Abstract
Introduction
A critical step to ameliorate diagnosis and extend patient survival is Benign-malignant Pulmonary Nodule (PN) classification at earlier detection. On account of the noise of Computed Tomography (CT) images, the prevailing Lung Nodule (LN) detection techniques exhibit broad variation in accurate prediction.
Methods
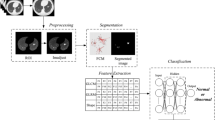
Thus, a novel Nodule Detection along with Classification algorithm for early diagnosis of Lung Cancer (LC) has been proposed. Initially, employing the Adaptive Mode Ostu Binarization (AMOB) technique, the Lung Volumes (LVs) isextortedas of the image together with the extracted lung regions is pre-processed. Then, detection of LNs takes place, and utilizing Geodesic Fuzzy C-Means Clustering (GFCM) Segmentation Algorithm, it is segmented.Next, the vital features are extracted, and the Nodules are classified by utilizing Logarithmic Layer Xception Neural Network (LLXcepNN) Classifier grounded on the extracted feature.
Results
The nodules are classified as Benign Nodules (BN) and Malignant Nodules (MN) by the proposed classifier. Lastly, the Lung CT images are scrutinized.
Discussion
Thus, when weighed against the prevailing techniques, the proposed systems’ acquired outcomes exhibit that the rate of accuracy of classification is enhanced.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Asuntha A, Srinivasan A (2020) Deep learning for lung cancer detection and classification. Multimedia Tools Appl 79(9–10):7731–7762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-08394-3
Bhatia S, Sinha Y, Goel L (2019) Lung cancer detection a deep learning approach, 1st edn. Springer, Singapore
Cao H, Liu H, Song E, Ma G, **angyang Xu, ** R, Liu T, Hung C-C (2017) Multi-branch ensemble learning architecture based on 3D CNN for false positive reduction in lung nodule detection. IEEE Access 7:67380–67391. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2906116
Cao H, Liu H, Song E, Ma G, **angyang Xu, ** R, Liu T, Hung C-C (2020) Two stage convolutional neural network architecture for lung nodule detection. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 24(7):1–29. https://doi.org/10.1109/jbhi.2019.2963720
Gunaydin O, Gunay M, Sengel O(2019) Comparison of lung cancer detection algorithms. Scientific meeting on electrical-electronics & biomedical engineering and computer science, IEEE, 24-26 April 2019, Istanbul, Turkey. https://doi.org/10.1109/EBBT.2019.8741826
Halder A, Dey D, Sadhu AK (2020) Lung nodule detection from feature engineering to deep learning in thoracic CT images a comprehensive review. J Digit Imaging 33(3):655–677. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-020-00320-6
Harsono IW, Liawatimena S, Cenggoro TW (2020) Lung nodule detection and classification from thorax CT-scan using retinanet with transfer learning. J King Saud Univ Comput Inf Sci 34(3):567–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2020.03.013
Jerald Prasath G, Parimala Geetha K, Mohanalin J, Beena Mol M, Prinza (2019) Enhancement of mammogram by hyper-elastic property of non-rigid images: a histogram modification scheme. J Electr Eng 20(1):459–464
Jha M, Gupta R, Saxena R (2020) A review on non-invasive biosensors for early detection of lung cancer. 6th International conference on signal processing and communication, IEEE, 5–7 March 2020, Noida, India. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSC48311.2020.9182775
Jothilakshmi R, Ramya M, Prajwala G, Ramya Geetha SV (2020) Early lung cancer detection using machine learning and image processing. J Eng Sci 11(7):510–514
Kumar V, Bakariya B (2021) Classification of malignant lung cancer using deep learning. J Med Eng Technol 45(2):85–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/03091902.2020.1853837
Masud M, Muhammad G, Shamim Hossain M, Alhumyani H, Alshamrani SS, Cheikhrouhouand O, Ibrahim S (2020) Light deep model for pulmonary nodule detection from CT scan images for mobile devices. Wirel Commun Mob Comput. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8893494
Meraj T, Hassan A, Zahoor S, Rauf HT, Lali MIU, Ali L, Bukhari SAC (2019) Lungs nodule detection using semantic segmentation and classification with optimal features. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints201909.0139.v1a
Mhaske D, Rajeswari K, Tekade R (2019) Deep learning algorithm for classification and prediction of lung cancer using ct scan images. 5th International conference on computing, communication, control and automation, IEEE, 19–21 September 2019, Pune, India. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCUBEA47591.2019.9128479
Mohamed Shakeel P, Tolba A, Al-Makhadmeh Z, Jaber MM (2019a) Automatic detection of lung cancer from biomedical data set using discrete AdaBoost optimized ensemble learning generalized neural networks. Neural Comput Appl 32(3):777–1790. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-03972-2
Mohamed Shakeel P, Burhanuddin MA, Desa MI (2019b) Lung cancer detection from CT image using improved profuse clustering and deep learning instantaneously trained neural networks. Measurement 145(3):702–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2019.05.027
Nisha Jenipher V, Radhika S (2021) SVM kernel methods with data normalization for lung cancer survivability prediction application. 3rd International conference on intelligent communication technologies and virtual mobile networks, IEEE, 4–6 February 2021, Tirunelveli, India. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICV50876.2021.9388543
Radhika PR, Rakhi AS Nair, Veena G (2019) A comparative study of lung cancer detection using machine learning algorithms. IEEE International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Technologies, IEEE, 20–22 February, Coimbatore, India. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICECCT.2019.8869001
Roointan A, Mir TA, Wani SI, Mati-ur-Rehman KK, Hussain BA, Abrahim S, Savardashtaki A, Gandomani G, Gandomani M, Chinnappan R, Akhtar MH (2018) Early detection of lung cancer biomarkers through biosensor technology a review. J Pharm Biomed Anal 164:93–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2018.10.017
Sungheetha A, Sharma RR (2020) Comparative study statistical approach and deep learning method for automatic segmentation methods for lung CT image segmentation. J Innov Image Process 2(4):187–193. https://doi.org/10.36548/jiip.2020.4.003
Thakur SK, Singh DP, Choudhary J (2020) Lung cancer identification a review on detection and classification. Cancer Metastasis Rev 39(3):989–998. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-020-09901-x
Yang D, Liu Y, Bai C, Wang X, Powell CA (2019a) Epidemiology of lung cancer and lung cancer screening program in China and the United States. Cancer Lett 481:82–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2019.10.009
Yang G, **ao Z, Tang C, Deng Y, Huang H, He Z (2019b) Recent advances in biosensor for detection of lung cancer biomarkers. Biosens Bioelectron 141(1):1–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111416
Zhang G, Yang Z, Gong Li, Shan Jiang Lu, Wang HZ (2020) Classification of lung nodules based on CT images using squeezeandexcitation network and aggregated residual transformations. Radiol Med (torino) 125(4):374–383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-019-01130-9
Acknowledgements
We thank the anonymous referees for their useful suggestions.
Funding
This work has no funding resource.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by VKG, SB. The first draft of the manuscript was written by VKG and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript.All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent of publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gugulothu, V.K., Balaji, S. An automatic classification of pulmonary nodules for lung cancer diagnosis using novel LLXcepNN classifier. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 6049–6057 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04539-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04539-4