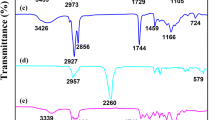
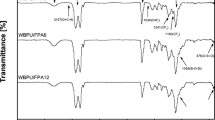
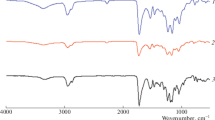
Abstract
Waterborne polyurethane (WPU) has gained widespread attention. However, conventional linear WPU emulsions have lower mechanical properties, poor water resistance, and other disadvantages. In this study, polyurethane prepolymers containing branched chains were successfully synthesized by using diphenylmethane diisocyanate (MDI), polytetramethylene ether glycol (PTMG) and castor oil (CO) as the main raw materials. On this basis, epoxy resin was used to further modify the obtained polyurethane prepolymers, which results in an increase in mechanical properties, water resistance, and heat resistance due to the formation of a network cross-linked structure during the film formation. The type and addition amount of epoxy resin were determined by centrifugal stability and particle size of WPU emulsions, water absorption, and mechanical properties of WPU films. The results showed that the prepared epoxy resin–modified WPU (EWPU) emulsions have excellent centrifugal stability. If 7% epoxy resin was added after the polyurethane chain expansion, the corresponding EWPU films have good mechanical properties (the tensile strength of 28.7 MPa and the elongation at break of 379%), water resistance (water absorption of 4.21%), and the thermal stability due to the cross-linked structure in EWPU. This kind of EWPU emulsions may have promising applications in coating material, adhesives, and the textile industry.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Honarkar H (2017) Waterborne polyurethanes: a review. J Dispersion Sci Technol 39:507–516
Zeng XG, Gong M, Liu ZH (2018) Research status of waterborne polyurethane coatings. Electroplating and coating 37:49–56
Li XN (2021) Progress in the modification of waterborne polyurethane. The Chinese Leather 50:139–142
Liu YX, Gao J, Fan ZR, Gu YX, Yu YW, Wang XD (2023) Study on preparation of epoxy resin modified waterborne polyurethane emulsion. New Chem Mater 51:92–95+101
Fang ZH (2010) Preparation and characterization of the heat-resistant UV curable waterborne polyurethane coating modified by bisphenol A. Express Polym Lett 4:704–711
Ge Z, Luo Y (2013) Synthesis and characterization of siloxane-modified two-component waterborne polyurethane. Prog Org Coat 76:1522–1526
Yeganeh H, Lakouraj MM, Jamshidi S (2005) Synthesis and properties of biodegradable elastomeric epoxy modified polyurethanes based on poly(ε-caprolactone) and poly(ethylene glycol). Eur Polym J 41:2370–2379
Miao S, Wang P, Su ZG, Zhang SP (2014) Vegetable-oil-based polymers as future polymeric biomaterials. Acta Biomater 10:1692–1704
Gao ZZ, Peng J, Zhong TH, Sun J, Wang XB, Yue C (2012) Biocompatible elastomer of waterborne polyurethane based on castor oil and polyethylene glycol with cellulose nanocrystals. Carbohydr Polym 87:2068–2075
Ren LF, Ma XD, Qiang TT (2019) Preparation and properties of waterborne polyurethane based on castor-oil. Chinese Leather 48:42–48
Liu Z, Tian Y, Kang S, Zhang XJ (2012) Synthesis and characterization of novel epoxy-modified waterborne polyurethanes and their use in carbon fiber sizing. J Appl Polym Sci 125:3490–3499
Lai XJ, Li XR, Wang L (2009) Synthesis and properties of waterborne polyurethane modified by epoxy resin. Chin J Polym Sci 009:1107–1112
Hu Q, Lu L, Wu X, Liao J, Pan JL, Xu ZS (2015) Synthesis and properties of highly branched waterborne polyurethane modified by epoxy resin. Electroplating & coating 34:1026–1031
Zhuang CH, Xue WL, Zeng ZX (2021) Synthesis and characterization of epoxy resins-modified waterborne polyurethane emulsion. Asian Journal of Applied Chemistry Research 9:1–9
Zhan B, Li QS, Hong W, **a YZ, Wang GW, **ng GZ (2013) Preparation and properties of epoxy resin modified waterborne polyurethane. Appl Mech Mater 2371:607–610
**e LJ, Wang YP, Qu W, **e ZB, Wang CZ, Liu BH (2021) Heat stabilization of epoxy modified PPC water-based polyurethane emulsion. Yunnan Chemical Technology 48:61–63
Chen JB, Guo WH, Qian JM, Zhu H, Yang C (2015) Study on the storage performance at normal temperature of waterborne polyurethane modified by epoxy resin. Appl Chem Ind 44:1963–1965+1970
Dong YB, Wang G, Zhou YL, Ji X, Yuan LP (2021) Preparation and properties of waterborne polyurethane adhesive modified by epoxy resin. Chinese Leather 50:104–108
Guo J, Zhao S, Wu L (2016) Study on preparation of epoxy castor aqueous oil modified waterborne polyurethane emulsion and its film properties. China Adhesives 25:26–29 + 62
Yao X, Zhao HB, Wu B, Fu XW, Hu K, Zhou CL, Lei JX (2018) Preparation and characterization of waterborne polyurethane based on diphenylmethane diisocyanate-50. Adv Polym Technol 37:596–605
Feng X, Xu S, Yan Y, Cao Y, Zhang J, Zhu J (2020) Study on the polyurethane elastomer modified by epoxy resin. Special Purpose Rubber Products 41(4):6–9
Wang M, Zhao C, Yuan Y, Diao S (2021) Preparation of high solid content waterborne polyurethane modified by epoxy resin. Polyurethane Industry 36(1):8–11
Li L (2010) Study on Synthesis and properties of waterborne polyurethane modified by epoxy resin. Polyurethane Industry 25(1):42–45
** ZM, Guo WL, Gao CH (2013) Study on synthesis and properties of waterborne polyurethane modified by epoxy resin. Appl Mech Mater 2659:423–426
Wu X, Wei X, Qiu S (2006) The study on synthesis technology and properties of waterborne polyurethane modified by epoxy resin. J Basic Sci Eng 14(2):153–159
W J, Huang Y, Tao C, Yu B, **e Z, Li L, Xu G, (2014) Study on synthesis and properties of waterborne polyurethane modified with ring-opened epoxy resin by diethanolamine. Paint Coatings Industry 44(2):32–38
Y L, Li J, Peng X, Cao X, Zhang Y, Guan Z, Chen X, (2015) Preparation and properties of high solid content and low gloss waterborne polyurethane modified with epoxy. Paint Coatings Industry 45(12):51–58
Funding
This work was funded by List of Key Science and Technology Projects in Transportation Industry in 2021, China (project no. 2021-MS1-010), and the Project of Shandong Hi-Speed Group Innovation Research Institute (project no. (2022)SDHSIRI-CL-002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
**ufen Liu: Methodology, Data curation, Writing-Original draft preparation. Fengyuan Sun: Visualization, Investigation. Yifan Liu: Visualization, Investigation. Baojian Yao: Methodology, Formal analysis. Haishan Liang: Formal analysis, Investigation. Minghao Mu: Formal analysis, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Project administration. **nqiang Liu: Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration. Haisong Bi: Methodology, Editing. Zheng Wang: Methodology, Formal analysis. Chengduo Qian: Formal analysis, Investigation. Xue Li: Conceptualization, Methodology, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing-Reviewing and Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Competing interests
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work; there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Sun, F., Liu, Y. et al. Synthesis and properties of castor oil–based cationic waterborne polyurethane modified by epoxy resin. Colloid Polym Sci 302, 13–22 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-023-05174-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-023-05174-2