Abstract
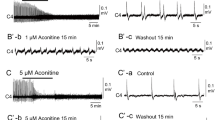
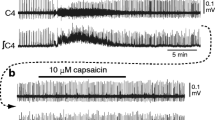
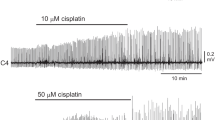
Eugenol is contained in several plants including clove and is used as an analgesic drug. In the peripheral and central nervous systems, this compound modulates neuronal activity through action on voltage-gated ionic channels and/or transient receptor potential channels. However, it is unknown whether eugenol exerts any effects on the respiratory center neurons in the medulla. We examined the effects of eugenol on respiratory rhythm generation in the brainstem-spinal cord preparation from newborn rat (P0-P3). The preparations were superfused by artificial cerebrospinal fluid at 25–26 °C, and inspiratory C4 ventral root activity was monitored. Membrane potentials of respiratory neurons were recorded in the parafacial region of the rostral ventrolateral medulla. Bath application of eugenol (0.5–1 mM) decreased respiratory rhythm accompanied by strong inhibition of the burst activity of pre-inspiratory neurons. After washout, respiratory rhythm partly recovered, but the inspiratory burst duration was extremely shortened, and this continued for more than 60 min after washout. The shortening of C4 inspiratory burst by eugenol was not reversed by capsazepine (TRPV1 antagonist) or HC-030031 (TRPA1 antagonist), whereas the depression was partially blocked by GABAA antagonist bicuculline and glycine antagonist strychnine or GABAB antagonist phaclofen. A spike train of action potentials in respiratory neurons induced by depolarizing current pulse was depressed by application of eugenol. Eugenol decreased the negative slope conductance of pre-inspiratory neurons, suggesting blockade of persistent Na+ current. These results suggest that changes in both membrane excitability and synaptic connections are involved in the shortening of respiratory neuron bursts by eugenol.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballanyi K, Onimaru H, Homma I (1999) Respiratory network function in the isolated brainstem-spinal cord of newborn rats. Prog Neurobiol 59:583–634
Ballanyi K, Ruangkittisakul A, Onimaru H (2009) Opioids prolong and anoxia shortens delay between onset of preinspiratory (pFRG) and inspiratory (preBotC) network bursting in newborn rat brainstems. Pflugers Arch 458:571–587
Ben-Mabrouk F, Tryba AK (2010) Substance P modulation of TRPC3/7 channels improves respiratory rhythm regularity and ICAN-dependent pacemaker activity. Eur J Neurosci 31:1219–1232
Cho JS, Kim TH, Lim JM, Song JH (2008) Effects of eugenol on Na+ currents in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Brain Res 1243:53–62
Chung G, Im ST, Kim YH, Jung SJ, Rhyu MR, Oh SB (2014) Activation of transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 by eugenol. Neuroscience 261:153–160
Chung G, Rhee JN, Jung SJ, Kim JS, Oh SB (2008) Modulation of CaV2.3 calcium channel currents by eugenol. J Dent Res 87:137–141
Crill WE (1996) Persistent sodium current in mammalian central neurons. Annu Rev Physiol 58:349–362
Crowder EA, Saha MS, Pace RW, Zhang H, Prestwich GD, Del Negro CA (2007) Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate regulates inspiratory burst activity in the neonatal mouse preBotzinger complex. J Physiol 582:1047–1058
Del Negro CA, Koshiya N, Butera RJ Jr, Smith JC (2002) Persistent sodium current, membrane properties and bursting behavior of pre-botzinger complex inspiratory neurons in vitro. J Neurophysiol 88:2242–2250
Fernandes ES, Fernandes MA, Keeble JE (2012) The functions of TRPA1 and TRPV1: moving away from sensory nerves. Br J Pharmacol 166:510–521
Gavva NR, Tamir R, Qu Y, Klionsky L, Zhang TJ, Immke D, Wang J, Zhu D, Vanderah TW, Porreca F, Doherty EM, Norman MH, Wild KD, Bannon AW, Louis JC, Treanor JJ (2005) AMG 9810 [(E)-3-(4-t-butylphenyl)-N-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4] dioxin-6-yl)acrylamide], a novel vanilloid receptor 1 (TRPV1) antagonist with antihyperalgesic properties. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 313:474–484
Guenette SA, Beaudry F, Marier JF, Vachon P (2006) Pharmacokinetics and anesthetic activity of eugenol in male Sprague-Dawley rats. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 29:265–270
Huang CW, Chow JC, Tsai JJ, Wu SN (2011) Characterizing the effects of Eugenol on neuronal ionic currents and hyperexcitability. Psychopharmacology 221:575–587
Inoue M, Fujita T, Goto M, Kumamoto E (2012) Presynaptic enhancement by eugenol of spontaneous excitatory transmission in rat spinal substantia gelatinosa neurons is mediated by transient receptor potential A1 channels. Neuroscience 210:403–415
Irie Y, Keung WM (2003) Rhizoma acori graminei and its active principles protect PC-12 cells from the toxic effect of amyloid-beta peptide. Brain Res 963:282–289
Jorkjend L, Skoglund LA (1990) Effect of non-eugenol- and eugenol-containing periodontal dressings on the incidence and severity of pain after periodontal soft tissue surgery. J Clin Periodontol 17:341–344
Kabuto H, Tada M, Kohno M (2007) Eugenol [2-methoxy-4-(2-propenyl)phenol] prevents 6-hydroxydopamine-induced dopamine depression and lipid peroxidation inductivity in mouse striatum. Biol Pharm Bull 30:423–427
Kawai A, Onimaru H, Homma I (2006) Mechanisms of CO2/H+ chemoreception by respiratory rhythm generator neurons in the medulla from newborn rats in vitro. J Physiol 572:525–537
Klein AH, Carstens MI, Carstens E (2013) Eugenol and carvacrol induce temporally desensitizing patterns of oral irritation and enhance innocuous warmth and noxious heat sensation on the tongue. Pain 154:2078–2087
Koizumi H, Smith JC (2008) Persistent Na+ and K+-dominated leak currents contribute to respiratory rhythm generation in the pre-Botzinger complex in vitro. J Neurosci 28:1773–1785
Kotani S, Onimaru H (2014) Neuronal mechanisms of shortening of respiratory neuron burst by eugenol. J Physiol Sci 64:s280
Kotani S, Onimaru H (2017) Neuronal mechanisms of inhibitory effects of eugenol on respiratory neuron activity in the brainstem-spinal cord preparation. J Physiol Sci 67:S113
Lee MH, Yeon KY, Park CK, Li HY, Fang Z, Kim MS, Choi SY, Lee SJ, Lee S, Park K, Lee JH, Kim JS, Oh SB (2005) Eugenol inhibits calcium currents in dental afferent neurons. J Dent Res 84:848–851
Li HY, Park CK, Jung SJ, Choi SY, Lee SJ, Park K, Kim JS, Oh SB (2007) Eugenol inhibits K+ currents in trigeminal ganglion neurons. J Dent Res 86:898–902
Li J, Baccei ML (2011) Pacemaker neurons within newborn spinal pain circuits. J Neurosci 31:9010–9022
Lin ST, Onimaru H (2015) Effects of riluzole on respiratory rhythm generation in the brainstem-spinal cord preparation from newborn rat. Neurosci Res 94:28–36
Markowitz K, Moynihan M, Liu M, Kim S (1992) Biologic properties of eugenol and zinc oxide-eugenol: a clinically oriented review. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 73:729–737
Mironov SL (2008) Metabotropic glutamate receptors activate dendritic calcium waves and TRPM channels which drive rhythmic respiratory patterns in mice. J Physiol 586:2277–2291
Moraes DJ, da Silva MP, Bonagamba LG, Mecawi AS, Zoccal DB, Antunes-Rodrigues J, Varanda WA, Machado BH (2013) Electrophysiological properties of rostral ventrolateral medulla presympathetic neurons modulated by the respiratory network in rats. J Neurosci 33:19223–19237
Moran MM, Xu H, Clapham DE (2004) TRP ion channels in the nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol 14:362–369
Muller M, Pape HC, Speckmann EJ, Gorji A (2006) Effect of eugenol on spreading depression and epileptiform discharges in rat neocortical and hippocampal tissues. Neuroscience 140:743–751
Onimaru H, Ballanyi K, Homma I (2003) Contribution of Ca2+-dependent conductances to membrane potential fluctuations of medullary respiratory neurons of newborn rats in vitro. J Physiol 552:727–741
Onimaru H, Homma I (1992) Whole cell recordings from respiratory neurons in the medulla of brainstem-spinal cord preparations isolated from newborn rats. Pflugers Arch 420:399–406
Onimaru H, Homma I (2003) A novel functional neuron group for respiratory rhythm generation in the ventral medulla. J Neurosci 23:1478–1486
Onimaru H, Ikeda K, Kawakami K (2008) CO2-sensitive preinspiratory neurons of the parafacial respiratory group express Phox2b in the neonatal rat. J Neurosci 28:12845–12850
Onimaru H, Kanamaru A, Homma I (1996) Optical imaging of respiratory burst activity in newborn rat medullary block preparations. Neurosci Res 25:183–190
Park CK, Li HY, Yeon KY, Jung SJ, Choi SY, Lee SJ, Lee S, Park K, Kim JS, Oh SB (2006) Eugenol inhibits sodium currents in dental afferent neurons. J Dent Res 85:900–904
Parnas M, Peters M, Dadon D, Lev S, Vertkin I, Slutsky I, Minke B (2009) Carvacrol is a novel inhibitor of Drosophila TRPL and mammalian TRPM7 channels. Cell Calcium 45:300–309
Segal MM, Douglas AF (1997) Late sodium channel openings underlying epileptiform activity are preferentially diminished by the anticonvulsant phenytoin. J Neurophysiol 77:3021–3034
Shakuo T, Lin ST, Onimaru H (2016) The Effects of lidocaine on central respiratory neuron activity and nociceptive-related responses in the brainstem-spinal cord preparation of the newborn rat. Anesth Analg 122:1586–1593
Stafstrom CE (2007) Persistent sodium current and its role in epilepsy. Epilepsy Curr 7:15–22
Sterner O, Szallasi A (1999) Novel natural vanilloid receptor agonists: new therapeutic targets for drug development. Trends Pharmacol Sci 20:459–465
Suzue T (1984) Respiratory rhythm generation in the in vitro brain stem-spinal cord preparation of the neonatal rat. J Physiol 354:173–183
Szallasi A, Blumberg PM (1999) Vanilloid (Capsaicin) receptors and mechanisms. Pharmacol Rev 51:159–212
Tani M, Kotani S, Hayakawa C, Lin ST, Irie S, Ikeda K, Kawakami K, Onimaru H (2016) Effects of a TRPV1 agonist capsaicin on respiratory rhythm generation in brainstem-spinal cord preparation from newborn rats. Pflugers Arch in press
Tani M, Onimaru H, Ikeda K, Kawakami K, Homma I (2010) Menthol inhibits the respiratory rhythm in brainstem preparations of the newborn rats. Neuroreport 21:1095–1099
Tani M, Yazawa I, Ikeda K, Kawakami K, Onimaru H (2015) Long-lasting facilitation of respiratory rhythm by treatment with TRPA1 agonist, cinnamaldehyde. J Neurophysiol 114:989–998
Vennekens R, Menigoz A, Nilius B (2012) TRPs in the brain. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 163:27–64
Won MH, Lee JC, Kim YH, Song DK, Suh HW, Oh YS, Kim JH, Shin TK, Lee YJ, Wie MB (1998) Postischemic hypothermia induced by eugenol protects hippocampal neurons from global ischemia in gerbils. Neurosci Lett 254:101–104
Yang BH, Piao ZG, Kim YB, Lee CH, Lee JK, Park K, Kim JS, Oh SB (2003) Activation of vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1) by eugenol. J Dent Res 82:781–785
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (KAKENHI: 25430012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kotani, S., Irie, S., Izumizaki, M. et al. Effects of eugenol on respiratory burst generation in newborn rat brainstem-spinal cord preparations. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 470, 385–394 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-017-2074-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-017-2074-z