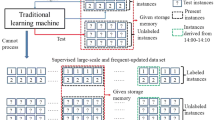
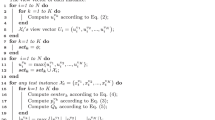Abstract
Multi-view learning improves the performance of existing learning tasks by using complementary information between multiple feature sets. In the latest research, multi-view learning model using privileged information is proposed; specific models are PSVM-2V and MCPK. In these models, views complement each other by acting as privileged information policies; however, a single view contains privileged information that can guide the classifier, and the existing framework does not consider it. In order to use this information to correct multi-view support vector machine classifier, we propose a framework for generating a series of small-scale views based on information hidden in a single view, which extends the original multi-view parallel structure to a hierarchical structure with sub-view mechanism. In this paper, two sub-view learning structures SL-PSVM-2V and SL-MCPK are constructed. The two new models fully exploit the data features in the view. Similarly, they follow the principles of consistency and complementarity. We use the standard quadratic programming solver to solve the new model. In 55 groups of classification experiments, the proposed model improves the classification accuracy by about 1.91% on the original basis. SL-MCPK ranks 1.3846 on average in the accuracy experiment, indicating that they have good classification ability. In addition, the computational time statistics and noise data set experiments are carried out to prove the effectiveness of the proposed method from multiple perspectives.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Ahmed OB, Lecellier F, Paccalin M, et al (2017) Multi-view visual saliency-based MRI classification for alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. In: Seventh International Conference on Image Processing Theory, Tools and Applications, IPTA 2017, Montreal, QC, Canada, November 28 - December 1, 2017. IEEE, pp 1–6, 10.1109/IPTA.2017.8310118
Appice A, Malerba D (2016) A co-training strategy for multiple view clustering in process mining. IEEE Trans Serv Comput 9(6):832–845. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSC.2015.2430327
Beck JR, Shultz EK (1986) The use of relative operating characteristic (roc) curves in test performance evaluation. Arch Pathol Lab Med 110(1):13–20
Chao G, Sun S (2016) Consensus and complementarity based maximum entropy discrimination for multi-view classification. Inf Sci 367–368:296–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2016.06.004
Chao G, Sun J, Lu J et al (2019) Multi-view cluster analysis with incomplete data to understand treatment effects. Inf Sci 494:278–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.04.039
Che Z, Liu B, **ao Y et al (2021) Twin support vector machines with privileged information. Inf Sci 573:141–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2021.05.069
Demšar J (2006) Statistical comparisons of classifiers over multiple data sets. J Mach Learn Res 7:1–30
Eidenberger H (2004) Statistical analysis of content-based mpeg-7 descriptors for image retrieval. Multimed Syst 10(2):84–97
Farquhar JDR, Hardoon DR, Meng H, et al (2005) Two view learning: Svm-2k, theory and practice. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 18 [Neural Information Processing Systems, NIPS 2005, December 5-8, 2005, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada], pp 355–362, https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2005/hash/46b2644cbdf489fac0e2d192212d206d-Abstract.html
Grant M, Boyd S (2014) Cvx: Matlab software for disciplined convex programming, version 2.1
Guo Y, **ao H, Kan Y et al (2018) Learning using privileged information for hrrp-based radar target recognition. IET Signal Process 12(2):188–197. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-spr.2016.0625
Han L, **g X, Wu F (2018) Multi-view local discrimination and canonical correlation analysis for image classification. Neurocomputing 275:1087–1098
Houthuys L, Langone R, Suykens JAK (2018) Multi-view least squares support vector machines classification. Neurocomputing 282:78–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2017.12.029
Kim D, Seo D, Cho S et al (2019) Multi-co-training for document classification using various document representations: Tf-idf, lda, and doc2vec. Inf Sci 477:15–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2018.10.006
Lapin M, Hein M, Schiele B (2014) Learning using privileged information: SV M+ and weighted SVM. Neural Netw 53:95–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2014.02.002
Li Y, Wang Y, Zhou J et al (2018) Robust transductive support vector machine for multi-view classification. J Circuits Syst Comput 27(12):1850,185:1-1850,185:22. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218126618501852
Li Y, Sun H, Yan W et al (2021) R-CTSVM+: robust capped \(\text{ l}_{1}\)-norm twin support vector machine with privileged information. Inf Sci 574:12–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2021.06.003
Liang L, Cherkassky V (2007) Learning using structured data: Application to fmri data analysis. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, IJCNN 2007, Celebrating 20 years of neural networks, Orlando, Florida, USA, August 12-17, 2007. IEEE, pp 495–499, https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN.2007.4371006
Niu L, Wu J (2012) Nonlinear L-1 support vector machines for learning using privileged information. In: Vreeken J, Ling C, Zaki MJ, et al (eds) 12th IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops, ICDM Workshops, Brussels, Belgium, December 10, 2012. IEEE Computer Society, pp 495–499, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDMW.2012.79
Sinoara RA, Sundermann CV, Marcacini RM, et al (2014) Named entities as privileged information for hierarchical text clustering. In: Desai BC, Almeida AM, Bernardino J, et al (eds) 18th International Database Engineering & Applications Symposium, IDEAS 2014, Porto, Portugal, July 7-9, 2014. ACM, pp 57–66, https://doi.org/10.1145/2628194.2628225
Sun S, Chao G (2013) Multi-view maximum entropy discrimination. In: Rossi F (ed) IJCAI 2013, Proceedings of the 23rd International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Bei**g, China, August 3-9, 2013. IJCAI/AAAI, pp 1706–1712, http://www.aaai.org/ocs/index.php/IJCAI/IJCAI13/paper/view/6271
Sun S, **e X, Yang M (2015) Multiview uncorrelated discriminant analysis. IEEE Trans Cyber 46(12):3272–3284
Sun Y, Li L, Zheng L et al (2019) Image classification base on PCA of multi-view deep representation. J Vis Commun Image Represent 62:253–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2019.05.016
Tang J, Tian Y, Liu X et al (2018) Improved multi-view privileged support vector machine. Neural Netw 106:96–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2018.06.017
Tang J, Tian Y, Zhang P et al (2018) Multiview privileged support vector machines. IEEE Trans Neural Networks Learn Syst 29(8):3463–3477. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2728139
Tang J, Tian Y, Liu D et al (2019) Coupling privileged kernel method for multi-view learning. Inf Sci 481:110–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2018.12.058
Vapnik V, Vashist A, Pavlovitch N (2007) Learning using hidden information: Master-class learning. In: Fogelman-Soulié F, Perrotta D, Piskorski J, et al (eds) Mining Massive Data Sets for Security - Advances in Data Mining, Search, Social Networks and Text Mining, and their Applications to Security, Proceedings of the NATO Advanced Study Institute on Mining Massive Data Sets for Security, Gazzada (Varese), Italy, 10-21 September 2007, NATO Science for Peace and Security Series - D: Information and Communication Security, vol 19. IOS Press, pp 3–14, https://doi.org/10.3233/978-1-58603-898-4-3
Wilcoxon F (1992) Individual comparisons by ranking methods. In: Breakthroughs in statistics. Springer, pp 196–202
**e X (2018) Regularized multi-view least squares twin support vector machines. Appl Intell 48(9):3108–3115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-017-1129-3
Xu W, Liu W, Chi H et al (2019) Self-paced learning with privileged information. Neurocomputing 362:147–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.06.072
Yan Y, Nie F, Li W et al (2016) Image classification by cross-media active learning with privileged information. IEEE Trans Multim 18(12):2494–2502. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2016.2602938
Zhang C, Cheng J, Tian Q (2020) Multi-view image classification with visual, semantic and view consistency. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:617–627. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2019.2934576
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Tian** “Project + Team” Key Training Project under Grant No. XC202022 and Tian** Research Innovation Project for Postgraduate Students under Grant No. 2021YJSS095.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Qi Hao, Wenguang Zheng and Yingyuan **ao. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Qi Hao and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human participants or animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, Q., Zheng, W., **ao, Y. et al. Multi-view support vector machines with sub-view learning. Soft Comput 27, 6241–6259 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-07884-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-07884-9