF, Wang DZ, Liu CS, Shen WZ, Jiang YH (2003) Study on metallogenetic mechanism of **angshan uranium orefield. Uranium Geol 19:208–213 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Fan HH, Wang DZ, Liu CS, Zhao LZ, Shen WZ, Ling HF, Duan Y (2001b) Discovery of quenched enclaves in subvolcanic rocks at **angshan, Jiangxi Province and its genetic mechanism. Acta Petrol Sin 75 (1):64–69+146 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Fan HH, Wang DZ, Shen WZ, Liu CS, Wang X, Ling HF (2005) Formation age of the intermediate–basic dikes and volcanic–Intrusive complex at **angshan. Jiangxi Province Geol Rev 51(1):86–91 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Fang XH, Hou WY, Wan GL (1982) Petrographic studies of the volcanic complex in the **angshan caldera. Acta Petrol Mineral Anal 1:1–10 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Gilder SA, Gill J, Coe RS, Zhao XX, Liu ZW, Wang GX, Yuan KR, Liu WL, Kuang GD, Wu HR (1996) Isotopic and paleomagnetic constraints on the Mesozoic tectonic evolution of south China. Geophys Res 101:16137–16154
Guo FS, Yang QK, Meng XJ, **e CF, Shi G, Chen LQ, Jiang ZP, Zeng T, Luo NH (2016) Geochemical characteristics and petrogenesis of the acidic volcano–intrusive complexes, **angshan. Jiangxi Acta Geol Sin 90(04):769–784 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Guo FS, Li ZH, Deng T, Qu MM, Zhou WP, Huang QY, Shang P, Zhang CY, Yan ZB (2020) Key factors controlling volcanic-related uranium mineralization in the **angshan basin, Jiangxi Province, South China: A review. Ore Geol Rev 122:103517
Guo J, Li ZY, Huang ZZ, Li XZ, Nie JT, Wang J (2014) Determination of fine porphyry in the scientific drill hole of **angshan uranium ore field and its geological significance. Miner Depo S1:195–196 (in Chinese with English abstract)
He S, Li Z, Guo D, Wang Y, Zhang C, Guo J, Fan Z (2020) Early mineralization age of the Hengjian uranium deposit: constraints from zircon SIMS U-Pb dating. Acta Geol Sin (engl Ed) 94:212–213
He ZY, Xu XS (2012) Petrogenesis of the late Yanshanian mantle derived intrusions in southeastern China, response to the geodynamics of paleo–Pacific plate subduction. Chem Geol 328:208–221
Hoskin PW, Schaltegger U (2003) The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis. Rev Miner Geochem 53(1):27–62
Hou KJ, Li YH, Zou TR, Qu XM, Shi YR, **e GQ (2007) Laser ablation–MC–ICP–MS technique for Hf isotope microanalysis of zircon and its geological applications. Acta Petrol Sin 23(10):2595–2604 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hu RZ, Li CY, Ni SJ, Liu J, Yu JS (1993) Research on ΣCO2 source in ore-forming hydrothermal solution of granite-type uranium deposit, South China. Science in China Ser B 10:102–112
Hu RZ, Bi XW, Su WC, Peng JT, Li CY (2004) The relationship between uranium metallogenesis and crustal extension during the Cretaceous-Tertiary in South China. Earth Sci Fron 11:153–160 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hu RZ, Bi XW, Peng JT, Liu S, Zhong H, Zhao JH, Jiang GH (2008) Uranium metallogenesis in South China and its relationship to crustal extension during the Cretaceous to Tertiary. Econ Geol 103:583–598
Jiang YH, Ling HF, Jiang SY, Fan HH, Shen WZ, Ni P (2005) Petrogenesis of a late Jurassic peraluminous volcanic complex and its high–Mg, potassic, quenched enclaves at **angshan, Southeast China. Petrol 46:1121–1154
Jiang YH, Ling HF, Jiang SY, Fan HH, Shen WZ, Ni P (2006) Trace element and Sr–Nd isotope geochemistry of fluorite from the **angshan uranium deposit, Southeast China. Econ Geol 101:1613–1622
Jiang YH, Zhao P, Zhou Q, Liao SY, ** GD (2011) Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of Early Cretaceous S–and A–type granites in the northwest of the GanHang Rift, SE China. Lithos 121:55–73
Kemp AIS, Hawkesworth CJ, Foster GL, Paterson BA, Woodhead JD, Hergt JM, Gray CM (2007) Magmatic and crustal differentiation history of granitic rocks from Hf–O isotopes in zircon. Science 315:980–983
King EM, Valley JW, Davis DW, Edwards GR (1998) Oxygen isotope ratios of Archean plutonic zircons from granite-greenstone belts of the Superior Province: indicator of magmatic source. Precambrian Res 92:365–387
Li FW, Chen WF, Zhu KR (2011) Geochemical characteristics and genesis of Mesozoic acid dikes in Miaoershan area. Uranium Geol 6:337–344 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li JX, Qin KZ, Li GM, Richards JP, Zhao JX, Cao MJ (2014a) Geochronology, geochemistry, and zircon Hf isotopic compositions of Mesozoic intermediate–felsic intrusions in central Tibet: petrogenetic and tectonic implications. Lithos 198:77–91
Li KY, Shen JL, Wang XP (1989) Isotopic geochronology of Mesozoic terrestrial volcanic rocks in the Zhejiang–Fujian–Jiangxi area. J Stratigr 13:1–13 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li SZ, Zang YB, Wang PC, Suo YH, Li XY, Liu X, Zhou ZZ, Liu XG, Wang Q (2017) Mesozoic tectonic transition in South China and initiation of palaeo–Pacific subduction. Earth Sci Fron 24:2–13 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li XH, Hu RZ, Rao B (1997) Geochronology and geochemistry of Cretaceous mafic dikes from northern Guangdong, SE China. Geochimica 26:15–31 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li XH, Li WX, Li QL, Wang XC, Liu Y, Yang YH (2010) Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of the~ 850 Ma Gangbian alkaline complex in South China: evidence from in situ zircon U-Pb dating, Hf-O isotopes and whole-rock geochemistry. Lithos 114:1–15
Li ZY, Huang ZZ, Li XZ, Zhang YY, Zhang JD (2014b) Pyrogenesis and uranium metallogeny at **angshan volcanic basin. Bei**g: Geological Publishing House, pp 1–324 (in Chinese)
Lin JR, Hu ZH, **e GF, Wang YJ (2014) The characteristics of interfaces between formations and basement at **angshan volcanic basin and their controlls on uranium deposits. Uranium Geol 30:135–140 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lin JR, Hu ZH, Tao Y, Wang YJ, Wang F (2019) Zircon fission track ages and their responses to the ore-forming thermal events in Zoujiashan uranium deposit, **angshan ore field. Uranium Geol 35:193–198 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu L, Zhang SM, Rao ZH, Zhang X, **a YC, Wan K, Ouyang JY, Wu ZC (2020) Geochronology, geochemistry of lamprophyre and evidence of mantle-derived fluid in the western **angshan uranium orefield. Geol in China 1–32 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20201022.1135.004.html
Ludwig K (2003) ISOPLOT 3.00, A geochronological toolkit for microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronology Centre, Special Publication, pp 1–32
Luo JC, Hu RZ, Fayek M, Li CS, Bi XW, Abdu Y, Chen YW (2015) In–situ SIMS uraninite U-Pb dating and genesis of the **anshi granite–hosted uranium deposit, South China. Ore Geol Rev 65:968–978
Luo JC, Qi YQ, Wang LX (2019) Ar-Ar dating of mafic dykes from the **azhuang uranium ore field in northern Guangdong, South China: A reevaluation of the role of mafic dyke in uranium mineralization. Acta Petrol Sin 35:2660–2678 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Mao JW, Wang YT, Li HM, Franco P, Zhang CQ, Wang RT (2008) The relationship of mantle–derived fluids to gold metallogenesis in the Jiaodong Penisula: evidence from D-O–C–S isotope systematics. Ore Geol Rev 33:361–381
Mao JW, Pirajno F, Cook N (2011) Mesozoic metallogeny in East China and corresponding geodynamic settings-An introduction to the special issue. Ore Geol Rev 43:1–7
McDonough WF, Sun SS (1995) The composition of the earth. Chem Geol 120:223–253
Meng YN, Fan HH, Wang FG (2015) Geochronology of uranium-thorium minerals in Zoujiashan deposit of **angshan uranium ore field, Jiangxi Province. Acta Geol Sin 89:18–21 (in Chinese)
Min MZ, Luo XZ, Du GS, He BA, Camphell AR (1999) Mineralogical and geochemical constraints on the genesis of the granite–hosted Huangao uranium deposit, SE China. Ore Geol Rev 14:105–127
Qi Y, Hu R, Liu S, Coulson IM, Qi H, Tian J, Zhu J (2016) Petrogenesis and geodynamic setting of Early Cretaceous mafic–ultramafic intrusions, South China: A case study from the Gan-Hang tectonic belt. Lithos 258:149–162
Qiu AJ, Guo LZ, Zheng DY, Shu LS (1999) Constraints of Meso-Cenozoic tectonic evolution on formation of rich and large uranium deposit at **angshan, Jiangxi Province. Geol J China U 4:418–425 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Qin KZ, Su BX, Patrick AS, Tang DM, Li XH, Sun H, **ao QH, Liu PP (2011) SIMS Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Sr-Nd Isotopes of Ni-Cu-Bearing Mafic-ultramafic Intrusions in Eastern Tianshan and Beishan in Correlation with Flood Basalts in Tarim Basin (NW China): Constraints on a ca. 280 Ma Mantle Plume. Am J Sci 311:237–260
Qin KZ, Zhai MG, Li GM, Zhao JX, Zeng QD, Gao J, **ao WJ, Li JL, Sun S (2017) Links of collage orogenesis of multiblocks and crust evolution to characteristic metallogeneses in China. Acta Petrol Sinica 33:305–325 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Qin JF, Lai SC, Li YF (2005) Petrogenesis and geological significance of Yangba granodiorites from Bikou area, northern margin of Yangtze plate. Acta Petr Sin 21:697–710 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Rao ZH (2012) The characteristics of basic rocks at **angshan uranium ore field, Jiangxi Province. Master's Thesis of East China Institute of Technology (in Chinese with English abstract)
Song H, Xu ZQ, Song SW, Ni SJ, Zhang CJ, Yan WQ, Cheng FG, Li YP (2019) Geochemistry and LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb geochronological dating of diabase dykes and their relationship with mineralization of the carbonate-siliceous-pelitic rock type uranium deposits in Daxin-Qinjia, western Guangxi. Acta Petrol Sin 35:2845–2863 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Stern CR, Kilian R (1996) Role of the subducted slab, mantle wedge and continental crust in the generation of adakites from the Andean Austral Volcanic Zone. Contrib Mineral Petr 123:263–281
Tappa MJ, Ayuso RA, Bodnar RJ, Aylor JG, Beard J, Henika WS, Wooden JL (2014) Age of host rocks at the Coles Hill uranium deposit, Pittsylvania county, Virginia, based on zircon U-Pb geochronology. Econ Geol 109:513–530
Turner S, Arnaud N, Liu J, Rogers N, Hawkesworth C, Harris N, Deng W (1996) Post-collision, shoshonitic volcanism on the Tibetan Plateau: implications for convective thinning of the lithosphere and the source of ocean island basalts. J Petrol 37:45–71
Valley JW, Kinny PD, Schulze DJ, Spicuzza MJ (1998) Zircon megacrysts from kimberlite: oxygen isotope variability among mantle melts. Contrib Mineral Petr 133:1–11
Wan Y, Ma M, Dong C, **e H, **e S, Ren P, Liu D (2015) Widespread late Neoarchean reworking of Meso-to Paleoarchean continental crust in the Anshan-Benxi area, North China Craton, as documented by U-Pb-Nd-Hf-O isotopes. Am J Sci 315:620–670
Wang HZ, Wu JQ, Chen PR, Tang JW, Ling HF, Zhao YD (2016) Uranium-bearing volcanic-intrusive complexes in the Daqiaowu: magma mixing and implications for uranium metallogenic potential in the Gan-Hang tectonic belt. Geol J China U 22:30–42
Wang HZ, Chen PR, Wang KX, Ling HF, Wu JQ, Tang JW, Zhao YD (2018) Cretaceous A-type volcanic–intrusive rocks and simultaneous mafic rocks along the Gan-Hang Tectonic Belt, Southeast China: Petrogenesis and implications for the transition of crust–mantle interaction. Int Geol Rev 60:1684–1706
Wang LX, Ma CQ, Lai ZX, Marks MA, Zhang C, Zhong YF (2015) Early Jurassic mafic dikes from the **azhuang ore field (South China): Implications for tectonic evolution and uranium metallogenesis. Lithos 239:71–85
Wang Q, Wyman DA, Xu TF, Zhao ZH, Tian P, **ong XL, Bao ZW, Li CF, Bai ZH (2006) Petrogenesis of Cretaceous adalcitic and shoshonitic igneous rock in the Luzong area, Anhui Province (eastern China), implications for geodynamics and Cu–Au mineralization. Lithos 89:424–446
Wang XC, Zhang BT, Zhang ZH (1991) A study of the relationship between the dark dyke and the uranium mineralization. Mineral Deposits 10:359–370 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang YJ, Lin JR, Hu ZH, Dong Q, Liu RP, Pang YQ, Gao F, Tao Y (2021) Zircon U-Pb geochronology, geochemistry and Hf isotopic compositions of dacitic porphyry in Zoujiashan deposit of **angshan uranium ore field and its geological implication. Earth Sci 46:31–42 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Whitney DL, Evans BW (2010) Abbreviations for names of rock-forming minerals. Am Mineral 95:185–187
Wu FY, Li XH, Zheng YF, Gao S (2007) Lu–Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology. Acta Petrol Sin 23:185–220 (in Chinese with English abstract)
**a YL (2019) Geochronology of uranium mineralization in China. Bei**g: China Atomic Energy Press, pp 1–301 (in Chinese)
**n GF, Lu QD, Chen R, Zhang ZY, Nie TC, Li LM, Huang JL, Lin M (2008) Study on the ending time of late Mesozoic tectonic regime transition in South China—comparing to the Yanshan area in North China. Acta Geol Sin 82:451–463 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu WX, Tan ZY, Luo CW, Xu LL, Huang GL (2014) Geochemical characteristic and ore-forming geological significance of fine crystalline granite in Mianhuakeng uranium deposit, Northern Guangdong. Uranium Geol 6:345–355 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang JH, Wu FY, **e LW, Liu XM (2007) Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of Kuangdonggou syenites in the Liaodong peninsula, east North China Croton: constraints from in–situ zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes. Acta Petrol Sin 23:263–276 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang SY, Jiang SY, Jiang YH, Zhao KD (2011) Geochemical, constraints on zircon U-Pb dating and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopic the age and petrogenesis of an Early Cretaceous volcanic–intrusive complex at **angshan, southeast China. Miner Petrol 101:21–48
Yang SY, Jiang SY, Jiang YH, Zhao KD, Fan HH (2012a) Zircon U-Pb geochronology, geochemistry and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopic compositions of the rhyolite porphyry from the Zoujiashan deposit at **angshan uranium ore field, Jiangxi Province, SE China. Acta Petrol Sin 28:3915–3928 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang SY, Jiang SY, Zhao KD, Jiang YH, Ling HF, Luo L (2012b) Geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic significance of two Early Cretaceous A–type granites in the Gan-Hang Belt, Southeast China. Lithos 150:155–170
Yu XQ, Wu GG, Shu LS, Yan TZ, Zhang D, Di YJ (2006) The Cretaceous tectonism of the Gan-Hang Tectonic Belt, southeastern China. Earth Sci Fron 13:31–43 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yu DG, Ye FW, Wang Y (2001) Active succession establishment for volcanic intrusive complex in middle–late Lower Cretaceous in Guangfeng, Jiangxi and its geological implication. Geotectonic Et Metallo 25:271–276 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yu ZQ, Chen WF, Chen PR, Wang KX, Fang QC, Tang XS, Ling HF (2019) Chemical composition and Sr isotopes of apatite in the **angshan A–type volcanic–intrusive complex, southeast China, new insight into petrogenesis. J Asian Earth Sci 172:66–82
Zhang C, Cai YQ, Xu H, Dong Q, Liu JL, Hao RX (2017) Mechanism of mineralization in the Changjiang uranium ore field, South China: evidence from fluid inclusions, hydrothermal alteration, and H-O isotopes. Ore Geol Rev 86:225–253
Zhang C, Cai YQ, Dong Q, Xu H (2020) Cretaceous-Neogene basin control on the formation of uranium deposits in South China: evidence from geology, mineralization ages, and H-O isotopes. Int Geol Rev 62:263–310
Zhang D, Zhao KD, Chen W, Jiang SY (2018) Early Jurassic mafic dikes from the Aigao uranium ore deposit in South China: Geochronology, petrogenesis and relationship with uranium mineralization. Lithos 308:118–133
Zhang SM, Tang L, Rao ZH, **e GF (2012) Geological characteristics of lamprophyre and its significance at **angshan uranium ore field. Mineral Depo 31:241–242 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang YQ, Xu XB, Jia D, Shu LS (2009) Deformation record of the change from indosinian collision–related tectonic system to Yanshanian subductio–related tectonic system in South China during the Early Mesozoic. Earth Sci Fron 16:234–247 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zheng W, Mao JW, Pirajno F, Zhao HJ, Zhao CS, Mao ZH, Wang YJ (2015) Geochronology and geochemistry of the Shilu Cu–Mo deposit in the Yunkai area, Guangdong Province, South China and its implication. Ore Geol Rev 67:382–398
Zheng W, Mao JW, Zhao HJ, Zhao CS, Yu XF (2017) Two Late Cretaceous A-type granites related to the Yingwuling W-Sn polymetallic mineralization in Guangdong province, South China: Implications for petrogenesis, geodynamic setting, and mineralization. Lithos 274–275:106–122
Zhong FJ, Pan JY, Wu JH, **a F, Fu SC, Qi JM, Zhao QF (2019) Petrogenesis and its relationship with uranium mineralization of gabbro-diorite in Changjiang uranium ore-field, Northern Guangdong Province, China. Earth Sci 9:3042–3059 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhou TF, Fan Y, Yuan F, Song CZ, Zhang LJ, Qian CC, Lu SM, David RC (2010) Temporal–spatial framework of magmatic intrusions in Luzong volcanic basin in East China and their constrain to mineralizations. Acta Petrol Sin 26:2694–2714 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhou XM, Li WX (2000) Origin of late Mesozoic igneous rocks in southeastern China, implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas. Tectonophysics 326:269–287
Zorpi MJ, Coulon C, Orsini JB (1991) Hybridization between felsic and mafic magmas in calc–alkaline granitoids, a case study in northern Sardinia, Italy. Chem Geol 92:45–48
Acknowledgements
We thank ** Liu with LA-MC-ICP-MS Lu−Hf analyses, Mu Liu and **aotong Liu with major and trace element analyses. **`an Uranium Co., Ltd., of the Nuclear Industry is extremely appreciated for the assitance during field work. We are extremely grateful to Dr. Maarten A.T.M. Broekmans (Editor in Chief), Prof. Qiuli Li (Associate Editor) and two anonymous reviewers for their thoughtful reviews and constructive comments. This paper was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (41703042), the Key Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology, China (2017YFC0602600) and the Basic Research Programs from China National Nuclear Cooperation (D2002).
Funding
The authors received research fellowship from the National Natural Science Foundation, China (No. 41703042), the Key Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology, China (No. 2017YFC0602600) and the Basic Research Programs from China National Nuclear Cooperation, China (No. D2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yong-Jian Wang, Jiang-Tao Nie and **-Rong Lin conceived, designed and carried out the research. Yong-Jian Wang drafted the manuscript. Hong-Zuo Wang processed and explained some geochronological and geochemical data. All authors contributed to data interpretation, discussion, and revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Editorial handling: Q. Li
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• A relatively concentrated felsic-intermediate dike intrusion that occurred at ca. 136-122 Ma.
• Different proportions of mantle-derived materials involved in the various dikes.
• **angshan dike intrusions induced by progressive rollback of the Paleo-Pacific Plate.
• No direct relationship in origin between uranium mineralization and various types of dikes.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, YJ., Nie, JT., Lin, JR. et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the felsic-intermediate dikes from **angshan uranium ore field, South China: Implications for petrogenesis, tectonic setting and uranium mineralization. Miner Petrol 116, 287–310 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-022-00780-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-022-00780-4