Abstract
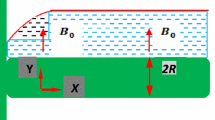
The current study theoretically analyzes the magnetohydrodynamic Williamson fluid flow along with convective boundary conditions over a stretching cylinder. The modified Fourier’s and modified Fick’s law is considered in view of the response of heat and mass transfer. The effect of heat generation/absorption is also considered. With the suitable similarity transformations, the flow equations are converted into dimensionless ordinary differential equations. Runge–Kutta method is used to solve the current problem numerically by adopting shooting scheme. Influences of various physical parameters on the flow fields are shown graphically and skin friction parameter, local Nusselt and Sherwood numbers are presented in tabular form. To verify the accuracy of our numerical results in light of previous results, a comparison table has been generated. The results revealed that the velocity of fluid increases by increasing curvature parameter while decreases for magnetic parameter and Williamson fluid parameter. The temperature and concentration profiles rises due to increase in heat and mass Biot number parameters.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alamri SZ, Khan AA, Azeez M, Ellahi R (2019) Effects of mass transfer on MHD second grade fluid towards stretching cylinder: a novel perspective of Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model. Phys Lett A 383:276–281
Ali L, Wang Y, Ali B, Liu X, Din A, Al Mdallal Q (2021) The function of nanoparticle’s diameter and Darcy–Forchheimer flow over a cylinder with effect of magnetic field and thermal radiation. Case Stud Thermal Eng 28:101392
Al-Mdallal Q, Aman S, Al Fahel S, Dadoa S, Kreishan T (2019) Numerical study of unsteady flow of a fluid over shrinking long cylinder in a porous medium under magnetic force. J Nanofluids 8:1609–1615
Al Sakkaf LY, Al-Mdallal QM, Al Khawaja U (2018) A numerical algorithm for solving higher-order nonlinear BVPs with an application on fluid flow over a shrinking permeable infinite long cylinder. Complexity. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8269541
Bhatti MM, Khalique CM, Bég TA, Bég OA, Kadir A (2020) Numerical study of slip and radiative effects on magnetic Fe3O4-water-based nanofluid flow from a nonlinear stretching sheet in porous media with Soret and Dufour diffusion. Mod Phys Lett B 34:2050026
Cattaneo C (1948) Sulla conduzione del calore. Atti Sem Mat Fis Univ Modena 3:83–101
Christov CI (2009) On frame indifferent formulation of the Maxwell–Cattaneo model of finite-speed heat conduction. Mech Res Commun 36:481–486
Eswaramoorthi S, Bhuvaneswari M, Sivasankaran S, Makinde OD (2018) Heterogeneous and homogeneous reaction analysis on MHD Oldroyd-B fluid with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model and convective heating. Defect Diffus Forum 387:194–206
Fang T, Zhang J, Yao S (2009) Slip MHD viscous flow over a stretching sheet–an exact solution. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 14:3731–3737
Fourier J (1878) The analytical theory of heat. The University Press, Cambridge
Hayat T, Ashraf MB, Shehzad SA, Alsaedi A (2015) Mixed convection flow of Casson nanofluid over a stretching sheet with convectively heated chemical reaction and heat source/sink. J Appl Fluid Mech 8:803–813
Iqbal W, Naeem MN, Jalil M (2019) Numerical analysis of Williamson fluid flow along an exponentially stretching cylinder. AIP Adv 9:055118
Khan I, Malik MY, Salahuddin T, Khan M, Rehman KU (2018) Homogenous–heterogeneous reactions in MHD flow of Powell-Eyring fluid over a stretching sheet with Newtonian heating. Neural Comput Appl 30:3581–3588
Khan AA, Batool R, Kousar N (2021) MHD micropolar fluid over curved stretching surface with modified Fourier law. Sci Iran 28:223–230
Kumar RK, Raju CSK, Mahanthesh B, Gireesha BJ, Varma SVK (2017) Chemical reaction effects on nano Carreau liquid flow past a cone and a wedge with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model. Int J Chem React Eng. https://doi.org/10.1515/ijcre-2017-0108
Lyubimov DV, Perminov AV (2002) Motion of a thin oblique layer of a pseudoplastic fluid. J Eng Phys Thermophys 75:920–924
Metwally ASM, Khalid A, Khan AA, Iskakova K, Gorji MR, Ehab M (2022) Radiation consequences on Sutterby fluid over a curved surface. J Eng Thermophys 31:315–327
Muhammad N, Nadeem S, Mustafa MT (2019) Impact of magnetic dipole on a thermally stratified ferrofluid past a stretchable surface. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part E J Process Mech Eng 233:177–183
Nadeem S, Hussain ST (2014) Heat transfer analysis of Williamson fluid over exponentially stretching surface. Appl Math Mech 35:489–502
Ramzan M, Shaheen N, Chung JD, Kadry S, Chu Y, Howari F (2021) Impact of Newtonian heating and Fourier and Fick’s laws on a magnetohydrodynamic dusty Casson nanofluid flow with variable heat source/sink over a stretching cylinder. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-81747-x
Rehman KU, Mahmood R, Kousar N, Bilal S, Zehra I (2019) On magnetized liquid stream statistics in grooved channel: a finite element visualization. Physica A 535:122463
Rehman KU, Shatanawi W, Al-Mdallal QM (2022) A comparative remark on heat transfer in thermally stratified MHD Jeffrey fluid flow with thermal radiations subject to cylindrical/plane surfaces. Case Stud Thermal Eng 32:101913
Saranya S, Al-Mdallal QM (2020) Non-Newtonian ferrofluid flow over an unsteady contracting cylinder under the influence of aligned magnetic field. Case Stud Thermal Eng 21:100679
Sardar H, Ahmad L, Khan M (2020) Scrutinization of 2D and mixed convection flow of generalized Newtonian fluid with nanoparticles and magnetic field. Can J Phys 98:65–75
Shafiq A, Çolak AB, Sindhu TN, Al-Mdallal QM, Abdeljawad T (2021) Estimation of unsteady hydromagnetic Williamson fluid flow in a radiative surface through numerical and artificial neural network modeling. Sci Rep 11:14509
Shafiq A, Çolak AB, Sindhu TN (2022) Significance of bioconvective flow of MHD thixotropic nanofluid passing through a vertical surface by machine learning algorithm. Chin J Phys 80:427–444
Shafiq A, Çolak AB, Sindhu TN (2023a) Significance of EMHD graphene oxide (GO) water ethylene glycol nanofluid flow in a Darcy–Forchheimer medium by machine learning algorithm. Eur Phys J plus 138:213
Shafiq A, Çolak AB, Sindhu TN (2023b) Construction of neural network based intelligent computing for treatment of Darcy-forchheimer sisko nanofluid flow with rosseland’s radiative process. Heat Transfer Res 54(9):77–98
Shafiq A, Çolak AB, Sindhu TN (2023c) Optimization of the numerical treatment of the Darcy–Forchheimer flow of Ree–Eyring fluid with chemical reaction by using artificial neural networks. Int J Numer Meth Fluids 95:176–192
Shafiq A, Çolak AB, Sindhu TN (2023d) Analyzing activation energy and binary chemical reaction effects with artificial intelligence approach in axisymmetric flow of third grade nanofluid subject to Soret and Dufour effects. Heat Transfer Res 54(3):75–94
Shafiq A, Çolak AB, Sindhu TN (2023e) Modeling of Darcy–Forchheimer magnetohydrodynamic Williamson nanofluid flow towards nonlinear radiative stretching surface using artificial neural network. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 95(9):1502–1520
Siddiqui AM, Haroon T, Hayat T, Asghar S (2001) Unsteady MHD flow of a non-Newtonian fluid due to eccentric rotations of a porous disk and a fluid at infinity. Acta Mech 147:99–109
Williamson RV (1929) The flow of pseudoplastic materials. Ind Eng Chem 21:1108–1111
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest with any person/organization.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, A.A., Mir, S. & Zaman, A. Heat sink/source impact on Williamson liquid flow over a stretching cylinder with modified Fourier and Fick’s law. Soft Comput 28, 4791–4798 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09160-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09160-2