Abstract
Purpose
A dozen clinical trials examining a combination of temsirolimus and cetuximab in treating metastatic colon cancer are currently underway. We investigated the role of cancerous inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A (CIP2A) in the synergism between temsirolimus and cetuximab in colon cancer.
Methods
Five colon cancer cell lines were used for in vitro studies. Signal transduction pathways were assessed by immunoblotting. The synergism between studied drugs was analyzed with combination indexes. Gene silencing was performed using small interfering RNAs. The efficacies of temsirolimus and cetuximab were tested in nude mice with colon cancer xenografts. Transcriptional activity was assessed using a reporter assay. The inhibitors leupeptin, chloroquine, and MG132 were used to assess protein degradation. The association between CIP2A, clinicopathological parameters, and survival was examined by immunohistochemical staining using a tumor tissue microarray.
Results
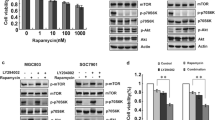
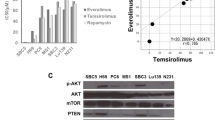
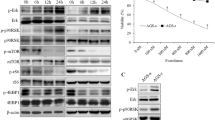
Temsirolimus decreased the resistance of cells to cetuximab by both inhibiting transcription of CIP2A and increasing degradation of CIP2A through the lysosomal-autophagy pathway. The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) protein immunoprecipitated along with CIP2A. Temsirolimus decreased expression of phosphorylated extracellular regulated protein kinase (pErk) and phosphorylated v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene (pAKT) and decreased the interaction of CIP2A and mTOR in cell lines without the K-ras codon 12 mutation. CIP2A was a prognostic marker only in colon cancer patients with weak expression of pErk or pAKT.
Conclusions
Temsirolimus decreases cellular resistance to cetuximab by regulating CIP2A expression in colon cancer cells. Potential biomarkers for CIP2A inhibitors include pErk and pAKT.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bockelman C, Lassus H, Hemmes A, Leminen A, Westermarck J, Haglund C, Butzow R, Ristimaki A (2011) Prognostic role of CIP2A expression in serous ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer 105(7):989–995. doi:10.1038/bjc.2011.346
Bockelman C, Koskensalo S, Hagstrom J, Lundin M, Ristimaki A, Haglund C (2012) CIP2A overexpression is associated with c-Myc expression in colorectal cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 13(5):289–295. doi:10.4161/cbt.18922
Bokemeyer C, Van Cutsem E, Rougier P, Ciardiello F, Heeger S, Schlichting M, Celik I, Kohne CH (2012) Addition of cetuximab to chemotherapy as first-line treatment for KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer: pooled analysis of the CRYSTAL and OPUS randomised clinical trials. Eur J Cancer 48(10):1466–1475. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2012.02.057
Chen W, Arroyo JD, Timmons JC, Possemato R, Hahn WC (2005) Cancer-associated PP2A Aalpha subunits induce functional haploinsufficiency and tumorigenicity. Cancer Res 65(18):8183–8192. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1103
Chen KF, Liu CY, Lin YC, Yu HC, Liu TH, Hou DR, Chen PJ, Cheng AL (2010a) CIP2A mediates effects of bortezomib on phospho-Akt and apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncogene. doi:10.1038/onc.2010.357
Chen XG, Liu F, Song XF, Wang ZH, Dong ZQ, Hu ZQ, Lan RZ, Guan W, Zhou TG, Xu XM, Lei H, Ye ZQ, Peng EJ, Du LH, Zhuang QY (2010b) Rapamycin regulates Akt and ERK phosphorylation through mTORC1 and mTORC2 signaling pathways. Mol Carcinog 49(6):603–610. doi:10.1002/mc.20628
Chou TC, Talalay P (1984) Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul 22:27–55
Coenen EA, Zwaan CM, Meyer C, Marschalek R, Pieters R, van der Veken LT, Beverloo HB, van den Heuvel-Eibrink MM (2010) KIAA1524: a novel MLL translocation partner in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2010.08.017
Come C, Laine A, Chanrion M, Edgren H, Mattila E, Liu X, Jonkers J, Ivaska J, Isola J, Darbon JM, Kallioniemi O, Thezenas S, Westermarck J (2009) CIP2A is associated with human breast cancer aggressivity. Clin Cancer Res 15(16):5092–5100. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-3283
Dong QZ, Wang Y, Dong XJ, Li ZX, Tang ZP, Cui QZ, Wang EH (2010) CIP2A is overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer and correlates with poor prognosis. Ann Surg Oncol. doi:10.1245/s10434-010-1313-8
Fang JY, Richardson BC (2005) The MAPK signalling pathways and colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol 6(5):322–327. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(05)70168-6
Hess G, Herbrecht R, Romaguera J, Verhoef G, Crump M, Gisselbrecht C, Laurell A, Offner F, Strahs A, Berkenblit A, Hanushevsky O, Clancy J, Hewes B, Moore L, Coiffier B (2009) Phase III study to evaluate temsirolimus compared with investigator’s choice therapy for the treatment of relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 27(23):3822–3829. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.20.7977
Hudes G, Carducci M, Tomczak P, Dutcher J, Figlin R, Kapoor A, Staroslawska E, Sosman J, McDermott D, Bodrogi I, Kovacevic Z, Lesovoy V, Schmidt-Wolf IG, Barbarash O, Gokmen E, O’Toole T, Lustgarten S, Moore L, Motzer RJ (2007) Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356(22):2271–2281. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa066838
Hui L, Rodrik V, Pielak RM, Knirr S, Zheng Y, Foster DA (2005) mTOR-dependent suppression of protein phosphatase 2A is critical for phospholipase D survival signals in human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 280(43):35829–35835. doi:10.1074/jbc.M504192200
Junttila MR, Westermarck J (2008) Mechanisms of MYC stabilization in human malignancies. Cell Cycle 7(5):592–596
Junttila MR, Puustinen P, Niemela M, Ahola R, Arnold H, Bottzauw T, Ala-aho R, Nielsen C, Ivaska J, Taya Y, Lu SL, Lin S, Chan EK, Wang XJ, Grenman R, Kast J, Kallunki T, Sears R, Kahari VM, Westermarck J (2007) CIP2A inhibits PP2A in human malignancies. Cell 130(1):51–62. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.04.044
Khanna A, Bockelman C, Hemmes A, Junttila MR, Wiksten JP, Lundin M, Junnila S, Murphy DJ, Evan GI, Haglund C, Westermarck J, Ristimaki A (2009) MYC-dependent regulation and prognostic role of CIP2A in gastric cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 101(11):793–805. doi:10.1093/jnci/djp103
Kroemer G, Marino G, Levine B (2010) Autophagy and the integrated stress response. Mol Cell 40(2):280–293. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.023
Laplante M, Sabatini DM (2012) mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 149(2):274–293. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.017
Li W, Ge Z, Liu C, Liu Z, Bjorkholm M, Jia J, Xu D (2008) CIP2A is overexpressed in gastric cancer and its depletion leads to impaired clonogenicity, senescence, or differentiation of tumor cells. Clin Cancer Res 14(12):3722–3728. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4137
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Abrams SL, Lee JT, Chang F, Bertrand FE, Navolanic PM, Terrian DM, Franklin RA, D’Assoro AB, Salisbury JL, Mazzarino MC, Stivala F, Libra M (2006) Roles of the RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathways in malignant transformation and drug resistance. Adv Enzyme Regul 46:249–279. doi:10.1016/j.advenzreg.2006.01.004
Migliardi G, Sassi F, Torti D, Galimi F, Zanella ER, Buscarino M, Ribero D, Muratore A, Massucco P, Pisacane A, Risio M, Capussotti L, Marsoni S, Di Nicolantonio F, Bardelli A, Comoglio PM, Trusolino L, Bertotti A (2012) Inhibition of MEK and PI3K/mTOR suppresses tumor growth but does not cause tumor regression in patient-derived xenografts of RAS-mutant colorectal carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 18(9):2515–2525. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2683
Peterson RT, Desai BN, Hardwick JS, Schreiber SL (1999) Protein phosphatase 2A interacts with the 70-kDa S6 kinase and is activated by inhibition of FKBP12-rapamycinassociated protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(8):4438–4442
Populo H, Lopes JM, Soares P (2012) The mTOR signalling pathway in human cancer. Int J Mol Sci 13(2):1886–1918. doi:10.3390/ijms13021886
Qin L, Wang Z, Tao L, Wang Y (2010) ER stress negatively regulates AKT/TSC/mTOR pathway to enhance autophagy. Autophagy 6(2):239–247
Saltz LB, Clarke S, Diaz-Rubio E, Scheithauer W, Figer A, Wong R, Koski S, Lichinitser M, Yang TS, Rivera F, Couture F, Sirzen F, Cassidy J (2008) Bevacizumab in combination with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy as first-line therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: a randomized phase III study. J Clin Oncol 26(12):2013–2019. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.14.9930
Teng HW, Huang YC, Lin JK, Chen WS, Lin TC, Jiang JK, Yen CC, Li AF, Wang HW, Chang SC, Lan YT, Lin CC, Wang HS, Yang SH (2012a) BRAF mutation is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal liver metastasectomy. J Surg Oncol 106(2):123–129. doi:10.1002/jso.23063
Teng HW, Yang SH, Lin JK, Chen WS, Lin TC, Jiang JK, Yen CC, Li AF, Chen PC, Lan YT, Lin CC, Hsu YN, Wang HW, Chen KF (2012b) CIP2A is a predictor of poor prognosis in colon cancer. J Gastrointest surg 16(5):1037–1047. doi:10.1007/s11605-012-1828-3
Tseng LM, Liu CY, Chang KC, Chu PY, Shiau CW, Chen KF (2012) CIP2A is a target of bortezomib in human triple negative breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res BCR 14(2):R68. doi:10.1186/bcr3175
Vaarala MH, Vaisanen MR, Ristimaki A (2010) CIP2A expression is increased in prostate cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 29(1):136. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-29-136
Wiegering A, Pfann C, Uthe FW, Otto C, Rycak L, Mader U, Gasser M, Waaga-Gasser AM, Eilers M, Germer CT (2013) CIP2A influences survival in colon cancer and is critical for maintaining Myc expression. PLoS ONE 8(10):e75292. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0075292
Windsor AC, Cohen R, Jiao LR, Stebbing J (2008) Cetuximab in the first-line therapy of metastatic colorectal carcinoma: not so CRYSTAL clear. Future Oncol 4(6):741–744. doi:10.2217/14796694.4.6.741
Zhao D, Liu Z, Ding J, Li W, Sun Y, Yu H, Zhou Y, Zeng J, Chen C, Jia J (2010) Helicobacter pylori CagA upregulation of CIP2A is dependent on the Src and MEK/ERK pathways. J Med Microbiol 59(Pt 3):259–265. doi:10.1099/jmm.0.014704-0
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Division of Experimental Surgery of the Department of Surgery, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, and by the Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan Clinical Oncology Research Foundation, Department of Health, Taiwan (Center of Excellence for Cancer Research at Taipei Veterans General Hospital (102DHA0100184, 101DHA0100369).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, HW., Yang, SH., Huang, GD. et al. Temsirolimus enhances the efficacy of cetuximab in colon cancer through a CIP2A-dependent mechanism. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 140, 561–571 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1596-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1596-4