Abstract
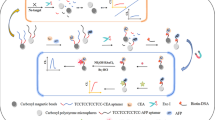
A smartphone-based electrochemical aptasensing platform was developed for the point-of-care testing (POCT) of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) based on the ferrocene (Fc) and PdPt@PCN-224 dual-signal labeled strategy. The prepared PdPt@PCN-224 nanocomposite showed a strong catalytic property for the reduction of H2O2. Phosphate group-labeled aptamer could capture PdPt@PCN-224 by Zr–O–P bonds to form PdPt@PCN-224-P-Apt. Therefore, a dual signal labeled probe was formed by the hybridization between Fc-DNA and PdPt@PCN-224-P-Apt. The presence of CEA forced PdPt@PCN-224-P-Apt to leave the electrode surface due to the specific affinity, leading to the decrease of the reduction current of H2O2. At the same time, the Fc-DNA strand changed to hairpin structure, which made Fc closer to the electrode and resulted in the increase of the oxidation current of Fc. Thus, CEA can be accurately determined through both signals: the decrease of H2O2 reduction current and the increase of Fc oxidation current, which could avoid the false positive signal. Under the optimal conditions, the prepared aptasensor exhibited a wide linear range from 1 pg·mL−1 to 100 ng·mL−1 and low detection limits of 0.98 pg·mL−1 and 0.27 pg·mL−1 with Fc and PdPt@PCN-224 as signal labels, respectively. The aptasensor developed in this study has successfully demonstrated its capability to detect CEA in real human serum samples. These findings suggest that the proposed sensing platform will hold great potential for clinical tumor diagnosis and monitoring.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Shi SS, Li XJ, Ma RN, Shang L, Zhang W, Zhao HQ, Jia LP, Wang HS (2024) A smartphone-based electrochemical POCT for CEA based on signal amplification of Zr6MOFs. Lab Chip 24(2):367–374. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3lc00748k
**ang W, Lv Q, Shi H, **e B, Gao L (2020) Aptamer-based biosensor for detecting carcinoembryonic antigen. Talanta 214:120716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.120716
Chikkaveeraiah BV, Bhirde AA, Morgan NY, Eden HS, Chen X (2012) Electrochemical immunosensors for detection of cancer protein biomarkers. ACS Nano 6(8):6546–6561. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn3023969
Hanash SM, Pitteri SJ, Faca VM (2008) Mining the plasma proteome for cancer biomarkers. Nature 452(7187):571–579. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06916
Tobi M, O’Kieffe D, Trujillo N, Nochomovitz LE, Steinberg WM (1992) Detection of carcinoembryonic antigen in colonic effluent by specific anti-CEA monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Lett 67(1):47–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3835(92)90007-I
Lai G, Wu J, Leng C, Ju H, Yan F (2011) Disposable immunosensor array for ultrasensitive detection of tumor markers using glucose oxidase-functionalized silica nanosphere tags. Biosens Bioelectron 26(9):3782–3787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2011.02.032
Wu W, Wu Q, Ren S-N, Liu Z, Chen F-F (2022) Ti3C2-MXene-assisted signal amplification for sensitive and selective surface plasmon resonance biosensing of biomarker. Chin J Anal Chem 50(2):13–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjac.2021.11.005
Wu K, Chu C, Ma C, Yang H, Yan M, Ge S, Yu J, Song X (2015) Immunoassay for carcinoembryonic antigen based on the Zn2+-enhanced fluorescence of magnetic-fluorescent nanocomposites. Sens Actuators B: Chem 206:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.09.041
Yang X, Zhuo Y, Zhu S, Luo Y, Feng Y, Xu Y (2015) Selectively assaying CEA based on a creative strategy of gold nanoparticles enhancing silver nanoclusters’ fluorescence. Biosens Bioelectron 64:345–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.09.029
Lin X, Wang Y, Wang L, Lu Y, Li J, Lu D, Zhou T, Huang Z, Huang J, Huang H, Qiu S, Chen R, Lin D, Feng S (2019) Interference-free and high precision biosensor based on surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy integrated with surface molecularly imprinted polymer technology for tumor biomarker detection in human blood. Biosens Bioelectron 143:111599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111599
Shahbazi N, Hosseinkhani S, Ranjbar B (2017) A facile and rapid aptasensor based on split peroxidase DNAzyme for visual detection of carcinoembryonic antigen in saliva. Sens Actuators B: Chem 253:794–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.06.024
Wang D, Li Y, Lin Z, Qiu B, Guo L (2015) Surface-enhanced electrochemiluminescence of Ru@SiO2 for ultrasensitive detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Anal Chem 87(12):5966–5972. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b01038
Tan Y-Y, Tan H-S, Liu M, Li S-S (2023) Electrochemical ratiometric dual-signal immunoassay for accurate detection of carcinoembryonic antigen in clinical serum based on rGO-Pd@Au-Thi and Chi-Fc-Au. Sens Actuators B: Chem 380:133340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2023.133340
Liu J, Shang Y, Zhu Q, Zhang X, Zheng J (2019) A voltammetric immunoassay for the carcinoembryonic antigen using silver(I)-terephthalate metal-organic frameworks containing gold nanoparticles as a signal probe. Microchim Acta 186:509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3638-8
Gua X, She Z, Ma T, Tian S, Kraatz H-B (2018) Electrochemical detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 102:610–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.12.014
Feng Q, Wang M, Qin L, Wang P (2019) Dual-signal readout of DNA methylation status based on the assembly of a supersandwich electrochemical biosensor without enzymatic reaction. ACS Sensors 4(10):2615–2622. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.9b00720
Han Y, Ding C, Zhou J, Tian Y (2015) Single probe for imaging and biosensing of pH, Cu2+ ions, and pH/Cu2+ in live cells with ratiometric fluorescence signals. Anal Chem 87(10):5333–5339. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b00628
Shustova NB, Cozzolino AF, Reineke S, Baldo M, Dincă M (2013) Selective turn-on ammonia sensing enabled by high-temperature fluorescence in metal–organic frameworks with open metal sites. J Am Chem Soc 135(36):13326–13329. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja407778a
Daneshpour M, Karimi B, Omidfar K (2018) Simultaneous detection of gastric cancer-involved miR-106a and let-7a through a dual-signal-marked electrochemical nanobiosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 109:197–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.03.022
Lu H, Ding B, Tong L, Wu F, Yi X, Wang J (2020) Toehold-mediated strand displacement reaction for dual-signal electrochemical assay of apolipoprotein E genoty**. ACS Sensors 5(9):2959–2965. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.0c01511
Zhang G, Liu Z, Fan L, Han Y, Guo Y (2021) A novel dual signal and label-free electrochemical aptasensor for mucin 1 based on hemin/graphene@PdPtNPs. Biosens Bioelectron 173:112785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112785
Ma R-N, Wang L-L, Zhang M, Jia L-P, Zhang W, Shang L, Jia W-L, Wang H-S (2018) A novel one-step triggered “signal-on/off” electrochemical sensing platform for lead based on the dual-signal ratiometric output and electrode-bound DNAzyme assembly. Sens Actuators B: Chem 257:678–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.10.158
Li L, Yang L-W, Zhang S, Sun Y, Li F, Qin T-T, Liu X-Q, Zhou Y, Alwarappan S (2020) A NiCo2S4@N/S–CeO2 composite as anelectrocatalytic signal amplification labelfor aptasensing. J Mater Chem C 8(42):14723–14731. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0tc02738c
Dan Z, Geng C, Liu X-Q, ** X, Zhao Z, Liu Y, Alwarappan S (2023) Photoelectrochemical detection of superoxide anions released from mitochondria in HepG2 cells based on the synergistic effect of MnO2@Co3O4 core-shell p-n heterojunction. Biosens Bioelectron 237:115368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2023.115368
Ning Y, Lu F, Liu Y, Yang S, Wang F, Ji X, He Z (2021) Glow-type chemiluminescent hydrogels for point-of-care testing (POCT) of cholesterol. Analyst 146(15):4775–4780. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1AN00676B
Yin B, Wan X, Sohan A, Lin X (2022) Microfluidics-Based POCT for SARS-CoV-2 Diagnostics. Micromachines 13:1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13081238
Liu T, He J, Lu Z, Sun M, Wu M, Wang X, Jiang Y, Zou P, Rao H, Wang Y (2022) A visual electrochemiluminescence molecularly imprinted sensor with Ag+@UiO-66-NH2 decorated CsPbBr3 perovskite based on smartphone for point-of-care detection of nitrofurazone. Chem Eng J 429:132462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.132462
Lu Z, Dai S, Liu T, Yang J, Sun M, Wu C, Su G, Wang X, Rao H, Yin H, Zhou X, Ye J, Wang Y (2023) Machine learning-assisted Te–CdS@Mn3O4 nano-enzyme induced self-enhanced molecularly imprinted ratiometric electrochemiluminescence sensor with smartphone for portable and visual monitoring of 2,4-D. Biosens Bioelectron 222:114996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.114996
Zhang Y, Cui Y, Sun M, Wang T, Liu T, Dai X, Zou P, Zhao Y, Wang X, Wang Y, Zhou M, Su G, Wu C, Yin H, Rao H, Lu Z (2022) Deep learning-assisted smartphone-based molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence detection sensing platform: protable device and visual monitoring furosemide. Biosens Bioelectron 209:114262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.114262
Li F, Guo L, Li Z, He J, Cui H (2020) Temporal-spatial-color multiresolved chemiluminescence imaging for multiplex immunoassays using a smartphone coupled with microfluidic chip. Anal Chem 92(10):6827–6831. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c01405
Li C, Liu C, Liu R, Wang Y, Li A, Tian S, Cheng W, Ding S, Li W, Zhao M, **a Q (2023) A novel CRISPR/Cas14a-based electrochemical biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of Burkholderia pseudomallei with PtPd@PCN-224 nanoenzymes for signal amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 225:115098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2023.115098
Park J, Jiang Q, Feng D, Mao L, Zhou H-C (2016) Size-controlled synthesis of porphyrinic metal–organic framework and functionalization for targeted photodynamic therapy. J Am Chem Soc 138(10):3518–3525. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b00007
Liu B, Liu J (2017) Freezing directed construction of bio/nano interfaces: reagentless conjugation, denser spherical nucleic acids, and better nanoflares. J Am Chem Soc 139(28):9471–9474. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b04885
Shang L, Shi B-J, Zhang W, Jia L-P, Ma R-N, Xue Q-W, Wang H-S (2022) Ratiometric electrochemiluminescence sensing of carcinoembryonic antigen based on luminol. Anal Chem 94(37):12845–12851. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c02803
Yu K, Wei T, Li Z, Li J, Wang Z, Dai Z (2020) Construction of molecular sensing and logic systems based on site-occupying effect-modulated MOF–DNA interaction. J Am Chem Soc 142(51):21267–21271. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c10442
Wang B, Liu S, Liu L, Song W-W, Zhang Y, Wang S-M, Han Z-B (2021) MOF/PEDOT/HPMo-based polycomponent hierarchical hollow micro-vesicles for high performance flexible supercapacitors. J Mater Chem A 9(5):2948–2958. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TA10603H
Shi S-S, Jia L-P, Ma R-N, Jia W-L, Wang H-S (2015) A label-free electrochemical aptasensor for 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine detection. J Electroanal Chem 759:107–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2015.10.040
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2020MB061) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21427808).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Biomedical Research Ethics Subcommittee of Liaocheng University (BRES). All the experiments were performed in compliance with the relevant laws and institutional guidelines of BRES.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, SS., Li, XJ., Ma, RN. et al. A novel dual-signal output strategy for POCT of CEA based on a smartphone electrochemical aptasensing platform. Microchim Acta 191, 407 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06493-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06493-z