Abstract
Introduction
Randomized clinical trials have generated doubts regarding the therapeutic effectiveness of spinal kyphoplasty to reduce pain and improve quality of life in patients with vertebral fractures. There is a paucity of data on the influence of kyphoplasty on spinal range of motion. To quantify early postoperative changes following kyphoplasty in spinal motion, a noninvasive, radiation-free measurement method was used and results related to clinical and radiological parameters.
Methods
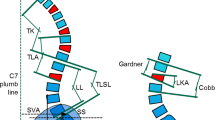
The study group included 30 patients with an overall number of 54 symptomatic pathological vertebral compression fractures. All patients were treated with balloon kyphoplasty. Clinical results were recorded using the visual analog scale, SF 36, Roland Morris Score and the Oswestry Disability Index, at three time points; preoperative, 2 days postoperative, and at 12 weeks postoperative. The kyphosis angle/sagittal index were determined with biplanar X-rays. Amplitude/velocity of motion in extension/flexion was measured at each time point by use of the EpionicsSPINE© system (Epionics Medical GmbH; Potsdam, Germany) using two external sensor strips.
Results
Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging scans showed bone marrow edema in all vertebral bodies indicative of a recent, non-consolidated fracture. Pain and quality of life was significantly improved by kyphoplasty, both for the immediate postoperative period, as well as at 12 weeks postoperative. Radiological parameters also showed significant improvement following surgery. Total ROM did not significantly change 2 days after kyphoplasty, but amplitude and velocity were found to be increased 12 weeks postoperatively. Significant positive correlations were observed between increased range of motion and improved clinical/radiological scores.
Conclusion
Significant clinical and radiological improvement following kyphoplasty supports the rational for cement augmentation in patients with pathological vertebral body fractures. To the knowledge of the authors, no prior study has assessed the influence of preservation and improvement of spinal range of motion on clinical outcome following kyphoplasty.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang HK, Lu K, Liang CL, Weng HC, Wang KW et al (2010) Comparing clinical outcomes following percutaneous vertebroplasty with conservative therapy for acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Pain Med 11:1659–1665
Dennison E, Cooper C (2000) Epidemiology of osteoporotic fractures. Horm Res 54(Suppl 1):58–63
Tamayo-Orozco J, Arzac-Palumbo P, Peon-Vidales H, Mota-Bolfeta R, Fuentes F (1997) Vertebral fractures associated with osteoporosis: patient management. Am J Med 103:44S–48S (discussion 8S–50S)
Alvarez L, Alcaraz M, Perez-Higueras A, Granizo JJ, de Miguel I et al (2006) Percutaneous vertebroplasty: functional improvement in patients with osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine 31:1113–1118
Fourney DR, Schomer DF, Nader R, Chlan-Fourney J, Suki D et al (2003) Percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for painful vertebral body fractures in cancer patients. J Neurosurg 98:21–30
Garfin SR, Buckley RA, Ledlie J, Balloon KOG (2006) Balloon kyphoplasty for symptomatic vertebral body compression fractures results in rapid, significant, and sustained improvements in back pain, function, and quality of life for elderly patients. Spine 31:2213–2220
Heini PF (2005) The current treatment–a survey of osteoporotic fracture treatment. Osteoporotic spine fractures: the spine surgeon’s perspective. Osteoporos Int: J Establ Result Cooper Eur Found Osteoporos Natl Osteoporos Found USA 16 Suppl 2:S85–S92
Klazen CA, Venmans A, de Vries J, van Rooij WJ, Jansen FH et al (2010) Percutaneous vertebroplasty is not a risk factor for new osteoporotic compression fractures: results from VERTOS II. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:1447–1450
Voormolen MH, Mali WP, Lohle PN, Fransen H, Lampmann LE et al (2007) Percutaneous vertebroplasty compared with optimal pain medication treatment: short-term clinical outcome of patients with subacute or chronic painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. The VERTOS study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:555–560
Diamond TH, Champion B, Clark WA (2003) Management of acute osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a nonrandomized trial comparing percutaneous vertebroplasty with conservative therapy. Am J Med 114:257–265
Ledlie JT, Renfro MB (2006) Kyphoplasty treatment of vertebral fractures: 2-year outcomes show sustained benefits. Spine 31:57–64
Lieberman IH, Dudeney S, Reinhardt MK, Bell G (2001) Initial outcome and efficacy of “kyphoplasty” in the treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine 26:1631–1638
Zampini JM, White AP, McGuire KJ (2010) Comparison of 5766 vertebral compression fractures treated with or without kyphoplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468:1773–1780
Kasperk C, Hillmeier J, Noldge G, Grafe IA, Dafonseca K et al (2005) Treatment of painful vertebral fractures by kyphoplasty in patients with primary osteoporosis: a prospective nonrandomized controlled study. J Bone Miner Res: Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 20:604–612
Edidin AA, Ong KL, Lau E, Kurtz SM (2011) Mortality risk for operated and nonoperated vertebral fracture patients in the medicare population. J Bone Miner Res: Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 26:1617–1626
Julka A, Tolhurst SR, Srinivasan RC, Graziano GP (2012) Functional outcomes and height restoration for patients with multiple myeloma-related osteolytic vertebral compression fractures treated with kyphoplasty. J Spinal Disord Tech [Epub ahead of print]
Taylor WR, Consmuller T, Rohlmann A (2010) A novel system for the dynamic assessment of back shape. Med Eng Phys 32:1080–1083
Consmuller T, Rohlmann A, Weinland D, Druschel C, Duda GN, Taylor WR (2012) Velocity of lordosis angle during spinal flexion and extension. PLoS One 7:e50135
Consmuller T, Rohlmann A, Weinland D, Druschel C, Duda GN, Taylor WR (2012) Comparative evaluation of a novel measurement tool to assess lumbar spine posture and range of motion. Eur Spine J: Off Publ Eur Spine Soc Eur Spinal Deformity Soc Eur Sect Cerv Spine Res Soc 21:2170–2180
Colon-Emeric CS, Saag KG (2006) Osteoporotic fractures in older adults. Best practice and research. Clin Rheumatol 20:695–706
Li X, Yang H, Tang T, Qian Z, Chen L, Zhang Z (2012) Comparison of kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty for treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: twelve-month follow-up in a prospective nonrandomized comparative study. J Spinal Disord Tech 25:142–149
Voggenreiter G, Brocker K, Rohrl B, Sadick M, Obertacke U (2008) Results of balloon kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Der Unfallchirurg 111:403–412
Ledlie JT, Renfro M (2003) Balloon kyphoplasty: one-year outcomes in vertebral body height restoration, chronic pain, and activity levels. J Neurosurg 98:36–42
Buchbinder R, Osborne RH, Ebeling PR, Wark JD, Mitchell P et al (2009) A randomized trial of vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic vertebral fractures. N Engl J Med 361:557–568
Kallmes DF, Comstock BA, Heagerty PJ, Turner JA, Wilson DJ et al (2009) A randomized trial of vertebroplasty for osteoporotic spinal fractures. N Engl J Med 361:569–579
Taylor RS, Fritzell P, Taylor RJ (2007) Balloon kyphoplasty in the management of vertebral compression fractures: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J: Off Publ Eur Spine Soc, Eur Spinal Deformity Soc, Eur Sect Cerv Spine Res Soc 16:1085–1100
Rohlmann A, Zander T, Bergmann G (2006) Spinal loads after osteoporotic vertebral fractures treated by vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. Eur Spine J: Off Publ Eur Spine Soc, Eur Spinal Deformity Soc, Eur Sect Cerv Spine Res Soc 15:1255–1264
Kumar K, Nguyen R, Bishop S (2010) A comparative analysis of the results of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Neurosurgery 67:ons171–ons188 (discussion ons88)
Liu JT, Liao WJ, Tan WC, Lee JK, Liu CH et al (2010) Balloon kyphoplasty versus vertebroplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a prospective, comparative, and randomized clinical study. Osteoporos Int: J Establ Result Cooper Eur Found Osteoporos Natl Osteoporos Found USA 21:359–364
Pradhan BB, Bae HW, Kropf MA, Patel VV, Delamarter RB (2006) Kyphoplasty reduction of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: correction of local kyphosis versus overall sagittal alignment. Spine 31:435–441
Stoffel M, Wolf I, Ringel F, Stuer C, Urbach H, Meyer B (2007) Treatment of painful osteoporotic compression and burst fractures using kyphoplasty: a prospective observational design. J Neurosurg Spine 6:313–319
Holt CA, Evans SL, Dillon D, Ahuja S (2005) Three-dimensional measurement of intervertebral kinematics in vitro using optical motion analysis. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part H J Eng Med 219:393–399
Lee BW, Lee JE, Lee SH, Kwon HK (2011) Kinematic analysis of the lumbar spine by digital videofluoroscopy in 18 asymptomatic subjects and 9 patients with herniated nucleus pulposus. J Manip Physiol Ther 34:221–230
Schulze M, Trautwein F, Vordemvenne T, Raschke M, Heuer F (2011) A method to perform spinal motion analysis from functional X-ray images. J Biomech 44:1740–1746
Williams JM, Haq I, Lee RY (2010) Dynamic measurement of lumbar curvature using fibre-optic sensors. Med Eng Phys 32:1043–1049
Dlugosz MM, Panek D, Maciejasz P, Chwala W, Alda W (2012) An improved kinematic model of the spine for three-dimensional motion analysis in the Vicon system. Stud Health Technol Inf 176:227–231
Phillips FM, Ho E, Campbell-Hupp M, McNally T, Todd Wetzel F, Gupta P (2003) Early radiographic and clinical results of balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine 28:2260–2265 (discussion 5–7)
Acknowledgments
No funding has been received for research on which this article is based.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Druschel, C., Schaser, KD., Rohlmann, A. et al. Prospective quantitative assessment of spinal range of motion before and after minimally invasive surgical treatment of vertebral body fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 134, 1083–1091 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-014-2035-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-014-2035-3