Abstract
Background/purpose
Sinisan, a traditional Chinese medicine, is effective for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders. In this study, we investigated the potential protective role of Sinisan against chronic pancreatitis (CP) in rats.
Methods
CP was induced in rats by intrapancreatic injection of trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS). Rats were randomly divided into a sham group, a TNBS-induced CP group and a Sinisan-treated group. Serum amylase and histological score were used to evaluate the severity of disease. The levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), interleukin-10 (IL-10) and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) were also measured in the three groups. Mechanical allodynia was measured with von Frey filaments. In addition, the protein levels of nerve growth factor (NGF) were measured in pancreatic tissues.
Results
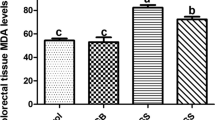
Administration of Sinisan significantly decreased the severity of CP. In the Sinisan-treated group, serum amylase, TNF-α, IL-1β, COX-2 and α-SMA levels were lower and the level of IL-10 was upregulated compared with the TNBS-induced CP group. Furthermore, treatment with Sinisan significantly, though not completely, attenuated the allodynia. Simultaneously NGF expression was also significantly downregulated in the Sinisan-treated group compared with the TNBS-induced CP group.
Conclusions
Sinisan could be an effective treatment modality for CP via its anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic and analgesic properties. It may be a promising drug candidate for the treatment of patients with CP.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao HF, Ito T, Gibo J, Kawabe K, Oono T, Kaku T, et al. Anti-monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 gene therapy attenuates experimental chronic pancreatitis induced by dibutyltin dichloride in rats. Gut. 2005;54:1759–67.
Chan E, Tan M, **n J, Sudarsanam S, Johnson DE. Interactions between traditional Chinese medicines and Western therapeutics. Curr Opin Drug Discov Dev. 2010;13:50–65.
Jiang J, Zhou C, Xu Q. Alleviating effects of si-ni-san, a traditional Chinese prescription, on experimental liver injury and its mechanisms. Biol Pharm Bull. 2003;26:1089–94.
Sun Y, Chen T, Xu Q. Si-Ni-San, a traditional Chinese prescription, and its drug-pairs suppress contact sensitivity in mice via inhibition of the activity of metalloproteinases and adhesion of T lymphocytes. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2003;55:839–46.
Sun Y, Dong Y, Jiang HJ, Cai TT, Chen L, Zhou X, et al. Dissection of the role of paeoniflorin in the traditional Chinese medicinal formula Si-Ni-San against contact dermatitis in mice. Life Sci. 2009;84:337–44.
Ohta Y, Kobayashi T, Nishida K, Nagata M, Ishiguro I. Therapeutic effect of Oren-gedoku-to extract on stress-induced acute gastric mucosal lesions in rats. Phytother Res. 1999;13:588–92.
Ohta Y, Kobayashi T, Hayashi T, Inui K, Yoshino J, Nakazawa S. Preventive effect of Shigyaku-san on progression of acute gastric mucosal lesions induced by compound 48/80, a mast cell degranulator, in rats. Phytother Res. 2006;20:256–62.
Sun Y, Cai TT, Shen Y, Zhou XB, Chen T, Xu Q. Si-Ni-San, a traditional Chinese prescription, and its active ingredient glycyrrhizin ameliorate experimental colitis through regulating cytokine balance. Int Immunopharmacol. 2009;9:1437–43.
Gironella M, Iovanna JL, Sans M, Gil F, Peñalva M, Closa D, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of pancreatitis associated protein in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 2005;54:1244–53.
Triantafillidis JK, Cheracakis P, Hereti IA, Argyros N, Karra E. Acute idiopathic pancreatitis complicating active Crohn’s disease: favorable response to infliximab treatment. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95:3334–6.
Akgül S, Erbil Y, Giris M, Alis H, Yanik BT, Olgaç V, et al. The effect of octreotide on pancreatic damage in TNBS-induced colitis. Surg Innov. 2006;13:102–8.
Feng QX, Wang W, Feng XY, Mei XP, Zhu C, Liu ZC, et al. Astrocytic activation in thoracic spinal cord contributes to persistent pain in rat model of chronic pancreatitis. Neuroscience. 2010;167:501–9.
Puig-Divi V, Molero X, Vaquero E, Salas A, Guarner F, Malagelada J. Ethanol feeding aggravates morphological and biochemical parameters in experimental chronic pancreatitis. Digestion. 1999;60:166–74.
Wang J, Li Q. Study on the effect of 100 chronic pancreatitis patients treated by Sinisan. Chin J Pract Int Med. 2008;22:38 (in Chinese).
Dong XF, Hu XP. Study on the effect of 18 chronic pancreatitis patients treated by Sinisan. Pract Clin J Integr Tradit Chin West Med. 2007;7:94 (in Chinese).
Dong XF, Hu XP. Therapeutic effect of Sinisan on 18 chronic pancreatitis patients. Chin J Clin Med Prog Res. 2007;13:661 (in Chinese).
Bartel M, Hänsch GM, Giese T, Penzel R, Ceyhan G, Ketterer K, et al. Abnormal crosstalk between pancreatic acini and macrophages during the clearance of apoptotic cells in chronic pancreatitis. J Pathol. 2008;215:195–203.
Daniel P, Mokrowiecka A, Gasiorowska A, Małecka-Panas E. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and its receptors: sTNF-alphaRI i sTNF-alphaRII in chronic pancreatitis. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2005;114:639–43.
Marrache F, Tu SP, Bhagat G, Pendyala S, Osterreicher CH, Gordon S, et al. Overexpression of interleukin-1beta in the murine pancreas results in chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:1277–87.
Koliopanos A, Friess H, Kleeff J, Roggo A, Zimmermann A, Büchler MW. Cyclooxygenase 2 expression in chronic pancreatitis: correlation with stage of the disease and diabetes mellitus. Digestion. 2001;64:240–7.
Qian NS, Xu XP, Chen Y, Dou KF, Wang YY, Yang YL. Protective effect of cyclosporin A on brain injury in rats with acute necrotic pancreatitis. Life Sci. 2010;87:64–8.
Demols A, Van Laethem JL, Quertinmont E, Degraef C, Delhaye M, Geerts A, et al. Endogenous interleukin-10 modulates fibrosis and regeneration in experimental chronic pancreatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002;282:G1105–12.
Winston JH, Toma H, Shenoy M, He ZJ, Zou L, **ao SY, Micci MA, et al. Acute pancreatitis results in referred mechanical hypersensitivity and neuropeptide up-regulation that can be suppressed by the protein kinase inhibitor k252a. J Pain. 2003;4:329–37.
Friess H, Zhu ZW, di Mola FF, Kulli C, Graber HU, Andren-Sandberg A, et al. Nerve growth factor and its high-affinity receptor in chronic pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 1999;230:615–24.
Nakata K, Hosono Y, Hosono H, Sakaguchi H, Hosono S. The treatment of Kampo medicine for chronic pancreatitis. Jpn J Orient Med. 1986;36:25–43 (in Japanese with English abstract).
Su SB, Motoo Y, **e MJ, Sakai J, Taga H, Sawabu N. Expression of pancreatitis-associated protein (PAP) in rat spontaneous chronic pancreatitis: effect of herbal medicine Saiko-keishi-to (TJ-10). Pancreas. 1999;19:239–47.
Su SB, Motoo Y, **e MJ, Taga H, Sawabu N. Antifibrotic effect of the herbal medicine Saiko-keishi-to (TJ-10) on chronic pancreatitis in the WBN/Kob rat. Pancreas. 2001;22:8–17.
Gong HL, Tang WF, Yu Q, **ang J, **a Q, Chen GY, et al. Effect of severe acute pancreatitis on pharmacokinetics of Da-Cheng-Qi Decoction components. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15:5992–9.
Liu HB, Huo HR, Guo JY, Li LF, Jiang TL. Effects of paeoniflorin on actin cytoskeletal changes of cultured rat brain microvessel endothelial cells stimulated by interleukin-1β. J US China Med Sci. 2006;3:31–9.
Yuan H, Ji WS, Wu KX, Jiao JX, Sun LH, Feng YT. Anti-inflammatory effect of diammonium glycyrrhizinate in a rat model of ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:4578–81.
Menegazzi M, Di Paola R, Mazzon E, Genovese T, Crisafulli C, Dal Bosco M, et al. Glycyrrhizin attenuates the development of carrageenan-induced lung injury in mice. Pharmacol Res. 2008;58:22–31.
Kao TC, Shyu MH, Yen GC. Glycyrrhizic acid and 18beta-glycyrrhetinic acid inhibit inflammation via PI3K/Akt/GSK3beta signaling and glucocorticoid receptor activation. J Agric Food Chem. 2010;58:8623–9.
Mollica L, De Marchis F, Spitaleri A, Dallacosta C, Pennacchini D, Zamai M, et al. Glycyrrhizin binds to high-mobility group box 1 protein and inhibits its cytokine activities. Chem Biol. 2007;14:431–41.
Oku H, Nakazato H, Horikawa T, Tsuruta Y, Suzuki R. Pirfenidone suppresses tumor necrosis factor-alpha, enhances interleukin-10 and protects mice from endotoxic shock. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002;446:167–76.
McMahon SB. NGF as a mediator of inflammatory pain. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1996;351:431–40.
Abe M, Akbar F, Hasebe A, Horiike N, Onji M. Glycyrrhizin enhances interleukin-10 production by liver dendritic cells in mice with hepatitis. J Gastroenterol. 2003;38:962–7.
Feng C, Wang H, Yao C, Zhang J, Tian Z. Diammonium glycyrrhizinate, a component of traditional Chinese medicine Gan-Cao, prevents murine T-cell-mediated fulminant hepatitis in IL-10 and IL-6-dependent manners. Int Immunopharmacol. 2007;7:1292–8.
Wu K, Zhang RL, Wang XP. The effects and mechanisms of glycyrrhizin on the TNBS-induced pancreatic fibrosis in rat. Chin Pharmacol Bull. 2003;12:1424–7 (in Chinese).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Chinese Government Scholarship no. 2009659015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Y. Tang and Y. Liao contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Y., Liao, Y., Kawaguchi-Sakita, N. et al. Sinisan, a traditional Chinese medicine, attenuates experimental chronic pancreatitis induced by trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid in rats. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 18, 551–558 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00534-010-0368-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00534-010-0368-z