Abstract
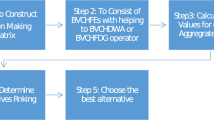
The technique for order preference by similarity to ideal solution (TOPSIS) is a popular multi-attribute decision making method. However, the increasing uncertain information with probability and the psychological factor of regret aversion of experts in some complicated situations bring new challenges to the application of traditional TOPSIS. The probabilistic hesitant fuzzy set (P-HFS) is an effective tool to depict the hesitant fuzzy information with the corresponding probability, which can remain more information. In addition, the regret theory indicates that experts may care more about the regret values than the absolute values of alternatives under the fuzzy environment. This paper investigates a new probabilistic hesitant fuzzy TOPSIS (PHFTOPSIS) method based on the regret theory. We propose the corresponding concepts of utility function, reject–rejoice function and perceived utility value of the probabilistic hesitant fuzzy element (P-HFE). The maximum deviation model under the probabilistic hesitant fuzzy environment is presented to determine the weights of attributes. The detailed implementation process of the PHFTOPSIS method based on the regret theory is also provided. Moreover, we apply the proposed method to the investment strategy. Compared with earlier methods, the proposed method can consider both the probabilistic hesitant fuzzy information and regret aversion of experts at the same time in actual applications. A comparative analysis with traditional TOPSIS and probabilistic hesitant fuzzy weighted averaging (PHFWA) operator is further conducted to illustrate its advantages.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Cheng F (2012) Maximum deviation of error density estimators in censored linear regression. Statist Probab Lett 82:1657–1664
Chorus CG (2012) Regret theory-based route choices and traffic equilibria. Transportmetrica 8(4):291–305
Gong XM, Yu CR, Wu ZH (2019) An extension of regret theory based on probabilistic linguistic cloud sets considering dual expectations: an application for the stock market. IEEE Access 7:171046–171060
Gou XJ, Xu ZS, Zhou W, Herrera-Viedma E (2021) The risk assessment of construction project investment based on prospect theory with linguistic preference orderings. Econ Res-Ekonomska Istraživanja 34:709–731
Guo J, Yin J, Zhang L et al (2020) Extended TODIM method for CCUS storage site selection under probabilistic hesitant fuzzy environment. Appl Soft Comput 93:106381
He Y, Xu ZS (2019) Multi-attribute decision making methods based on reference ideal theory with probabilistic hesitant information. Expert Syst Appl 118:4459–4469
Krishankumaar R, Mishra AR, Ravichandran KS, Gou XJ (2022) New ranking model with evidence theory under probabilistic hesitant fuzzy context and unknown weights. Neural Comput Appl 5:3923–3937
Krishankumar R, Ravichandran KS, Liu PD et al (2021) A decision framework under probabilistic hesitant fuzzy environment with probability estimation for multi-criteria decision making. Neural Comput Appl 33:1–17
Li Z (2021) VIKOR method for evaluating the management quality of teacher education with probabilistic hesitant fuzzy information. Discrete Dyn Nat Soc. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/1326202
Li DQ, Zeng WY, Zhao YB (2015) Note on distance measure of hesitant fuzzy sets. Inf Sci 321:103–115
Liu XD, Wang ZW, Zhang ST et al (2020) Probabilistic hesitant fuzzy multiple attribute decision-making based on regret for the evaluation of venture capital projects. Econ Res-Ekonomska Istraživanja 33:672–697
Lo TP, Guo SJ (2010) Effective weighting model based on the maximum deviation with uncertain information. Experts Syst Appl 37:8445–8449
Loomes G, Sugden R (1982) Regret theory: an alternative theory of rational choice under uncertainty. Econ J 92(368):805–824
Merigo JM, Gil-Lafuente AM (2010) New decision-making techniques and their application in the selection of financial products. Inf Sci 180:2085–2094
Mu Z, Zeng S, Balezentis T (2015) A novel aggregation principle for hesitant fuzzy elements. Knowl-Based Syst 84:134–143
Sha XY, Yin CC, Xu ZS et al (2021) Probabilistic hesitant fuzzy TOPSIS emergency decision-making method based on the cumulative prospect theory. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 40:1–17
Tian XL, Xu ZS, Guo J (2019) An extended TODIM based on cumulative prospect theory and its application in venture capital. Informatica 30:413–429
Torra V (2010) Hesitant fuzzy sets. Int J Intell Syst 25:529–539
Torra V, Narukawa Y (2009) On hesitant fuzzy sets and decision. In: The 18th IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, Jeju Island, Korea, pp 1378–1382
Wang HD, Pan XH, Yan J et al (2020) A projection-based regret theory method for multi-attribute decision making under interval type-2 fuzzy sets environment. Inf Sci 512:108–122
Wang HD, Pan XH, Yan J, Yao JL, He SF (2020) A projection-based regret theory method for multi-attribute decision making under interval type-2 fuzzy sets environment. Inf Sci 512:108–122
**a MM, Xu ZS (2011) Hesitant fuzzy information aggregation in decision making. Int J Approx Reason 52:395–407
Xu ZS (2014) Hesitant fuzzy aggregation operators and their application. Springer
Xu ZS, **a MM (2011a) Distance and similarity measures for hesitant fuzzy sets. Inf Sci 181:2128–2138
Xu ZS, **a MM (2011b) On distance and correlation measures of hesitant fuzzy information. Int J Intell Syst 26:410–425
Xue WT, Xu ZS, Mi XM et al (2021) Dynamic reference point method with probabilistic linguistic information based on the regret theory for public health emergency decision-making. Econ Res-Ekonomska Istraživanja. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2021.1875254
Zhang ZM (2013) Hesitant fuzzy power aggregation operators and their application to multiple attribute group decision making. Inf Sci 234:150–181
Zhang ST, Zhu JJ, Liu XD, Chen Y (2016) Regret theory method-based group decision-making with multidimensional preference and incomplete weight information. Inf Fus 31:1–13
Zhang F, Li J, Chen J et al (2017a) Hesitant distance set on hesitant fuzzy sets and its application in urban road traffic state identification. Eng Appl Artif Intell 61:57–64
Zhang S, Xu ZS, He Y (2017b) Operations and integrations of probabilistic hesitant fuzzy information in decision making. Inf Fus 38:1–11
Zhu B (2014) Decision method for research and application based on preference relation. Nan**g Southeast University
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 72071135).
Funding
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 72071135).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This paper expands the application of regret theory to the probabilistic hesitant fuzzy environment and proposes the corresponding concepts of utility function, reject–rejoice function and perceived utility value of the probabilistic hesitant fuzzy element (P-HFE). The maximum deviation model under the probabilistic hesitant fuzzy environment is presented to determine the weights of attributes. Based on which, we propose a new probabilistic hesitant fuzzy TOPSIS (PHFTOPSIS) method based on the regret theory. The detailed implementation process of the PHFTOPSIS method based on the regret theory is also provided. Moreover, we apply the proposed PHFTOPSIS method based on the regret theory to the investment strategy. I hope this paper is suitable for “Soft Computing”. We deeply appreciate your consideration of our manuscript, and we look forward to receiving comments from the reviewers.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest exits in the submission of this manuscript, and manuscript is approved by all authors for publication. The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical and informed consent for data used
I would like to declare on behalf of my co-authors that the work described was original research that has not been published previously, and not under consideration for publication elsewhere, in whole or in part. All the authors listed have approved the ethical and information consent for the data used in the manuscript that is enclosed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, C., Xu, Z., Hou, J. et al. The probabilistic hesitant fuzzy TOPSIS method based on the regret theory and its application in investment strategy. Soft Comput 28, 4285–4298 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09594-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09594-8