Abstract
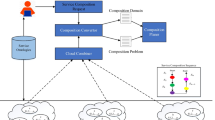
The multi-cloud environment (MCE) serves users on-demand by presenting miscellaneous online web services. Each web service which is delivered by every cloud provider has its own quality of features and also own pricing scheme. In the web service composition technology, the integration of the services required by the users is done with the aim of producing the efficient solutions with the desired quality. In some businesses, continuity of activities is very important and a business that fails a lot cannot be trusted by subscribers. In these businesses, it is necessary to maximize the reliability of the system along with minimizing the overall monetary costs. To this end, two new reliability and cost models are presented. All of the network equipment, communication, and elements affecting the total cost and reliability of the system are taken into consideration in the proposed models. Then, the web service composition issue is formulated to a multi-objective optimization problem. To solve this combinatorial problem in large search space of MCE, the multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm is suggested to maximize reliability while minimizing the cost of services and make Pareto optimal points. The results of the evaluations show that in different scenarios, the proposed solution proves the amount of 48%, 46%, and 12% averagely improvement over other comparative MOGWO, NSGA-II, and MOEA/D approaches in terms of service failure rate, service implementation cost in cloud providers, and the execution time respectively.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data will be available on logical request.
References
Abbasi S, Daneshmand-Mehr M, Ghane Kanafi A (2021) The sustainable supply chain of CO2 emissions during the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. J Ind Eng Int 17(4):83–108
Abbasi S, Daneshmand-Mehr M, Ghane Kanafi A (2023) Green closed-loop supply chain network design during the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic: a case study in the Iranian Automotive Industry. Environ Model Assess 28(1):69–103
Abdolazimi O, Salehi Esfandarani M, Salehi M, Shishebori D (2020a) A comparison of solution methods for the multi-objective closed loop supply chains. Adv Ind Eng 54(1):75–98
Abdolazimi O, Esfandarani MS, Salehi M, Shishebori D (2020b) Robust design of a multi-objective closed-loop supply chain by integrating on-time delivery, cost, and environmental aspects, case study of a Tire Factory. J Clean Prod 264:121566
Abdolazimi O, Esfandarani MS, Shishebori D (2021) Design of a supply chain network for determining the optimal number of items at the inventory groups based on ABC analysis: a comparison of exact and meta-heuristic methods. Neural Comput Appl 33:6641–6656
Abdolazimi O, Bahrami F, Shishebori D, Ardakani MA (2022) A multi-objective closed-loop supply chain network design problem under parameter uncertainty: comparison of exact methods. Environ Dev Sustain 24:10768–10802
Amazon EC2 pricing. https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/pricing. Accessed July 2023
Asghari Alaie Y, Hosseini Shirvani M, Rahmani AM (2022) A hybrid bi-objective scheduling algorithm for execution of scientific workflows on cloud platforms with execution time and reliability approach. J Supercomput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-022-04703-0
Birke R, Giurgiu I, Chen LY, Wiesmann D, Engbersen T (2014) Failure analysis of virtual and physical machines: patterns, causes and characteristics. In: 2014 44th annual IEEE/IFIP international conference on dependable systems and networks. IEEE, pp 1–12
Coello CC, Lechuga MS (2002) MOPSO: a proposal for multiple objective particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of the 2002 Congress on evolutionary computation. CEC'02 (Cat. No. 02TH8600), vol 2. IEEE, pp 1051–1056
Dahan F, Alwabel A (2023) Artificial Bee colony with cuckoo search for solving service composition. Intell Autom Soft Comput 35(3):3385–3402
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan TAMT (2002) A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 6(2):182–197
Dong JK, Wang HB, Li YY, Cheng SD (2014) Virtual machine placement optimizing to improve network performance in cloud data centers. J China Univ Posts Telecommun 21(3):62–70
Fang L, Zhang X, Sood K, Wang Y, Yu S (2020) Reliability-aware virtual network function placement in carrier networks. J Netw Comput Appl 154:102536
Farzai S, Hosseini Shirvani M, Rabbani M (2020) Multi-objective communication-aware optimization for virtual machine placement in cloud datacenters. Sustain Comput Inform Syst 28:100374
Ghobaei-Arani M, Rahmanian AA, Souri A, Rahmani AM (2018) A moth-flame optimization algorithm for web service composition in cloud computing: simulation and verification. Softw Pract Exp 48(10):1865–1892
Gill SS, Garraghan P, Stankovski V, Casale G, Thulasiram RK, Ghosh SK, Ghosh SK, Ramamohanarao K, Buyya R (2019) Holistic resource management for sustainable and reliable cloud computing: An innovative solution to global challenge. J Syst Softw 155:104–129
Hosseini Shirvani M (2020) Bi-objective web service composition problem in multi-cloud environment: a bi-objective time-varying particle swarm optimisation algorithm. J Exp Theoret Artif Intell 33:179–202
Hosseini Shirvani M, Noorian Talouki R (2022) Bi-objective scheduling algorithm for scientific workflows on cloud computing platform with makespan and monetary cost minimization approach. Complex Intell Syst 8:1085–1114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40747-021-00528-1
Hosseini Shirvani M, Rahmani AM, Sahafi A (2018) An iterative mathematical decision model for cloud migration: a cost and security risk approach. Softw Pract Exp 48(3):449–485
Iannaccone G, Chuah CN, Mortier R, Bhattacharyya S, Diot C (2002) Analysis of link failures in an IP backbone. In: Proceedings of the 2nd ACM SIGCOMM workshop on Internet measurement, pp 237–242
Ibrahimi A (2017) Cloud computing: pricing model. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl 8(6):434–441
Javadi B, Abawajy J, Buyya R (2012) Failure-aware resource provisioning for hybrid cloud infrastructure. J Parallel Distrib Comput 72(10):1318–1331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpdc.2012.06.012
Ju C, Ding H, Hu B (2023) A hybrid strategy improved whale optimization algorithm for web service composition. Comput J 66(3):662–677
Karimi MB, Isazadeh A, Rahmani AM (2017) QoS-aware service composition in cloud computing using data mining techniques and genetic algorithm. J Supercomput 73(4):1387–1415
Khababa G, Seghir F, Bessou S (2022) An extended artificial bee colony with local search for solving the Skyline-based web services composition under interval QoS properties. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 42(4):3855–3870
Li J, Zhu S (2023) Service composition considering energy consumption of users and transferring files in a multicloud environment. J Cloud Comput 12(1):1–12
Li X, Liu Y, Kang R, **ao L (2017) Service reliability modeling and evaluation of active-active cloud data center based on the IT infrastructure. Microelectron Reliab 75:271–282
Mallayya D, Ramachandran B, Viswanathan S (2015) An automatic web service composition framework using QoS-based web service ranking algorithm. Sci World J 2015:1–14
Mirjalili S, Saremi S, Mirjalili SM, Coelho LDS (2016) Multi-objective grey wolf optimizer: a novel algorithm for multi-criterion optimization. Expert Syst Appl 47:106–119
Moghaddam FF, Rohani MB, Ahmadi M, Khodadadi T, Madadipouya K (2015) Cloud computing: vision, architecture and characteristics. In: 2015 IEEE 6th control and system graduate research colloquium (ICSGRC). IEEE, pp 1–6
Mubarok K, Xu X, Ye X, Zhong RY, Lu Y (2018) Manufacturing service reliability assessment in cloud manufacturing. Procedia CIRP 72:940–946
Nazari A, Thiruvady D, Aleti A, Moser I (2016) A mixed integer linear programming model for reliability optimisation in the component deployment problem. J Oper Res Soc 67(8):1050–1060
Qiu X, Dai Y, **ang Y, **ng L (2015) A hierarchical correlation model for evaluating reliability, performance, and power consumption of a cloud service. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 46(3):401–412
Sadeghiram S, Ma H, Chen G (2023) Multi-objective distributed Web service composition—a link-dominance driven evolutionary approach. Future Gener Comput Syst 143:163–178
Saeedi P, Hosseini Shirvani M (2021) An improved thermodynamic simulated annealing-based approach for resource-skewness-aware and power-efficient virtual machine consolidation in cloud datacenters. Soft Comput 25(7):5233–5260
Seghir F, Khababa G (2023) An improved discrete flower pollination algorithm for fuzzy QoS-aware IoT services composition based on skyline operator. J Supercomput 79:10645–10676
Tarawneh H, Alhadid I, Khwaldeh S, Afaneh S (2022) An intelligent cloud service composition optimization using spider monkey and multistage forward search algorithms. Symmetry 2022(14):82
Wang X, Grabowski J (2015) A reliability assessment framework for cloud applications. Cloud Comput 2015:142
Wang X, Yeo CS, Buyya R, Su J (2011) Optimizing the makespan and reliability for workflow applications with reputation and a look-ahead genetic algorithm. Future Gener Comput Syst 27(8):1124–1134
Yousefipour A, Rahmani AM, Jahanshahi M (2018) Energy and cost-aware virtual machine consolidation in cloud computing. Softw Pract Exp 48(10):1758–1774
Yu H, Yang J, Wang H, Zhang H (2019) Towards predictable performance via two-layer bandwidth allocation in cloud datacenter. J Parallel Distrib Comput 126:34–47
Zhang Q, Li H (2007) MOEA/D: a multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 11(6):712–731
Zhang S, Liu Y, Meng W, Luo Z, Bu J, Yang S, Liang P, Pei D, Xu J, Zhang Y, Chen Y (2018) Prefix: switch failure prediction in datacenter networks. Proc ACM Meas Anal Comput Syst 2(1):1–29
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nezafat Tabalvandani, M.A., Hosseini Shirvani, M. & Motameni, H. Reliability-aware web service composition with cost minimization perspective: a multi-objective particle swarm optimization model in multi-cloud scenarios. Soft Comput 28, 5173–5196 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09201-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09201-w