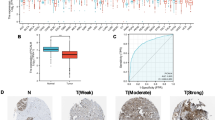
Abstract
Bax is a well-known universal proapoptotic protein. Bax protein is detected in almost all human organs, and its expression levels can be correlated with disease progression and therapeutic efficacy in certain settings. Interestingly, increasing evidence has shown that mature neuronal cell death is often not typical apoptosis. Most results on the expression of Bax proteins (predominantly Baxα) in the human brain come from disease-oriented studies, and the data on Bax protein expression in the normal brain are limited and lack consistency due to many variable factors. Here, we analyzed Bax RNA and protein expression data from multiple databases and performed immunostaining of over 80 samples from 25 healthy subjects across 7 different brain regions. We found that Bax protein expression was heterogeneous across brain regions and individual subjects. Both neurons and glial cells, such as astrocytes, could be Bax positive, but Bax positivity appeared to be highly selective, even within the same cell type in the same region. Furthermore, Bax proteins could be localized in the cytosol (evenly spread or concentrated to one region), nucleus or nucleolus depending on the cell type. Such variation and distribution in Bax expression suggest that Bax may function differently in the human brain than in other organs.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Most data used in this work are available in the corresponding public databases. Data generated during this study are available upon reasonable request.
References
Brayer S, Joannes A, Jaillet M et al (2017) The pro-apoptotic BAX protein influences cell growth and differentiation from the nucleus in healthy interphasic cells. Cell Cycle 16:2108–2118. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2017.1371882
Cartron P-F (2002) The expression of a new variant of the pro-apoptotic molecule Bax, Baxpsi, is correlated with an increased survival of glioblastoma multiforme patients. Hum Mol Genet 11:675–687. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/11.6.675
Cartron PF, Moreau C, Oliver L et al (2002) Involvement of the N-terminus of Bax in its intracellular localization and function. FEBS Lett 512:95–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(02)02227-5
Chen M, Wang J (2002) Initiator caspases in apoptosis signaling pathways. Apoptosis 7:313–319
Craig RW (1995) The BCL-2 gene family. Semin Cancer Biol 6:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1006/scbi.1995.0005
Death C, Chao DT, Korsmeyer SJ (1998) BCL-2 FAMILY : regulators of. 395–419
Dickens LS, Boyd RS, Jukes-Jones R et al (2012) A death effector domain chain DISC model reveals a crucial role for caspase-8 chain assembly in mediating apoptotic cell death. Mol Cell 47:291–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2012.05.004
Fu NY, Sukumaran SK, Kerk SY, Yu VC (2009) Baxβ: A constitutively active human Bax isoform that is under tight regulatory control by the proteasomal degradation mechanism. Mol Cell 33:15–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2008.11.025
Fuchs Y, Steller H (2011) Programmed cell death in animal development and disease. Cell 147:742–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.10.033
Gorman AM (2008) Neuronal cell death in neurodegenerative diseases: Recurring themes around protein handling: Apoptosis Review Series. J Cell Mol Med 12:2263–2280. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00402.x
Haferkamp B, Zhang H, Lin Y et al (2012) BaxΔ2 is a novel bax isoform unique to microsatellite unstable tumors. J Biol Chem 287:34722–34729. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.374785
Haferkamp B, Zhang H, Kissinger S et al (2013) BaxΔ2 family alternative splicing salvages Bax microsatellite-frameshift mutations. Genes Cancer 4:501–512. https://doi.org/10.1177/1947601913515906
Henshall DC, Clark RSB, Adelson PD et al (2000) Alterations in bcl-2 and caspase gene family protein expression in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurology 55:250–257. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.55.2.250
Hoetelmans RWM, Van Slooten HJ, Keijzer R et al (2000) Bcl-2 and Bax proteins are present in interphase nuclei of mammalian cells. Cell Death Differ 7:384–392. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4400664
** KL, Graham SH, Mao XO et al (2001) Bax κ, a novel Bax splice variant from ischemic rat brain lacking an ART domain, promotes neuronal cell death. J Neurochem 77:1508–1519. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00361.x
Jones TR, Carpenter AE, Lamprecht MR et al (2009) Scoring diverse cellular morphologies in image-based screens with iterative feedback and machine learning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:1826–1831. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0808843106
Joy A, Panicker S, Shapiro JR (2000) Altered nuclear localization of bax protein in BCNU-resistant glioma cells. J Neurooncol 49:117–129. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026574123273
Kampf C, Bergman J, Oksvold P et al (2012) A tool to facilitate clinical biomarker studies—a tissue dictionary based on the Human Protein Atlas. BMC Med. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-10-103
Krajewska M, Mai JK, Zapata JM et al (2002) Dynamics of expression of apoptosis-regulatory proteins Bid, Bcl-2, Bcl-X, Bax and Bak during development of murine nervous system. Cell Death Differ 9:145–157. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj/cdd/4400934
Krajewski S, Mai JK, Krajewska M et al (1995) Upregulation lschemia of bax protein levels in neurons following. J Neurosci 15:6364–6375
Lizio M, Harshbarger J, Shimoji H et al (2015) Gateways to the FANTOM5 promoter level mammalian expression atlas. Genome Biol 16:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0560-6
Lucantoni F, Lindner AU, O’donovan N et al (2018) Systems modeling accurately predicts responses to genotoxic agents and their synergism with BCL-2 inhibitors in triple negative breast cancer cells article. Cell Death Dis. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-017-0039-y
Mañas A, Davis A, Lamerand S, **ang J (2018) Detection of pro-apoptotic Bax∆2 proteins in the human cerebellum. Histochem Cell Biol 150:77–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-018-1669-6
Mañas A, Yao Q, Davis A et al (2020) Immunohistochemical detection of the pro-apoptotic Bax∆2 protein in human tissues. Histochem Cell Biol 154:41–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-020-01874-w
Martin LJ, Kaiser A, Yu JW et al (2001) Injury-induced apoptosis of neurons in adult brain is mediated by p53-dependent and p53-independent pathways and requires Bax. J Comp Neurol 433:299–311. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.1141
Navani S (2011) The human protein atlas. J Obstet Gynecol India 61:27–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13224-011-0013-z
Oltval ZN, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer SJ (1993) Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programed cell death. Cell 74:609–619. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(93)90509-O
Perier C, Bové J, Wu DC et al (2007) Two molecular pathways initiate mitochondria-dependent dopaminergic neurodegeneration in experimental Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:8161–8166. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0609874104
Pontén F (2008) The human protein atlas—a tool for pathology. J Pathol 216:387–393. https://doi.org/10.1002/path
Pontén FK, Schwenk JM, Asplund A, Edqvist PHD (2011) The human protein atlas as a proteomic resource for biomarker discovery. J Intern Med 270:428–446. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2796.2011.02427.x
Ravishankar S, Ashraf QM, Fritz K et al (2001) Expression of Bax and Bcl-2 proteins during hypoxia in cerebral cortical neuronal nuclei of newborn piglets: effect of administration of magnesium sulfate. Brain Res 901:23–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(01)02109-6
Reichenbach F, Wiedenmann C, Schalk E et al (2017) Mitochondrial BAX determines the predisposition to apoptosis in human AML. Clin Cancer Res 23:4805–4816. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1941
Robert SBC, Patrick MK, Minzhi C, Simon CW, Donald WM, Jun C, Ronald LH, Eric LA (2000) Increases in Bcl-2 and cleavage of caspase-1 and caspase-3 in human brain after head injury. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 12:279–280. https://doi.org/10.1097/00008506-200007000-00019
Salah-eldin AE, Inoue S, Tsuda M, Matsuura A (2000) Abnormal intracellular localization of Bax with a normal membrane anchor domain in human lung cancer cell lines. Jpn J Cancer Res 91:1269–1277. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2000.tb00914.x
Sani MA, Dufourc EJ, Gröbner G (2009) How does the Bax-α1 targeting sequence interact with mitochondrial membranes? The role of cardiolipin. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1788:623–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.12.014
Sarosiek KA, Fraser C, Muthalagu N et al (2017) Developmental regulation of mitochondrial apoptosis by c-Myc governs age- and tissue-specific sensitivity to cancer therapeutics. Cancer Cell 31:142–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2016.11.011
Schabitz W, Sommer C, Zoder W, et al (2000) Infarct size and counterregulates Bax and Bcl-2 expression. 2212–2217
Schmitt E, Paquet C, Beauchemin M et al (2000) Characterization of Bax-σ, a cell death-inducing isoform of Bax. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 270:868–879. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.2000.2537
Sedlak TW, Oltvai ZN, Yang E et al (1995) Multiple Bcl-2 family members demonstrate selective dimerizations with Bax. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:7834–7838. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.17.7834
Sen S (1992) Programmed cell death: concept, mechanism and control. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 67:287–319. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-185X.1992.tb00727.x
Shi B, Triebe D, Kajiji S et al (1999) Identification and characterization of Baxε, a novel Bax variant missing the BH2 and the transmembrane domains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 254:779–785. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1998.0130
Shimohama S, Fujimoto S, Sumida Y, Tanino H (1998) Differential expression of rat brain Bcl-2 family proteins in development and aging. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 252:92–96. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1998.9577
Su JH (1997) Bax protein expression is increased in Alzheimer’s brain: correlations with DNA damage, Bcl-2 expression, and brain pathology. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 56:86–93
Tortosa A, Löpez E, Ferrer I (1998) Bcl-2 and Bax protein expression in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 95:407–412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004010050817
Uhlén M, Fagerberg L, Hallström BM et al (2015) Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1260419
Warren CFA, Wong-Brown MW, Bowden NA (2019) BCL-2 family isoforms in apoptosis and cancer. Cell Death Dis. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1407-6
**ao-Ming Y, Zoltan NO, Stanley JK (1994) BH1 and BH2 domains of Bcl-2 are required for inhibition of apoptosis and heterodimerization with Bax. Nature 369:321–323
**e B, Yao Q, **ang J, Minh DDL (2020) A structural model for bax∆2-mediated activation of caspase 8-dependent apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci 21:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155476
Yamada K, Watanabe M (2002) Cytodifferentiation of Bergmann glia and its relationship with Purkinje cells. Anat Sci Int / Japanese Assoc Anat 77:94–108. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0022-7722.2002.00021.x
Yang B, Praysono RA (2000) Expression of Bax, Bcl-2, and P53 in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Mod Pathol 13:1115–1120. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.3880206
Yin XM, Oltvai ZN, Veis-Novack DJ et al (1994) Bcl-2 gene family and the regulation of programmed cell death. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 59:387–393. https://doi.org/10.1101/SQB.1994.059.01.043
Zha H, Aimé-Sempé C, Sato T, Reed JC (1996) Proapoptotic protein Bax heterodimerizes with Bcl-2 and homodimerizes with Bax via a novel domain (BH3) distinct from BH1 and BH2. J Biol Chem 271:7440–7444. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.271.13.7440
Zhang H, Lin Y, Mañas A et al (2014) Baxδ2 promotes apoptosis through caspase-8 activation in microsatellite-unstable colon cancer. Mol Cancer Res 12:1225–1232. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-14-0162
Zhao Y, Sui X, Hong R (2010) From procaspase-8 to caspase-8: Revisiting structural functions of caspase-8. J Cell Physiol 225:316–320
Zong WX, Li C, Hatzivassiliou G et al (2003) Bax and Bak can localize to the endoplasmic reticulum to initiate apoptosis. J Cell Biol 162:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200302084
Zubrow AB, Delivoria-Papadopoulos M, Ashraf QM et al (2002) Nitric oxide-mediated expression of Bax protein and DNA fragmentation during hypoxia in neuronal nuclei from newborn piglets. Brain Res 954:60–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(02)03342-5
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the Illinois Institution of Technology research fund. The data used for the analyses described in this manuscript were obtained from the Human Protein Atlas, including Consensus, HPA, GTEx, and FANTOM5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YQ designed and performed experiments, data collection and analysis, and prepared figures and manuscript; HZ and AM, imaging processing and data analysis; CS, and JG data collection. JX managed the project, data interpretation, and manuscript preparation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, Q., Zhang, H., Standish, C. et al. Expression profile of the proapoptotic protein Bax in the human brain. Histochem Cell Biol 159, 209–220 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-022-02146-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-022-02146-5