Abstract
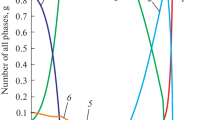
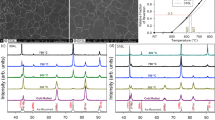
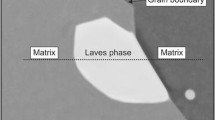
This research focusses on a complex precipitation (Ni3(Ti,Al)) hardenable metastable stainless steel. Dual phase (austenite, γ/martensite, α′) and ultrafine grained austenitic microstructures obtained after applying isochronal heat treatments (0.1–10 ℃/s) to a cold-rolled (CR) metastable stainless steel have been microstructurally and mechanically characterized using different experimental techniques (optical microscopy, SEM, TEM, magnetic measurements, tensile tests). A wide range of strength (2.1–1.1 GPa) and elongation (3–25%) values have been obtained using sub-size samples (7 mm in gauge length). The scientific aim is the understanding of those microstructural parameters and mechanisms that influence the achievement of ultra-fine grained microstructures and control or the mechanical behaviour of different complex microstructures in this type of steels. Whereas the industrial aim would be to expand the applicability of this steel and use this scientific knowledge to design steels with optimized microstructures and mechanical properties.
Zusammenfassung
Diese Forschung konzentriert sich auf einen komplexen aushärtbaren metastabilen Edelstahl (Ni3(Ti,Al)). Doppelphasen- (austenit, γ/martensit, α′) und ultrafeinkörnige austenitische Mikrostrukturen, die nach Anwendung isochroner Wärmebehandlungen (0.1–10 ºC/s) auf einen kaltgewalzten (CR) metastabilen rostfreien Stahl erhalten wurden, wurden mikrostrukturell und mechanisch unter Verwendung verschiedener charakterisiert experimentelle techniken (optische Mikroskopie, SEM, TEM, magnetische Messungen, Zugversuche). Ein breiter Bereich von Festigkeitswerten (2.1–1.1 GPa) und Dehnungswerten (3–25 %) wurde unter Verwendung von ben mit geringer Größe (7 mm Messlänge) erhalten. Das wissenschaftliche Ziel ist das Verständnis der mikrostrukturellen Parameter und Mechanismen, die das chen von ultrafeinen Mikrostrukturen und die Kontrolle oder das mechanische Verhalten verschiedener komplexer Mikrostrukturen in dieser Art von Stählen beeinflussen. während das industrielle Ziel darin besteht, die Anwendbarkeit dieses Stahls zu erweitern und diese wissenschaftlichen Erkenntnisse zu nutzen, um Stähle mit optimierten Mikrostrukturen und mechanischen Eigenschaften zu konstruieren.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Post, J.; Datta, K.; Huetink, J.: Constitutive behaviour of the metastable stainless steel: Sandvik Nanoflex, AIP Conference Proceeding, 712 (2004), pp 1670–1675
Slunder, C. J.; Hoenie, A. F.; Hall, A. M.: Thermal and Mechanical Treatment for precipitation-hardening stainless steel, NASA SP (Series), 5089 (1967), pp 1–192
Eskandari, M.; Najafizadeh, A.; Kermanpur, A.; Karimi, M.: Potential application of nanocrystalline 301 austenitic stainless steel in lightweight vehicle structures, Materials & Design, 30 (2009), no. 9, pp 3869–3872
Hamada, A. S.; Kisko, A. P.; Sahu, P.; Karjalainen, L. P.: Enhancement of mechanical properties of a TRIP-aided austenitic stainless steel by controlled reversion annealing, Materials Science Engineering A, 628 (2015), pp 154–159
Celada Casero, C.; San Martín, D.: Austenite formation in a cold-rolled semi-austenitic stainless steel, Metallurgical & Materials Transactions A, 45 (2014), no. 4, pp 1767–1777
Celada, C.; Toda-Caraballo, I.; Kim, B.; San Martín, D.: Chemical banding revealed by chemical etching in a cold-rolled metastable stainless steel, Materials Characterization, 84 (2013), pp 142–152
Lichtenegger, P.; Blöch, R.: Colour etching of high alloy steels, Practical Metallography, 12 (1975), pp 567–673
San Martin, D.; Rivera Diaz del Castillo, P. E. J.; Peekstok, E.; van der Zwaag, S.: A new etching route for revealing the austenite grain boundaries in an 11.4 % Cr precipitation hardening semi-austenitic stainless steel, Materials Characterization, 58 (2007), no. 5, pp 455–460
Kasper, J. S.; The ordering of atoms in the χ‑phase of the Iron–Chromium–Molybdenum System, Acta Metallurgica, 2 (1954), pp 456–461
Scheller, P. R.; Flesch, R.; Bleck, W.: Solidification morphology and microstructure properties at increased cooling rates for 18‑8 Cr–Ni stainless steel, Advanced Engineering Materials, 1 (1999), no. 3–4, pp 209–214
Salmon Cox, P. H.; Reisdorf, B. G.; Pellissier, G. E.: The origin and significance of banding in 18Ni (250) maraging steel, Trans AIME, 239 (1967), pp 1809–1817
Han, J.; Lee, Y.-K.: The effects of the heating rate on the reverse transformation mechanism and the phase stability of reverted austenite in medium Mn steels, Acta Materialia, 67 (2014), pp 354–361
Apple, C. A.; Krauss, G.: The effect of heating rate on the martensite to austenite transformation in Fe-Ni‑C alloys, Acta Metallurgica, 20 (1972), no. 7, pp 849–85
Tomimura, K.; Takaki, S.; Tokunaga, Y.: Reversion mechanism from deformation induced martensite to austenite in metastable austenitic stainless steels, ISIJ International, 31 (1991), no 12, pp 1431–1437
Liu, P.: Relationships Between Microstructure and Properties of Stainless Steels‑A Few Working Examples, Materials Characterization, 44 (2000), no. 4–5, pp 413–424
Celada-Casero, C.; Huang, B. M.; Aranda, M. M.; Yang, J.-R.; San Martin, D.: Mechanisms of ultrafine-grained austenite formation under different isochronal conditions in a cold-rolled metastable stainless steel, Materials Characterization, 118 (2016), pp 129–141
Thuvander, M.; Andersson, M.; Stiller, K.: Precipitation process of martensitic PH stainless steel Nanoflex, Materials Science Technology, 28 (2012), no. 6, pp 695–701
Acknowledgements
C. Celada-Casero would like to thank the financial support from the Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) (JAEPre_2011_01167) in the form of a JAE-predoc grant, co-funded by the European Social Fund and to the National Science Council of Taiwan granting a research internship at the National Taiwan University (NTU). I. Toda-Caraballo is grateful for financial support through the fellowship 2016-T2/IND-1693 from the Programme Atracción de talento investigador (Consejería de Educación, Juventud y Deporte, Comunidad de Madrid). C. Celada-Casero and D. San-Martin acknowledge the financial support from the Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (project No. MAT2010-19522). The authors are grateful to CAI of Physical Techniques, (Complutense University of Madrid) and the Phase Transformations and Electron Microscopy labs of CENIM-CSIC for the experimental support. Authors are also grateful to Prof. Jan Post and Ir. Manso Groen from Philips Consumer Lifestyle for supplying the steels for this investigation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Celada-Casero, C., Urones-Garrote, E., Chao, J. et al. Tailoring the Mechanical Properties Through the Control of Heat Treatments in a Precipitation Hardening Metastable Stainless Steel. Berg Huettenmaenn Monatsh 165, 26–32 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00501-019-00930-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00501-019-00930-w
Keywords
- Metastable stainless steel
- Ultrafine grained steel
- Austenite
- Martensite
- Precipitation
- TRIP
- Mechanical testing