Abstract
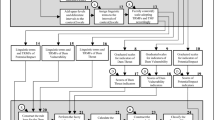
The Cash in Transit (CIT) deals with the money distribution and picking up between depot(s), central bank, bank branches, Automated Teller Machines (ATMs), jewelry stores, and exchange offices, safely and quickly. It is critical for companies carrying out CIT activities to identify risks and their priorities. It is one of the problems to be resolved for CIT companies to determine the risks that may occur on the route for each vehicle that will carry money from a certain center to the demand points. It is important for decision makers how critical these routes are concerning risks. Within the scope of the study, determining the risks, the weights of these risks, and high-risk routes accordingly are discussed. The literature review related to the problem is first consulted. After the literature review, interviews are made with experts on their subject. The main criteria and sub-criteria to define the risks are determined. Then, these criteria are weighted by the Interval-Valued Intuitionistic Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchy Process (IVIF-AHP), and risk assessment is made to alternative routes based on these weighted risks. The routes are evaluated by Interval-Valued Intuitionistic Fuzzy Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (IVIF-TOPSIS) methodology, and thus, it is determined which route has the highest risk and which route has the lowest risk. In this way, it is stated on which route should be used for the vehicles to distribute money and which routes should be improved.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Agrell PJ, Lindroth R, Norrman A (2004) Risk, information and incentives in telecom supply chains. Int J Prod Econ 90(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-5273(02)00471-1
Chan FTS, Kumar N (2007) Global supplier development considering risk factors using fuzzy extended AHP-based approach. Omega 35(4):417–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2005.08.004
OHSAS (2007) OHSAS 18001: 2007 Occupational health and safety management systems–requirements
Li YZ, Hu H, Huang DZ (2013) Develo** an effective fuzzy logic model for managing risks in marine oil transport. Int J Shipp Transp Logist 5(4–5):485–499. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJSTL.2013.055286
Gul M, Guneri AF, Nasirli SM (2019) A fuzzy-based model for risk assessment of routes in oil transportation. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16(8):4671–4686. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2078-z
Ayyildiz E, Taskin Gumus A (2021) Pythagorean fuzzy AHP based risk assessment methodology for hazardous material transportation: an application in Istanbul. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13223-y
Liu Y, Yu J, Sun H, Li T, He X, Lin Z (2022) Screening and prioritizing substances in groundwater in the Bei**g–Tian**–Hebei region of the North China Plain based on exposure and hazard assessments. J Hazard Mater 423:127142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127142
Lintukangas K, Kähkönen AK, Ritala P (2016) Supply risks as drivers of green supply management adoption. J Clean Prod 112:1901–1909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.10.089
Pourjavad E, Shahin A (2020) A hybrid model for analyzing the risks of green supply chain in a fuzzy environment. J Ind Prod Eng 37(8):422–433. https://doi.org/10.1080/21681015.2020.1833995
Meng Q, Liu X, Song Y, Wang W (2019) An extended generalized TODIM method for risk assessment of supply chain in social commerce under interval type-2 fuzzy environment. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 37(6):8551–8565. https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-190061
Farughi H, Mostafayi S (2017) A hybrid approach based on ANP, ELECTRE and SIMANP metaheuristic method for outsourcing manufacturing procedures according to supply chain risks—case study: a medical equipment manufacturer company in Iran. Decis Sci Lett 6(1):77–94. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.dsl.2016.6.003
Simic V, Gokasar I, Deveci M, Isik M (2021) Fermatean fuzzy group decision-making based CODAS approach for taxation of public transit investments. IEEE Trans Eng Manag pp 1–16
Linkov I, Satterstrom FK, Steevens J, Ferguson E, Pleus RC (2007) Multi-criteria decision analysis and environmental risk assessment for nanomaterials. J Nanoparticle Res 9(4):543–554. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-007-9211-0
Ganin AA et al (2020) Multicriteria decision framework for cybersecurity risk assessment and management. Risk Anal 40(1):183–199. https://doi.org/10.1111/risa.12891
Senthil S, Murugananthan K, Ramesh A (2018) Analysis and prioritisation of risks in a reverse logistics network using hybrid multi-criteria decision making methods. J Clean Prod 179:716–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.095
Gaudenzi B, Borghesi A (2006) Managing risks in the supply chain using the AHP method. Int J Logist Manag 17(1):114–136. https://doi.org/10.1108/09574090610663464
Zhou F, Chen TY (2021) An extended pythagorean fuzzy VIKOR method with risk preference and a novel generalized distance measure for multicriteria decision-making problems. Neural Comput Appl 33(18):11821–11844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-05829-7
Ansari ZN, Kant R, Shankar R (2020) Evaluation and ranking of solutions to mitigate sustainable remanufacturing supply chain risks: a hybrid fuzzy SWARA-fuzzy COPRAS framework approach. Int J Sustain Eng 13(6):473–494. https://doi.org/10.1080/19397038.2020.1758973
Ulutaş A, Topal A, Karabasevic D, Stanujkic D, Popovic G, Smarandache F (2022) Prioritization of logistics risks with plithogenic PIPRECIA method. Lect Notes Networks Syst 308:663–670. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85577-2_78
Zhou X, Cheng L, Li M (2020) Assessing and map** maritime transportation risk based on spatial fuzzy multi-criteria decision making: A case study in the South China sea. Ocean Eng 208:107403. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.OCEANENG.2020.107403
Radivojević G, Gajović V (2014) Supply chain risk modeling by AHP and Fuzzy AHP methods. J Risk Res 17(3):337–352. https://doi.org/10.1080/13669877.2013.808689
Chand M, Raj T, Shankar R (2015) A comparative study of multi criteria decision making approaches for risks assessment in supply chain. Int J Bus Inf Syst 18(1):67–84. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJBIS.2015.066128
Sattayaprasert W, Taneerananon P, Hanaoka S, Pradhananga R (2008) Creating a risk-based network for HazMat logistics by route prioritization with AHP—case study: gasoline logistics in Rayong, Thailand. IATSS Res 32(1):74–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0386-1112(14)60202-8
Soeanu A et al (2015) Transportation risk analysis using probabilistic model checking. Expert Syst Appl 42(9):4410–4421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2014.12.052
Anbuudayasankar SP, Ganesh K, Lenny-Koh SC, Ducq Y (2012) Modified savings heuristics and genetic algorithm for bi-objective vehicle routing problem with forced backhauls. Expert Syst Appl 39(3):2296–2305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.08.009
Zelenka J, Budinska I, Didekova Z (2012) A combination of heuristic and non-heuristic approaches for modified vehicle routing problem. In: Proceedings LINDI 2012–4th IEEE international symposium on logistics and industrial informatics, 2012, pp 107–112. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/LINDI.2012.6319471
Van Anholt RG, Coelho LC, Laporte G, Vis IFA (2016) An inventory-routing problem with pickups and deliveries arising in the replenishment of automated teller machines. Transp Sci 50(3):1077–1091. https://doi.org/10.1287/trsc.2015.0637
Bati S, Gozupek D (2019) Joint optimization of cash management and routing for new-generation automated teller machine networks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 49(12):2724–2738. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2017.2710359
Larrain H, Coelho LC, Cataldo A (2017) A Variable MIP Neighborhood Descent algorithm for managing inventory and distribution of cash in automated teller machines. Comput Oper Res 85:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2017.03.010
Koç Ç, Erbaş M, Özceylan E (2018) A rich vehicle routing problem arising in the replenishment of automated teller machines. Int J Optim Control Theor Appl 8(2):276–287. https://doi.org/10.11121/ijocta.01.2018.00572
Xu G, Li Y, Szeto WY, Li J (2019) A cash transportation vehicle routing problem with combinations of different cash denominations. Int Trans Oper Res 26(6):2179–2198. https://doi.org/10.1111/itor.12640
Yildiz A, Ayyildiz E, Gumus AT, Ozkan C (2020) A modified balanced scorecard based hybrid pythagorean fuzzy AHP-topsis methodology for ATM site selection problem. Int J Inf Technol Decis Mak 19(02):365–384. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219622020500017
Yildiz A, Ayyildiz E, Taskin-Gumus A, Ozkan C (2021) A framework to prioritize the public expectations from water treatment plants based on trapezoidal type-2 fuzzy ahp method. Environ Manage 67(3):439–448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-020-01367-5
Ayyildiz E, Taskin-Gumus A, Erkan M (2020) Individual credit ranking by an integrated interval type-2 trapezoidal fuzzy Electre methodology. Soft Comput 24(21):16149–16163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-04929-1
Ayyildiz E, Taskin-Gumus A (2020) A novel spherical fuzzy AHP-integrated spherical WASPAS methodology for petrol station location selection problem: a real case study for İstanbul. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(29):36109–36120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09640-0
Wang H, Qian G, Feng X (2011) An intuitionistic fuzzy AHP based on synthesis of eigenvectors and its application. Inf Technol J 10(10):1850–1866. https://doi.org/10.3923/itj.2011.1850.1866
Zhang Q, Huang Y (2012) Early warning index selection and weight assignment for city significant emergency in uncertain environment. Adv Inf Sci Serv Sci 4(23):490–497. https://doi.org/10.4156/AISS.vol4.issue23.61
Wu J, bin-Huang H, wei-Cao Q (2013) Research on AHP with interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets and its application in multi-criteria decision making problems. Appl Math Model 37(24):9898–9906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2013.05.035
Xu Z, Liao H (2014) Intuitionistic fuzzy analytic hierarchy process. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 22(4):749–761. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2013.2272585
Tavana M, Zareinejad M, Di Caprio D, Kaviani MA (2016) An integrated intuitionistic fuzzy AHP and SWOT method for outsourcing reverse logistics. Appl Soft Comput J 40:544–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.12.005
Büyüközkan G, Güleryüz S (2016) A new integrated intuitionistic fuzzy group decision making approach for product development partner selection. Comput Ind Eng 102:383–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2016.05.038
Tooranloo HS, Iranpour A (2017) Supplier selection and evaluation using interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy AHP method. Int J Procure Manag 10(5):539–554. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJPM.2017.086399
Nirmala G, Uthra G (2017) Quality of online shop** websites in india: A study using intuitionistic fuzzy AHP. J Adv Res Dyn Control Syst 9(4):117–124
Otay İ, Oztaysi B, Cevik-Onar S, Kahraman C (2017) Multi-expert performance evaluation of healthcare institutions using an integrated intuitionistic fuzzy AHP&DEA methodology. Knowledge-Based Syst 133:90–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2017.06.028
Sun J, Peng X, Xu Y, Sun B, Ma N, Lv P (2017) VIKOR-GRA based intuitionistic fuzzy multi-attribute WEB service selection. Bol Tec Bull 55(17):982–996
Tooranloo HS, Ayatollah AS, Iranpour A (2018) A model for supplier evaluation and selection based on integrated interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy AHP-TOPSIS approach. Int J Math Oper Res 13(3):401–417. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJMOR.2018.094854
Cebi S, Ilbahar E (2018) Warehouse risk assessment using interval valued intuitionistic fuzzy AHP. Int J Anal Hierarchy Process 10(2):243–253. https://doi.org/10.13033/ijahp.v10i2.549
Ouyang X, Guo F (2018) Intuitionistic fuzzy analytical hierarchical processes for selecting the paradigms of mangroves in municipal wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 197:634–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.102
Karasan A, Erdogan M, Ilbahar E (2018) Prioritization of production strategies of a manufacturing plant by using an integrated intuitionistic fuzzy AHP & TOPSIS approach. J Enterp Inf Manag 31(4):510–528. https://doi.org/10.1108/JEIM-01-2018-0001
Hinduja A, Pandey M (2018) Assessment of healthcare waste treatment alternatives using an integrated decision support framework. Int J Comput Intell Syst 12(1):318–333. https://doi.org/10.2991/ijcis.2018.125905685
Zhixiong C, Juan** C, **sha Y, Nan X, Dongsheng H (2019) Network access selection algorithm based on balanced profits between users and network. Wirel Commun Mob Comput. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6981657
Karasan A (2019) A novel hesitant intuitionistic fuzzy linguistic AHP method and its application to prioritization of investment alternatives. Int J Anal Hierarchy Process 11(1):127–142. https://doi.org/10.13033/ijahp.v11i1.610
Büyüközkan G, Göçer F, Karabulut Y (2019) A new group decision making approach with IF AHP and IF VIKOR for selecting hazardous waste carriers. Meas J Int Meas Confed 134:66–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2018.10.041
Taherkhani N, Sepehri MM, Shafaghi S, Khatibi T (2019) Identification and weighting of kidney allocation criteria: a novel multi-expert fuzzy method. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak 19(1):182. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12911-019-0892-y
Hinduja A, Pandey M (2019) An integrated intuitionistic fuzzy MCDM approach to select cloud-based ERP system for SMEs. Int J Inf Technol Decis Mak 18(6):1875–1908. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219622019500378
Kahraman C, Öztayşi B, Çevik Onar S (2020) An integrated intuitionistic fuzzy AHP and TOPSIS approach to evaluation of outsource manufacturers. J Intell Syst 29(1):283–297. https://doi.org/10.1515/jisys-2017-0363
Dogan O, Deveci M, Canıtez F, Kahraman C (2019) A corridor selection for locating autonomous vehicles using an interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy AHP and TOPSIS method. Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-04421-5
Büyüközkan G, Havle CA, Feyzioğlu O (2020) “A new digital service quality model and its strategic analysis in aviation industry using interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy AHP. J Air Transp Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jairtraman.2020.101817
Murat-Ar I, Erol I, Peker I, Ihsan Ozdemir A, Durmus Medeni T, Tolga Medeni I (2020) Evaluating the feasibility of blockchain in logistics operations: a decision framework. Expert Syst Appl. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113543
Tumsekcali E, Ayyildiz E, Taskin A (2021) Interval valued intuitionistic fuzzy AHP-WASPAS based public transportation service quality evaluation by a new extension of SERVQUAL Model: P-SERVQUAL 4.0. Expert Syst Appl 186:115757. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ESWA.2021.115757
Boran FE, Genç S, Kurt M, Akay D (2009) A multi-criteria intuitionistic fuzzy group decision making for supplier selection with TOPSIS method. Expert Syst Appl 36(8):11363–11368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2009.03.039
Boran F (2011) An integrated intuitionistic fuzzy multi criteria decision making method for facility location selection. Math Comput Appl 16(2):487–496. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca16020487
Ning X, Lam KC, Lam MCK (2011) A decision-making system for construction site layout planning. Autom Constr 20(4):459–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2010.11.014
Boran FE, Genç S, Akay D (2011) Personnel selection based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Hum Factors Ergon Manuf Serv Ind 21(5):493–503. https://doi.org/10.1002/hfm.20252
Su ZX, Chen MY, **a GP, Wang L (2011) An interactive method for dynamic intuitionistic fuzzy multi-attribute group decision making. Expert Syst Appl 38(12):15286–15295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.06.022
Daneshvar-Rouyendegh B (2011) The DEA and intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS approach to departments’ performances: a pilot study. J Appl Math 2011:16. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/712194
Boran FE, Boran K, Menlik T (2012) The evaluation of renewable energy technologies for electricity generation in Turkey using intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS. Energy Sources Part B Econ Plan Policy 7(1):81–90. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567240903047483
Rouyendegh BD (2012) Evaluating projects based on intuitionistic fuzzy group decision making. J Appl Math. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/824265
Zhang Q, Li X, Huang Y (2012) The study of alarm severity priority ordering method for the network public sentiment emergency in uncertain environment. Int J Adv Comput Technol 4(23):129–137. https://doi.org/10.4156/ijact.vol4.issue23.15
Bai ZY (2013) An interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS method based on an improved score function. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/879089
Wu Y, Xu H, Geng S (2014) Research on the optimization of solar-wind hybrid power station project selection based on intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS method. Energy Educ Sci Technol. Energy Sci Res 32(6):7039–7052
Joshi D, Kumar S (2014) Intuitionistic fuzzy entropy and distance measure based TOPSIS method for multi-criteria decision making. Egypt Informatics J 15(2):97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eij.2014.03.002
Maldonado-Macías A, Alvarado A, García JL, Balderrama CO (2014) Intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS for ergonomic compatibility evaluation of advanced manufacturing technology. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 70(9–12):2283–2292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-5444-5
Rouyendegh BD (2015) Develo** an integrated ANP and intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS model for supplier selection. J Test Eval 43(3):20130114. https://doi.org/10.1520/jte20130114
Li M, Wu C (2015) Green supplier selection based on improved intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS model. Metall Min Ind 7(6):193–205
Li C, Zhang L, Zeng S (2015) Typhoon disaster evaluation based on extension of intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS method in Zhejiang Province of China. Int J Earth Sci Eng 8(2):1031–1035
Yang S, Wang P, Li G, Huang K (2015) “Group decision making model for weapon selection using extended vikor method under intuitionistic fuzzy environment”, **tong Fangzhen Xuebao /. J Syst Simul 27(9):2169–2175
Omosigho SE, Omorogbe DEA (2015) Supplier selection using different metric functions. Yugosl J Oper Res 25(3):413–423. https://doi.org/10.2298/YJOR130706028O
Li X, Chen X (2015) Multi-criteria group decision making based on trapezoidal intuitionistic fuzzy information. Appl Soft Comput J 30:454–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.01.054
Wood DA (2016) Supplier selection for development of petroleum industry facilities, applying multi-criteria decision making techniques including fuzzy and intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS with flexible entropy weighting. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 28:594–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2015.12.021
Afful-Dadzie E, Afful-Dadzie A (2016) A decision making model for selecting start-up businesses in a government venture capital scheme. Manag Decis 54(3):714–734. https://doi.org/10.1108/MD-06-2015-0226
Büyüközkan G, Güleryüz S (2016) Multi criteria group decision making approach for smart phone selection using intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS. Int J Comput Intell Syst 9(4):709–725. https://doi.org/10.1080/18756891.2016.1204119
Aikhuele DO, Turan FBM (2016) Intuitionistic fuzzy-based model for failure detection. Springerplus 5(1):1938. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-3446-0
Aikhuele DO, Turan FM, Odofin SM, Ansah RH (2017) Interval-valued Intuitionistic Fuzzy TOPSIS-based model for troubleshooting marine diesel engine auxiliary system. Trans R Inst Nav Archit Part A Int J Marit Eng 159:107–114. https://doi.org/10.3940/rina.ijme.2016.al.402
Aikhuele DO, Turan FM (2017) Extended TOPSIS model for solving multi-attribute decision making problems in engineering. Decis Sci Lett 6(4):365–376. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.dsl.2017.2.002
Aikhuele DO, Turan FM (2017) An exponential-related function for decision-making in engineering and management. Open Eng 7(1):153–160. https://doi.org/10.1515/eng-2017-0022
Abdullah L (2017) A fuzzy decision making method in develo** environmental performance index. WSEAS Trans Environ Dev 13:350–359
Song X, Xu J, Shen C, Peña-Mora F, Zeng Z (2017) A decision making system for construction temporary facilities layout planning in large-scale construction projects. Int J Civ Eng 15(2):333–353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40999-016-0107-1
Afful-Dadzie E, Afful-Dadzie A, Oplatková ZK (2017) Assessing commercial viability of technology start-up businesses in a government venture capital under intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Int J Fuzzy Syst 19(2):400–413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-016-0141-9
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Li Y, Liu S, Yang J (2017) A study of rural logistics center location based on intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS. Math Probl Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2323057
Aikhuele DO, Sorooshian S, Ansah RH, Turan FM (2017) Application of intuitionistic fuzzy topsis model for troubleshooting an offshore patrol boat engine. Polish Marit Res 24(2):68–76. https://doi.org/10.1515/pomr-2017-0051
Aikhuele D, Turan F (2017) An intuitionistic fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making method based on an exponential-related function. Int J Fuzzy Syst Appl 6(4):33–46. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJFSA.2017100103
Liu Y, Bi JW, Fan ZP (2017) A method for ranking products through online reviews based on sentiment classification and interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy topsis. Int J Inf Technol Decis Mak 16(6):1497–1522. https://doi.org/10.1142/S021962201750033X
Babu AVS, Devi PM, Sharmila B (2018) Efficient enhanced intrusion identification and response system for MANETs. Int J Bus Inf Syst 29(4):535–546. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJBIS.2018.096036
Daneshvar-Rouyendegh B, Yildizbasi A, Arikan ÜZB (2018) Using intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS in site selection of wind power plants in Turkey. Adv Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6703798
Sen DK, Datta S, Mahapatra SS (2018) Sustainable supplier selection in intuitionistic fuzzy environment: a decision-making perspective. Benchmarking 25(2):545–574. https://doi.org/10.1108/BIJ-11-2016-0172
Shen F, Ma X, Li Z, Xu Z, Cai D (2018) An extended intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS method based on a new distance measure with an application to credit risk evaluation. Inf Sci (Ny) 428:105–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.10.045
Memari A, Dargi A, Akbari Jokar MR, Ahmad R, Abdul Rahim AR (2019) Sustainable supplier selection: a multi-criteria intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS method. J Manuf Syst 50:9–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2018.11.002
El Hachami K, Alaoui YL, Tkiouat M (2019) Sectorial evaluation of islamic banking contracts: a fuzzy multi-criteria-decision-making approach. Invest Manag Financ Innov 16(2):370–382. https://doi.org/10.21511/imfi.16(2).2019.31
Aikhuele DO (2019) A flexible model for supporting designers and determining design stakeholders’ preferences at the early product design stage. Int J Data Netw Sci 3(2):109–118. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.ijdns.2018.12.004
Cavallaro F, Zavadskas EK, Streimikiene D, Mardani A (2019) Assessment of concentrated solar power (CSP) technologies based on a modified intuitionistic fuzzy topsis and trigonometric entropy weights. Technol Forecast Soc Change 140:258–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2018.12.009
Anshu K, Gaur L (2019) E-satisfaction estimation: a comparative analysis using AHP and intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS. J Cases Inf Technol 21(2):65–87. https://doi.org/10.4018/JCIT.2019040105
Kansal Y, Kapur PK, Sachdeva N (2019) Determining best patch management software using intuitionistic fuzzy sets with TOPSIS. Int J Performability Eng 15(5):1297–1305. https://doi.org/10.23940/ijpe.19.05.p5.12971305
Pal K, Kumar V, Arora HD, Kumar S (2019) Application of TOPSIS in the diagnosis of vector borne diseases. Int J Eng Adv Technol 8(6):5217–5223. https://doi.org/10.35940/ijeat.F8585.088619
Roy SK, Midya S (2019) Multi-objective fixed-charge solid transportation problem with product blending under intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Appl Intell 49(10):3524–3538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-019-01466-9
Faghih-Roohi S, Akcay A, Zhang Y, Shekarian E, de Jong E (2020) A group risk assessment approach for the selection of pharmaceutical product ship** lanes. Int J Prod Econ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107774
Kilic HS, Yalcin AS (2020) Modified two-phase fuzzy goal programming integrated with IF-TOPSIS for green supplier selection. Appl Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106371
Zhang L, Zhan J, Yao Y (2020) Intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS method based on CVPIFRS models: an application to biomedical problems. Inf Sci (Ny) 517:315–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2020.01.003
Rouyendegh BD, Yildizbasi A, Üstünyer P (2020) Intuitionistic Fuzzy TOPSIS method for green supplier selection problem. Soft Comput 24(3):2215–2228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-04054-8
Rouyendegh BD, Yildizbasi A, Yilmaz I (2020) Evaluation of retail ındustry performance ability through ıntegrated ıntuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS and data envelopment analysis approach. Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-04669-2
Abdullah L, Goh C, Zamri N, Othman M (2020) Application of interval valued intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS for flood management. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 38(1):873–881. https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-179455
Olivares-Aguila J, ElMaraghy H (2020) Co-development of product and supplier platform. J Manuf Syst 54:372–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2020.01.010
Gao Y, Sheng-Li D, Zhong H (2020) A novel target threat assessment method based on three-way decisions under intuitionistic fuzzy multi-attribute decision making environment. Eng Appl Artif Intell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2019.103276
Ayyildiz E, Taskin-Gumus A (2021) Interval-valued Pythagorean fuzzy AHP method-based supply chain performance evaluation by a new extension of SCOR model: SCOR 4.0. Complex Intell. Syst. 7(1):559–576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40747-020-00221-9
Uyanik C, Tuzkaya G, Kalender ZT, Oguztimur S (2020) An integrated dematel–if-topsis methodology for logistics centers’ location selection problem: an application for Istanbul metropolitan area. Transport 35(6):548–556. https://doi.org/10.3846/transport.2020.12210
Talarico L, Sörensen K, Springael J (2017) A biobjective decision model to increase security and reduce travel costs in the cash-in-transit sector. Int Trans Oper Res 24(1–2):59–76. https://doi.org/10.1111/itor.12214
Liang Z-C, Yang Y, Liao S-G (2022) Interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy two-sided matching model considering level of automation. Appl Soft Comput 116:108252. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ASOC.2021.108252
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Aslihan Yildiz and Ertugrul Ayyildiz developed the theoretical formulation, performed the analytic calculations and numerical analysis. Ertugrul Ayyildiz and Alev Taskin contributed to the sensitivity analysis and final version of the manuscript. Aslihan Yildiz and Coskun Ozkan drafted the manuscript. Ali Fuat Guneri supervised the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Ethics approval
Ethics committee approval is not required.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
The authors confirm that the final version of the manuscript has been reviewed, approved, and consented to for publication by all authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Yildiz, A., Guneri, A.F., Ozkan, C. et al. An integrated interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy AHP-TOPSIS methodology to determine the safest route for cash in transit operations: a real case in Istanbul. Neural Comput & Applic 34, 15673–15688 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07236-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07236-y