Abstract
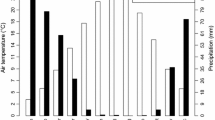
A regional analysis of soil temperature (ST) is essential for improving our understanding of the soil thermal regime and its link with the atmosphere. This study attempts to assess trends in the Poyang Lake Basin (PLB) ST magnitude during 1960–2016 from station observations at multiple depths. The Mann–Kendall, Thiel-Sen, linear regression, and probability density statistics (PDF) are used for ST trend assessment with a significance level of 95%. The ST seasonal variability shows minimum values in winter (8℃) and maximum in the summer season (32 ℃). On an interannual scale, spring and winter seasons exhibited a significant increase in both land surface temperature (LST) (0.4℃, 0.4℃) and ST (0.3 °C, 0.15℃) magnitude than summer (LST − 0.1℃, ST 0.2℃) and autumn seasons (LST 0.3℃, ST 0.2℃). The northern basin exhibited a significant increase in LST, and ST magnitude, especially during the cold seasons (spring, winter) than the warm seasons. The maximum and minimum temperature trend and their diurnal difference infer an increase in the minimum temperature, especially during the summer, autumn, and winter seasons. The PDF further inferred that extreme cold events’ frequency decreased, and a significant increase in extreme warm events is obvious in the recent decade. The increasing trend in soil temperature magnitude is more in the northern basin than the high-altitude southern basin. Large-scale global warming and regional water and energy cycle changes can be the leading factors of such a warming trend.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to confidentiality of meteorological observation data but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Change history
22 July 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-023-04558-2
References
Ahani H, Kherad M, Kousari MR, Rezaeian-Zadeh M, Karampour MA, Ejraee F, Kamali S (2012) An investigation of trends in precipitation volume for the last three decades in different regions of Fars province. Iran Theor Appl Climatol 109:361–382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-011-0572-z
Araghi A, Mousavi-Baygi M, Adamowski J (2017) Detecting soil temperature trends in Northeast Iran from 1993 to 2016. Soil Tillage Res 174:177–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2017.07.010
Baptist F, Yoccoz NG, Choler P (2010) Direct and indirect control by snow cover over decomposition in alpine tundra along a snowmelt gradient. Plant Soil 328:397–410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-0119-6
Baqa MF, Lu L, Chen F, Nawaz-ul-Huda S, Pan L, Tariq A, Qureshi S, Li B, Li Q (2022) Characterizing spatiotemporal variations in the urban thermal environment related to land cover changes in Karachi, Pakistan, from 2000 to 2020. Remote Sens 14:2164. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092164
Bhatti AS, Wang G, Ullah W, Ullah S, Hagan DFT, Nooni IK, Lou D, Ullah I (2020) Trend in extreme precipitation indices based on long term in situ precipitation records over Pakistan. Water (switzerland) 12:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030797
Bond-Lamberty B, Thomson A (2010) Temperature-associated increases in the global soil respiration record. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08930
Calderón R, Lucena C, Trapero-Casas JL, Zarco-Tejada PJ, Navas-Cortés JA (2014) Soil temperature determines the reaction of olive cultivars to verticillium dahliae pathotypes. PLoS One 9. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0110664
Couradeau E, Karaoz U, Lim H et al (2016) Bacterial production of sunscreen pigments increase arid land soil surface temperature 17:10373. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10373
Dinpashoh Y, Jhajharia D, Fakheri-Fard A, Singh VP, Kahya E (2011) Trends in reference crop evapotranspiration over Iran. J Hydrol 399:422–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.01.021
Edwards AC, Scalenghe R, Freppaz M (2007) Changes in the seasonal snow cover of alpine regions and its effect on soil processes: a review. Quat Int 162–163:172–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2006.10.027
Freppaz M, Celi L, Marchelli M, Zanini E (2008) Snow removal and its influence on temperature and N dynamics in alpine soils (Vallée d’Aoste, northwest Italy). J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 171:672–680. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.200700278
Guan BC, Liu X, Gong X, Ge G (2017) Identification of evolutionary hotspots in the Poyang Lake Basin based on genetic data from multiple rare and endangered plant species. Ecol Inform 42:114–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2017.10.011
Hagan DFT, Wang GJ, Parinussa RM, Shi X (2019) Inter-comparing and improving land surface temperature estimates from passive microwaves over the Jiangsu province of the People’s Republic of China. Int J Remote Sens 40:5563–5584. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2019.1580790
Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K, Fujita M (2013) Extreme temperature responses, oxidative stress and antioxidant defense in plants. In: Vahdati K, Leslie C (eds) Abiotic Stress - Plant Responses and Applications in Agriculture. InTech, Rijeka. https://doi.org/10.5772/54833
Hu Q, Feng S (2003) A daily soil temperature dataset and soil temperature climatology of the contiguous United States. J Appl Meteorol 42:1139–1156. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(2003)042%3c1139:ADSTDA%3e2.0.CO;2
Hu G, Zhao L, Wu X, Li R, Wu T, Su Y, Hao J (2019) Evaluation of reanalysis air temperature products in permafrost regions on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Theor Appl Climatol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-019-02888-8
IPCC (2022) Climate change 2022: impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability [R]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, USA
Jiang Y, Luo Y, Zhao Z, Tao S (2010) Changes in wind speed over China during 1956–2004. Theor Appl Climatol 99:421–430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-009-0152-7
Jungqvist G, Oni SK, Teutschbein C, Futter MN (2014) Effect of climate change on soil temperature in Swedish boreal forests. PLoS ONE 9:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0093957
Knight JH, Minasny B, McBratney AB, Koen TB, Murphy BW (2018) Soil temperature increase in eastern Australia for the past 50 years. Geoderma 313:241–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.11.015
Kousari MR, Ahani H, Hendi-zadeh R (2013) Temporal and spatial trend detection of maximum air temperature in Iran during 1960–2005. Glob Planet Change 111:97–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2013.08.011
Lai X, Shankman D, Huber C, Yesou H, Huang Q, Jiang J (2014) Sand mining and increasing Poyang Lake’s discharge ability: a reassessment of causes for lake decline in China. J Hydrol 519:1698–1706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.09.058
Liao W, Wang X, Fan Q, Zhou S, Chang M, Wang Z, Wang Y, Tu Q (2015) Long-term atmospheric visibility, sunshine duration and precipitation trends in South China. Atmos Environ 107:204–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.02.015
Lin C, Yang K, Qin J, Fu R (2013) Observed coherent trends of surface and upper-air wind speed over China since 1960. J Clim 26:2891–2903. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00093.1
Liu YB, Song P, Peng J, Fu QN, Dou CC (2011) Recent increased frequency of drought events in Poyang Lake Basin, China: climate change or anthropogenic effects? Hydro-Climatology Var. Chang 344:99–104
Liu J, Linderholm H, Chen D, Zhou X, Flerchinger GN, Yu Q, Du J, Wu D, Shen Y, Yang Z (2015) Changes in the relationship between solar radiation and sunshine duration in large cities of China. Energy 82:589–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.01.068
Liu Z, Lu J, Huang J, Chen X, Zhang L (2021) Projection of reference crop evapotranspiration under future climate change in Poyang Lake watershed, China. J Hydrol Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)he.1943-5584.0002020
Lu E, Zeng X, Jiang Z, Wang Y, Zhang Q (2009) Precipitation and precipitable water: their temporal-spatial behaviors and use in determining monsoon onset/retreat and monsoon regions. J Geophys Res Atmos 114:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JD012146
Mann HB (1945) Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 13:245. https://doi.org/10.2307/1907187
Maurice GK (1975) Rank correlation methods, London Griffin
Mei X, Dai Z, Fagherazzi S, Chen J (2016) Dramatic variations in emergent wetland area in China’s largest freshwater lake. Poyang Lake Adv Water Resour 96:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2016.06.003
Nossal SM, Qian L, Solomon SC, Burns AG, Wang W (2016) Thermospheric hydrogen response to increases in greenhouse gases. J Geophys Res A Sp Phys 121:3545–3554. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JA022008
Parinussa RM, Holmes TRH, Yilmaz MT, Crow WT, Sciences G (2011) The impact of land surface temperature on soil moisture anomaly detection from passive microwave observations 3135–3151. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-15-3135-2011
Qian B, Gregorich EG, Gameda S, Hopkins DW, Wang XL (2011) Observed soil temperature trends associated with climate change in Canada. J Geophys Res Atmos 116:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JD015012
Qin Y, Zhang P, Liu W, Guo Z, Xue S (2020) The application of elevation corrected MERRA2 reanalysis ground surface temperature in a permafrost model on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Cold Reg Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2020.103067
Renner M, Seppelt R, Bernhofer C (2012) Evaluation of water-energy balance frameworks to predict the sensitivity of streamflow to climate change 1419–1433. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-16-1419-2012
Sen PK (1968) Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s Tau. J Am Stat Assoc 63:1379–1389. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.1968.10480934
Shen X, Liu B, Jiang M, Lu X (2020) Marshland loss warms local land surface temperature in China. Geophys Res Lett 47:e2020GL087648
Shen X, Liu Y, Liu B, Zhang J, Wang L, Lu X, Jiang M (2022) Effect of shrub encroachment on land surface temperature in semi-arid areas of temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Agric for Meteorol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2022.108943
Shirvani A, Moradi-Choghamarani F, Zand-Parsa S, Moosavi AA (2018) Analysis of long-term trends in air and soil temperature in a semi-arid region in Iran. Environ Earth Sci 77:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7372-z
Sviličić P, Vučetić V, Filić S, Smolić A (2016) Soil temperature regime and vulnerability due to extreme soil temperatures in Croatia. Theor Appl Climatol 126:247–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1558-z
Tabari H, Sabziparvar A-A, Ahmadi M (2011) Comparison of artificial neural network and multivariate linear regression methods for estimation of daily soil temperature in an arid region. Meteorol Atmos Phys 110:135–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-010-0110-z
Tang X, Li H, Xu X, Yang G, Liu G, Li X, Chen D (2016) Changing land use and its impact on the habitat suitability for wintering Anseriformes in China’s Poyang Lake region. Sci Total Environ 557–558:296–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.108
Tao H, Fraedrich K, Menz C, Zhai J (2014) Trends in extreme temperature indices in the Poyang Lake Basin. China Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 28:1543–1553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-014-0863-x
Thurgood A, Singh B, Jones E, Barbour MM (2014) Temperature sensitivity of soil and root respiration in contrasting soils. Plant Soil 382:253–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2159-9
Tian Q, Yang S (2017) Regional climatic response to global warming: trends in temperature and precipitation in the Yellow, Yangtze and Pearl River basins since the 1950s. Quat Int 440:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2016.02.066
Tian P, Zhao G, Li J, Tian K (2011) Extreme value analysis of streamflow time series in. Water Sci Eng 4:121–132. https://doi.org/10.3882/j.issn.1674-2370.2011.02.001
Tian Q, Prange M, Merkel U (2016) Precipitation and temperature changes in the major Chinese river basins during 1957–2013 and links to sea surface temperature. J Hydrol 536:208–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.02.048
Toreti A, Kuglitsch FG, Xoplaki E, Della-Marta PM, Aguilar E, Prohom M, Luterbacher J (2011) A note on the use of the standard normal homogeneity test to detect inhomogeneities in climatic time series. Int J Climatol 31:630–632. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.2088
Ullah S, You Q, Ullah W, Hagan DFT, Ali A, Ali G, Zhang Y, Jan MA, Bhatti AS, **e W (2019a) Daytime and nighttime heat wave characteristics based on multiple indices over the China-Pakistan economic corridor. Clim Dyn 53:6329–6349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-04934-7
Ullah W, Wang G, Ali G, Tawia Hagan D, Bhatti A, Lou D (2019b) Comparing multiple precipitation products against in-situ observations over different climate regions of Pakistan. Remote Sens 11:628. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11060628
Voigt C, Lamprecht RE, Marushchak ME, Lind SE, Novakovskiy A, Aurela M, Martikainen PJ, Biasi C (2017) Warming of subarctic tundra increases emissions of all three important greenhouse gases – carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. Glob Chang Biol 23:3121–3138. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13563
Wang G, Gong T, Lu J, Lou D, Hagan DFT, Chen T (2018) On the long-term changes of drought over China (1948–2012) from different methods of potential evapotranspiration estimations. Int J Climatol 38:2954–2966. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5475
Xu CY, Gong L, Jiang T, Chen D, Singh VP (2006) Analysis of spatial distribution and temporal trend of reference evapotranspiration and pan evaporation in Changjiang (Yangtze River) catchment. J Hydrol 327:81–93
Xu L, Zhu M, He B, Wang X, Zhang Q, Jiang J, Razafindrabe BHN (2014) Analysis of water Balance in Poyang Lake Basin and subsequent response to climate change. J Coast Res 136–143. https://doi.org/10.2112/SI68-018.1
Yang Y, Wu Z, He H, Du H, Wang L, Guo X, Zhao W (2018) Differences of the changes in soil temperature of cold and mid-temperate zones, Northeast China. Theor Appl Climatol 134:633–643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-017-2297-0
Yang S, Li R, Wu T, Hu G, **ao Y, Du Y, Zhu X, Ni J, Ma J, Zhang Y, Shi J, Qiao Y (2020) Evaluation of reanalysis soil temperature and soil moisture products in permafrost regions on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Geoderma. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114583
Ye XC, Liu J, Zhang Q (2013) Trends of estimated potential evapotranspiration in the Poyang Lake Basin, China, in: Advances in Environmental Technologies, Advanced Materials Research. Trans Tech Publications, pp. 3299–3302. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.726-731.3299
Yeşilirmak E (2014) Soil temperature trends in B??y??k Menderes Basin. Turkey Meteorol Appl 21:859–866. https://doi.org/10.1002/met.1421
Yue T, Du Z, Lu M, Fan Z, Wang C, Tian Y, Xu B (2015) Surface modeling of ecosystem responses to climatic change in Poyang Lake Basin of China. Ecol Modell 306:16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2014.09.015
Zhai R, Tao F (2017) Contributions of climate change and human activities to runoff change in seven typical catchments across China. Sci Total Environ 605–606:219–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.210
Zhan M, Wang Y, Wang G, Hartmann H, Cao L (2017) Long-term changes in soil moisture conditions and their relation to atmospheric circulation in the Poyang Lake basin. China Quat Int 440:23–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2016.01.003
Zhang T, Barry RG, Gilichinsky D, Bykhovets SS, Sorokovikov VA, Ye J (2001) An amplified signal of climatic change in soil temperatures during the last century at Irkutsk, Russia. Clim Change. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010790203146
Zhang Q, Xu CY, Zhang Z, Ren G, Chen YD (2008) Climate change or variability? The case of Yellow river as indicated by extreme maximum and minimum air temperature during 1960–2004. Theor Appl Climatol 93:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-007-0328-y
Zhang Q, **ao M, Li J, Singh VP, Wang Z (2014a) Topography-based spatial patterns of precipitation extremes in the Poyang Lake basin, China : changing properties and causes. J Hydrol 512:229–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.03.010
Zhang SY, Li XY, Ma YJ, Zhao GQ, Li L, Chen J, Jiang ZY, Huang YM (2014b) Interannual and seasonal variability in evapotranspiration and energy partitioning over the alpine riparian shrub Myricaria squamosa Desv. on qinghai-tibet plateau. Cold Reg Sci Technol 102:8–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2014.02.001
Zhang D, Chen P, Zhang Q, Li X (2017) Copula-based probability of concurrent hydrological drought in the Poyang lake-catchment-river system ( China ) from 1960 to 2013. J Hydrol 553:773–784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.08.046
Zhou Y, ** S, Tenzer R, Feng J (2016) Water storage variations in the Poyang Lake Basin estimated from GRACE and satellite altimetry. Geod Geodyn 7:108–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geog.2016.04.003
Zhu F, Cuo L, Zhang Y, Luo JJ, Lettenmaier DP, Lin Y, Liu Z (2018) Spatiotemporal variations of annual shallow soil temperature on the Tibetan Plateau during 1983–2013. Clim Dyn 51:2209–2227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-4008-z
Funding
This study is financially supported by Young Scientific and Technological Talents Promotion Project of Jiangsu Association for Science and Technology (TJ-2021–21) and Jiangsu Meteorological Bureau Scientific Research Project (KM202111).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, D. L and X. S; methodology, D. L and Y. C; validation D. L, W. U, and H. Z; formal analysis, D. L and W. U; investigation, D. L and W. U; resources, D. S; data curation, C. L and Y. C; writing, D. L and W. U; writing review and editing, D. L, X. S, W. U, and H. Z; visualization, C. L and Y. C; supervision, D. L and X. S; project administration, X. S; funding acquisition, D. S.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: Due to the affiliation numbers of the first and second authors are wrong.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lou, D., Shi, X., Ullah, W. et al. Long-term changes in observed soil temperature over Poyang Lake Basin, China, during 1960–2016. Theor Appl Climatol 154, 717–731 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-023-04522-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-023-04522-0