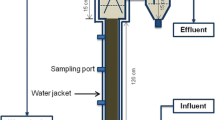
Abstract
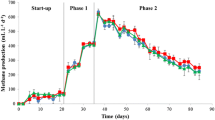
Molasses wastewater contains high levels of organic compounds, cations, and anions, causing operational problems for anaerobic biological treatment. In this study, an upflow anaerobic filter (UAF) reactor was employed to establish a high organic loading treatment system for molasses wastewater and further investigated the microbial community dynamics in response to this stressful operation. The biogas production increased with an increase in total organic carbon (TOC) loading rate from 1.0 to 14 g/L/day, and then it decreased with further TOC loading rate addition until 16 g/L/day. The UAF reactor achieved a maximum biogas production of 6800 mL/L/day with a TOC removal efficiency of 66.5% at a TOC loading rate of 14 g/L/day. Further microbial analyses revealed that both the bacterial and archaeal communities developed multiple strategies to maintain stable operation of the reactor at high organic loading (e.g., Proteiniphilum and Defluviitoga maintained high abundances throughout the operation; Tissierella temporarily dominated the bacterial community at TOC loading rates of 8.0 to 14 g/L/day; and multi-trophic Methanosarcina shifted as the dominant methanogen at the TOC loading rates of 8.0 to 16 g/L/day). This study presents insights into a high organic loading molasses wastewater treatment system and the microbial flexibility in methane fermentation in response to process disturbances.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christofoletti CA, Escher JP, Correia JE, Marinho JFU, Fontanetti CS (2013) Sugarcane vinasse: environmental implications of its use. Waste Manage 33(12):2752–2761
Meng X, Yuan X, Ren J, Wang X, Cui Z (2017) Methane production and characteristics of the microbial community in a two-stage fixed-bed anaerobic reactor using molasses. Biores Technol 241:1050–1059
Satyawali Y, Balakrishnan M (2008) Wastewater treatment in molasses-based alcohol distilleries for COD and color removal: A review. J Environ Manage 86(3):481–497
Yan X, Bilad MR, Gerards R, Vriens L, Piasecka A, Vankelecom I (2012) Comparison of MBR performance and membrane cleaning in a single-stage activated sludge system and a two-stage anaerobic/aerobic (A/A) system for treating synthetic molasses wastewater. J Membr Sci 394:49–56
Onodera T, Sase S, Choeisai P, Yoochatchaval W, Sumino H, Yamaguchi T, Ebie Y, Xu K, Tomioka N, Mizuochi M, Syutsubo K (2013) Development of a treatment system for molasses wastewater: The effects of cation inhibition on the anaerobic degradation process. Bioresoruce Technology 131:295–320
Syutsubo K, Onodera T, Choeisai P, Khodphuvieng J, Prammanee P, Yoochatchaval W, Kaewpradit W, Kubota K (2013) Development of appropriate technology for treatment of molasses-based wastewater. J Environ Sci Health Part A Toxic/Hazard Subst Environ Eng 48:1114–1121
Boopathy R, Tilche A (1991) Anaerobic digestion of high-strength molasses wastewater using a hybrid anaerobic baffled reactor. Water Res 25(7):785–790
Kuroda K, Chosei T, Nakahara N, Hatamoto M, Wakabayashi T, Kawai T, Araki N, Syutsubo K, Yamaguchi T (2015) High organic loading treatment for industrial molasses wastewater and microbial community shifts corresponding to system development. Biores Technol 196:225–234
De Vrieze J, Coma M, Debeuckelaere M, Van der Meeren P, Rabaey K (2016) High salinity in molasses wastewaters shifts anaerobic digestion to carboxylate production. Water Res 98:293–301
Yun J, Lee SD, Cho KS (2016) Biomethane production and microbial community response according to influent concentration of molasses wastewater in a UASB reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(10):4675–4683
Van Lier JB, Van der Zee FP, Frijters CTMJ, Ersahin ME (2015) Celebrating 40 years anaerobic sludge bed reactors for industrial wastewater treatment. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology 14(4):681–702
Chen YT, Yu N, Sun ZY, Gou M, **a ZY, Tang YQ, Kida K (2020) Acclimation improves methane production from molasses wastewater with high salinity in an upflow anaerobic filter reactor: Performance and microbial community dynamics. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 191(1):397–411
Alonso RM, Pérez García M, Solera Del Río R (2014) Performance of upflow anaerobic fixed bed reactor of the treatment of sugar beet pulp lixiviation in a thermophilic range. Bioresoruce Technology 154:305–312
Sun ZY, Tang YQ, Morimura S, Kida K (2013) Reduction in environmental impact of sulfuric acid hydrolysis of bamboo for production of fuel ethanol. Biores Technol 128:87–93
Nabi M, Liang J, Zhang P, Wu Y, Fu C, Wang S, Ye J, Gao D, Shah FA, Dai J (2021) Anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge pretreated by high pressure homogenization using expanded granular sludge blanket reactor: Feasibility, operation optimization and microbial community. J Environ Chem Eng 9(1):104720
Allison SD, Martiny JB (2008) Resistance, resilience, and redundancy in microbial communities. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:11512–11519
Werner JJ, Knights D, Garcia ML, Scalfone NB, Smith S, Yarasheski K, Cummings TA, Beers AR, Knight R, Angenent LT (2011) Bacterial community structures are unique and resilient in full-scale bioenergy systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108(10):4158–4163
Niu Q, Takemura Y, Kubota K, Li YY (2015) Comparing mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic digestion of chicken manure: Microbial community dynamics and process resilience. Waste Manage 43:114–122
De Vrieze J, Christiaens ME, Walraedt D, Devooght A, Ijaz UZ, Boon N (2017) Microbial community redundancy in anaerobic digestion drives process recovery after salinity exposure. Water Res 111:109–117
Goberna M, Gadermaier M, Franke-Whittle I, García C, Wett B, Insam H (2015) Start-up strategies in manure-fed biogas reactors: Process parameters and methanogenic communities. Biomass Bioenergy 75:46–56
Walter A, Probst M, Hinterberger S, Müller H, Insam H (2016) Biotic and abiotic dynamics of a high solid-state anaerobic digestion box-type container system. Waste Manage 49:26–35
Tokuda M, Ohta N, Morimura S, Kida K (1998) Methane fermentation of pot ale from a whisky distillery after enzymatic or microbial treatment. J Ferment Bioeng 85(5):495–501
Sun ZY, Yamaji S, Cheng QS, Yang L, Tang YQ, Kida K (2014) Simultaneous decrease in ammonia and hydrogen sulfide inhibition during the thermophilic anaerobic digestion of protein-rich stillage by biogas recirculation and air supply at 60 °C. Process Biochem 49(12):2214–2219
Griffiths RI, Whiteley AS, O’Donnell AG, Bailey MJ (2000) Rapid method for coextraction of DNA and RNA from natural environments for analysis of ribosomal DNA-and rRNA-based microbial community composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(12):5488–5491
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D, Lozupone CA, Turnbaugh PJ, Fierer N, Knight R (2011) Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108(1):4516–4522
Tamaki H, Wright CL, Li X, Lin Q, Hwang C, Wang S, Thimmapuram J, Kamagata Y, Liu WT (2011) Analysis of 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing options on the Roche/454 next-generation titanium sequencing platform. PLoS ONE 6(9):e25263
Yang Z, Sun H, Liu Y, Liu C, Zhang R, Liu G, Wang W (2019) Comparison of anaerobic methane fermentation performance and ammonia resistance with different inoculum configurations. Energy Fuels 33(9):8711–8720
Sasaki D, Hori T, Haruta S, Ueno Y, Ishii M, Igarashi Y (2011) Methanogenic pathway and community structure in a thermophilic anaerobic digestion process of organic solid waste. J Biosci Bioeng 111(1):41–46
De Vrieze J, Hennebel T, Boon N, Verstraete W (2012) Methanosarcina: The rediscovered methanogen for heavy duty biomethanation. Bioresource of Technology 112:1–9
Kaloi GM, Memon M, Memon KS, Tunio S (2015) Integrated use of spentwash and mineral fertilizers on germination and initial growth of sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.). Soil & Environment 34(1):1–8
Selvamurugan M, Doraisamy P, Maheswari M (2011) Effect of biomethanated distillery spentwash and pressmud biocompost on microbial and enzyme dynamics in sugarcane grown soil. J Biol Sci 11(6):417–422
Saha S, Basak B, Hwang JH, Salama ES, Chatterjee PK, Jeon BH (2020) Microbial symbiosis: a network towards biomethanation. Trends Microbiol 28(12):968–984
Maus I, Klocke M, Derenkó J, Stolze Y, Beckstette M, Jost C, Wibberg D, Blom J, Henke C, Willenbücher K, Rumming M, Rademacher A, Pühler A, Sczyrba A, Schlüter A (2020) Impact of process temperature and organic loading rate on cellulolytic/hydrolytic biofilm microbiomes during biomethanation of ryegrass silage revealed by genome-centered metagenomics and metatranscriptomics. Environmental Microbiome 15:1–21
Westerholm M, Liu T, Schnürer A (2020) Comparative study of industrial-scale high-solid biogas production from food waste: Process operation and microbiology. Biores Technol 304:122981
Chen S, Dong X (2005) Proteiniphilum acetatigenes gen. nov., sp. Nov., from a UASB reactor treating brewery wastewater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55(6):2257–2261
Guo X, Wang C, Sun F, Zhu W, Wu W (2014) A comparison of microbial characteristics between the thermophilic and mesophilic anaerobic digesters exposed to elevated food waste loadings. Biores Technol 152:420–428
Jiang M, Qiao W, Wang Y, Zou T, Lin M, Dong R (2022) Balancing acidogenesis and methanogenesis metabolism in thermophilic anaerobic digestion of food waste under a high loading rate. Sci Total Environ 824:153867
Lee J, Shin SG, Han G, Koo T, Hwang S (2017) Bacteria and archaea communities in full-scale thermophilic and mesophilic anaerobic digesters treating food wastewater: Key process parameters and microbial indicators of process instability. Biores Technol 245:689–697
Wu Z, Nguyen D, Lam TY, Zhuang H, Shrestha S, Raskin L, Khanal SK, Lee PH (2021) Synergistic association between cytochrome bd-encoded Proteiniphilum and reactive oxygen species (ROS)-scavenging methanogens in microaerobic-anaerobic digestion of lignocellulosic biomass. Water Res 190:116721
Hania WB, Godbane R, Postec A, Hamdi M, Ollivier B, Fardeau ML (2012) Defluviitoga tunisiensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a thermophilic bacterium isolated from a mesothermic and anaerobic whey digester. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:1377–1382
Maus I, Cibis KG, Bremges A, Stolze Y, Wibberg D, Tomazetto G, Blom J, Sczyrba A, König H, Pühler A (2016) Genomic characterization of Defluviitoga tunisiensis L3, a key hydrolytic bacterium in a thermophilic biogas plant and its abundance as determined by metagenome fragment recruitment. Jornal of Biotechnology 232:50–60
Zhuravleva EA, Shekhurdina SV, Kotova IB, Loiko NG, Popova NM, Kryukov E, Kovalev DA, Litti YV (2022) Effects of various materials used to promote the direct interspecies electron transfer on anaerobic digestion of low-concentration swine manure. Sci Total Environ 839:156073
Ao T, **e Z, Zhou P, Liu X, Wan L, Li D (2021) Comparison of microbial community structures between mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic digestion of vegetable waste. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 44:1201–1214
Alauzet C, Marchandin H, Courtin P, Mory F, Lemée L, Pons JL, Chapot-Chartier MP, Lozniewski A, Jumas-Bilak E (2014) Multilocus analysis reveals diversity in the genus Tissierella: description of Tissierella carlieri sp. Nov. in the new class Tissierellia classis nov. Syst Appl Microbiol 37(1):23–34
Nolla-Ardèvol V, Peces M, Strous M, Tegetmeyer HE (2015) Metagenome from a Spirulina digesting biogas reactor: analysis via binning of contigs and classification of short reads. BMC Microbiol 15(1):1–16
Chen S, Dong B, Dai X, Wang H, Li N, Yang D (2019) Effects of thermal hydrolysis on the metabolism of amino acids in sewage sludge in anaerobic digestion. Waste Manage 88:309–318
Merlino G, Rizzi A, Schievano A, Tenca A, Scaglia B, Oberti R, Adani F, Daffonchio D (2013) Microbial community structure and dynamics in two-stage vs single-stage thermophilic anaerobic digestion of mixed swine slurry and market bio-waste. Water Res 47(6):1983–1995
Mosbæk F, Kjeldal H, Mulat DG, Albertsen M, Ward AJ, Feilberg A, Nielsen JL (2016) Identification of syntrophic acetate-oxidizing bacteria in anaerobic digesters by combined protein-based stable isotope probing and metagenomics. ISME J 10(10):2405–2418
Zheng D, Wang H-Z, Gou M, Nobu MK, Narihiro T, Hu B, Nie Y, Tang YQ (2019) Identification of novel potential acetate-oxidizing bacteria in thermophilic methanogenic chemostats by DNA stable isotope probing. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103(20):8631–8645
Sun L, Müller B, Westerholm M, Schnürer A (2014) Syntrophic acetate oxidation in industrial CSTR biogas digesters. J Biotechnol 171:39–44
Fotidis IA, Karakashev D, Kotsopoulos TA, Martzopoulos GG, Angelidaki I (2013) Effect of ammonium and acetate on methanogenic pathway and methanogenic community composition. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 83(1):38–48
Karakashev D, Batstone DJ, Trably E, Angelidaki I (2006) Acetate oxidation is the dominant methanogenic pathway from acetate in the absence of Methanosaetaceae. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(7):5138–5141
Lü F, Hao L, Guan D, Qi Y, Shao L, He P (2013) Synergetic stress of acids and ammonium on the shift in the methanogenic pathways during thermophilic anaerobic digestion of organics. Water Res 47(7):2297–2306
Dolfing J (2014) Thermodynamic constraints on syntrophic acetate oxidation. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(4):1539–1541
Noll M, Klose M, Conrad R (2010) Effect of temperature change on the composition of the bacterial and archaeal community potentially involved in the turnover of acetate and propionate in methanogenic rice field soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 73(2):215–225
Yirong C, Heaven S, Banks C (2015) Effect of a trace element addition strategy on volatile fatty acid accumulation in thermophilic anaerobic digestion of food waste. Waste and Biomass Valorization 6:1–12
Hu Y, Kobayashi T, Zhen G, Shi C, Xu KQ (2018) Effects of lipid concentration on thermophilic anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and grease waste in a siphon-driven self-agitated anaerobic reactor. Biotechnology Reports 19:e00269
Yang Z, Wang W, He Y, Zhang R, Liu G (2018) Effect of ammonia on methane production, methanogenesis pathway, microbial community and reactor performance under mesophilic and thermophilic conditions. Renewable Energy 125:915–925
Werner JJ, Garcia ML, Perkins SD, Yarasheski KE, Smith SR, Muegge BD, Stadermann FJ, DeRito CM, Floss C, Madsen EL (2014) Microbial community dynamics and stability during an ammonia-induced shift to syntrophic acetate oxidation. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(11):3375–3383
Dyksma S, Jansen L, Gallert C (2020) Syntrophic acetate oxidation replaces acetoclastic methanogenesis during thermophilic digestion of biowaste. Microbiome 8(1):105
Pan X, Zhao L, Li C, Angelidaki I, Lv N, Ning J, Cai G, Zhu G (2021) Deep insights into the network of acetate metabolism in anaerobic digestion: focusing on syntrophic acetate oxidation and homoacetogenesis. Water Res 190:116774
Goberna M, Insam H, Franke-Whittle I (2009) Effect of biowaste sludge maturation on the diversity of thermophilic bacteria and archaea in an anaerobic reactor. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(8):2566–2572
Maus I, Koeck DE, Cibis KG, Hahnke S, Kim YS, Langer T, Kreubel J, Erhard M, Bremges A, Off S, Stolze Y, Jaenicke S, Goesmann A, Sczyrba A, Scherer P, König M, Schwarz WH, Zverlov VV, Liebl W, Pühler A, Schlüter A, Klocke M (2016) Unraveling the microbiome of a thermophilic biogas plant by metagenome and metatranscriptome analysis complemented by characterization of bacterial and archaeal isolates. Biotechnology of Biofuels 9(1):1–28
Koeck DE, Ludwig W, Wanner G, Zverlov VV, Liebl W, Schwarz WH (2015) Herbinix hemicellulosilytica gen. nov., sp. Nov., a thermophilic cellulose-degrading bacterium isolated from a thermophilic biogas reactor. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65(8):2365–2371
Chojnacka A, Szczęsny P, Błaszczyk MK, Zielenkiewicz U, Detman A, Salamon A, Sikora A (2015) Noteworthy facts about a methane-producing microbial community processing acidic effluent from sugar beet molasses fermentation. PLoS ONE 10(5):e0128008
Conklin A, Stensel HD, Ferguson J (2006) Growth kinetics and competition between Methanosarcina and Methanosaeta in mesophilic anaerobic digestion. Water Environment Researchi 78(5):486–496
Westerholm M, Müller B, Arthurson V, Schnürer A (2011) Changes in the acetogenic population in a mesophilic anaerobic digester in response to increasing ammonia concentration. Microbes Environ 26(4):347–353
Onodera T, Sase S, Choeisai P, Yoochatchaval W, Sumino H, Yamaguchi T, Ebie Y, Xu K, Tomioka N, Syutsubo K (2011) High-rate treatment of molasses wastewater by combination of an acidification reactor and a USSB reactor. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A 46(14):1721–1731
van Haandel A, De Vrieze J, Verstraete W, dos Santos VS (2014) Methanosaeta dominate acetoclastic methanogenesis during high-rate methane production in anaerobic reactors treating distillery wastewaters. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 89(11):1751–1759
Demirel B, Scherer P (2008) The roles of acetotrophic and hydrogenotrophic methanogens during anaerobic conversion of biomass to methane: A review. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology 7:173–190
Chen YT, Zeng Y, Wang HZ, Zheng D, Kamagata Y, Narihiro T, Nobu MK, Tang YQ (2020) Different interspecies electron transfer patterns during mesophilic and thermophilic syntrophic propionate degradation in chemostats. Microb Ecol 80:120–132
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key Program for International S&T Cooperation Projects of China (2022YFE0108500), and Sichuan Science and Technology Program (23NSFSC1201).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Z., He, J., Yu, N. et al. Biomethane production and microbial strategies corresponding to high organic loading treatment for molasses wastewater in an upflow anaerobic filter reactor. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 46, 1033–1043 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-023-02882-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-023-02882-5