Abstract
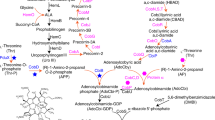
Vitamin B12 is a crucial fine chemical that is widely used in the pharmaceutical, food and chemical industries, and its production solely dependents on microbial fermentation. We previously constructed an artificial vitamin B12 biosynthesis pathway in Escherichia coli, but the yield of the engineered strains was low. Here, we removed metabolic bottlenecks of the vitamin B12 biosynthesis pathway in engineered E. coli strains. After screening cobB genes from different sources, optimizing the expression of cobN and customizing the ribosome binding sites of cobS and cobT, the vitamin B12 yield increased to 152.29 μg/g dry cell weight (DCW). Optimization of the downstream module, which converts co(II)byrinic acid a,c-diamide into adenosylcobinamide phosphate, elevated the vitamin B12 yield to 249.04 μg/g DCW. A comparison of a variety of equivalent components indicated that glucose and corn steep liquor are optimal carbon and nitrogen sources, respectively. Finally, an orthogonal array design was applied to determine the optimal concentrations of glucose and nitrogen sources including corn steep liquor and yeast extract, through which a vitamin B12 yield of 530.29 μg/g DCW was obtained. The metabolic modifications and optimization of fermentation conditions achieved in this study offer a basis for further improving vitamin B12 production in E. coli and will hopefully accelerate its industrial application.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Martens JH, Barg H, Warren MJ, Jahn D (2002) Microbial production of vitamin B12. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58(3):275–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-001-0902-7
Fang H, Kang J, Zhang D (2017) Microbial production of vitamin B12: a review and future perspectives. Microb Cell Fact 16(1):15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-017-0631-y
Martin VJJ, Pitera DJ, Withers ST, Newman JD, Keasling JD (2003) Engineering a mevalonate pathway in Escherichia coli for production of terpenoids. Nat Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt833
Choi SY, Park SJ, Kim WJ, Yang JE, Lee H, Shin J, Lee SY (2016) One-step fermentative production of poly(lactate-co-glycolate) from carbohydrates in Escherichia coli. Nat Biotechnol 34(4):435–440. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3485
Liu Y, Liu Q, Krivoruchko A, Khoomrung S, Nielsen J (2019) Engineering yeast phospholipid metabolism for de novo oleoylethanolamide production. Nat Chem Biol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-019-0431-2
Fang H, Li D, Kang J, Jiang P, Sun J, Zhang D (2018) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for de novo biosynthesis of vitamin B12. Nat Commun 9(1):4917. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07412-6
Park SY, Yang D, Ha SH, Lee SY (2018) Metabolic engineering of microorganisms for the production of natural compounds. Adv Biosyst 2(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1002/adbi.201700190
Yang D, Park SY, Park YS, Eun H, Lee SY (2020) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for natural product biosynthesis. Trends Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2019.11.007
Keasling JD (2008) Synthetic biology for synthetic chemistry. ACS Chem Biol 3(1):64–76. https://doi.org/10.1021/cb7002434
Lee SY, Kim HU (2015) Systems strategies for develo** industrial microbial strains. Nat Biotechnol 33(10):1061–1072. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3365
Kim B, Du J, Eriksen DT, Zhao H (2013) Combinatorial design of a highly efficient xylose-utilizing pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the production of cellulosic biofuels. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(3):931–941. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02736-12
Nybo SE, Saunders J, McCormick SP (2017) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for production of valerenadiene. J Biotechnol 262:60–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.10.004
Ling M, Liu Y, Li J, Shin HD, Chen J, Du G, Liu L (2017) Combinatorial promoter engineering of glucokinase and phosphoglucoisomerase for improved N-acetylglucosamine production in Bacillus subtilis. Biores Technol 245(Pt A):1093–1102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.063
Shukal S, Chen X, Zhang C (2019) Systematic engineering for high-yield production of viridiflorol and amorphadiene in auxotrophic Escherichia coli. Metab Eng 55:170–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2019.07.007
Yang P, Wang J, Pang Q, Zhang F, Wang J, Wang Q, Qi Q (2017) Pathway optimization and key enzyme evolution of N-acetylneuraminate biosynthesis using an in vivo aptazyme-based biosensor. Metab Eng 43(Pt A):21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2017.08.001
Yunus IS, Palma A, Trudeau DL, Tawfik DS, Jones PR (2020) Methanol-free biosynthesis of fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Metab Eng 57:217–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2019.12.001
Zhao D, Yuan S, **ong B, Sun H, Ye L, Li J, Zhang X, Bi C (2016) Development of a fast and easy method for Escherichia coli genome editing with CRISPR/Cas9. Microb Cell Fact 15(1):205. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-016-0605-5
Gibson DG, Young L, Chuang RY, Venter JC, Hutchison CA 3rd, Smith HO (2009) Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nat Methods 6(5):343–345. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1318
Qi D, Scholthof K-BG (2008) A one-step PCR-based method for rapid and efficient site-directed fragment deletion, insertion, and substitution mutagenesis. J Virol Methods 149(1):85–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2008.01.002
Wu X, Leung DYC (2011) Optimization of biodiesel production from camelina oil using orthogonal experiment. Appl Energy 88(11):3615–3624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.04.041
Debussche L, Couder M, Thibaut D, Cameron B, Crouzet J, Blanche F (1992) Assay, purification, and characterization of cobaltochelatase, a unique complex enzyme catalysing cobalt insertion in hydrogenobyrinic acid a, c-diamide during coenzyme B12 biosynthesis in Pseudomonas denitrificans. J Bacteriol 174(22):7445–7451
Lundqvist J, Elmlund D, Heldt D, Deery E, Soderberg CA, Hansson M, Warren M, Al-Karadaghi S (2009) The AAA(+) motor complex of subunits CobS and CobT of cobaltochelatase visualized by single particle electron microscopy. J Struct Biol 167(3):227–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2009.06.013
Heldt D, Lawrence AD, Lindenmeyer M, Deery E, Heathcote P, Rigby SE, Warren MJ (2005) Aerobic synthesis of vitamin B12: ring contraction and cobalt chelation. Biochem Soc Trans 33(4):815–819. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst0330815
Roy V, Roth R, Berge M, Chitta R, Vajrala S, Kuntumalla S (2017) A bicistronic vector with destabilized mRNA secondary structure yields scalable higher titer expression of human neurturin in E. coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 114(8):1753–1761. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26299
Wu G, Yan Q, Jones JA, Tang YJ, Fong SS, Koffas MAG (2016) Metabolic burden: cornerstones in synthetic biology and metabolic engineering applications. Trends Biotechnol 34(8):652–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.02.010
Ow DS-W, Nissom PM, Philp R, Oh SK-W, Yap MG-S (2006) Global transcriptional analysis of metabolic burden due to plasmid maintenance in Escherichia coli DH5α during batch fermentation. Enzyme Microbial Technol 39(3):391–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.11.048
Hedayati R, Hosseini M, Najafpour GD (2020) Optimization of semi-anaerobic vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) production from rice bran oil using Propionibacterium freudenreichii PTCC1674. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101444
Jalilian N, Najafpour GD, Khajouei M (2019) Enhanced vitamin B12 production using Chlorella vulgaris. Int J Eng Trans A 32(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.5829/ije.2019.32.01a.01
**a W, Chen W, Peng WF, Li KT (2015) Industrial vitamin B12 production by Pseudomonas denitrificans using maltose syrup and corn steep liquor as the cost-effective fermentation substrates. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38(6):1065–1073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1348-5
Yu AQ, Zhu JC, Zhang B, **ng LJ, Li M (2011) Effects of different carbon sources on the growth, fatty acids production, and expression of three desaturase genes of Mortierella alpina ATCC 16266. Curr Microbiol 62(5):1617–1622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-011-9902-8
Bhattacharya SK, Dubey AK (1997) High-level expression of a heterologous gene in Escherichia coli in response to carbon-nitrogen source and C/N ratio in a batch bioreactor. Biotechnol Prog 13(2):151–155. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp970007t
Shariati S, Zare D, Mirdamadi S (2019) Screening of carbon and nitrogen sources using mixture analysis designs for carotenoid production by Blakeslea trispora. Food Sci Biotechnol 28(2):469–479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0484-0
Wang X, **a K, Yang X, Tang C (2019) Growth strategy of microbes on mixed carbon sources. Nat Commun 10(1):1279. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09261-3
Perrin E, Giovannini M, Di Patti F, Cardazzo B, Carraro L, Fagorzi C, Ghini V, Turano P, Fani R, Fondi M (2019) Diauxie and co-utilization are not exclusive during growth in nutritionally complex environments. 752832
Ruiz B, Chavez A, Forero A, Garcia-Huante Y, Romero A, Sanchez M, Rocha D, Sanchez B, Rodriguez-Sanoja R, Sanchez S, Langley E (2010) Production of microbial secondary metabolites: regulation by the carbon source. Crit Rev Microbiol 36(2):146–167. https://doi.org/10.3109/10408410903489576
Wang P, Zhang Z, Jiao Y, Liu S, Wang Y (2015) Improved propionic acid and 5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole control strategy for vitamin B12 fermentation by Propionibacterium freudenreichii. J Biotechnol 193:123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.11.019
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFA0900300), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31900052, 31470787), Department of Science and Technology of Jilin Province (20190902014TC), and the Science and Technology Service Network (STS) Initiative of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) (KFJ-STS-ZDTP-065).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors indicate that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Fang, H., Gai, Y. et al. Metabolic engineering and optimization of the fermentation medium for vitamin B12 production in Escherichia coli. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 43, 1735–1745 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-020-02355-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-020-02355-z