Abstract
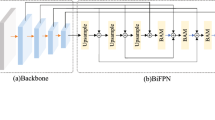
In marrying with Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), the person re-identification (re-ID) techniques are further strengthened in terms of mobility. However, the simple hybridization brings unavoidable scale diversity and occlusions caused by the altitude and attitude variations during the flight of UAVs. To harmoniously blend the two techniques, in this research, we argue that the pedestrian should be globally perceived regardless of the scale variation, and the internal occlusions should also be well suppressed. For this purpose, we propose a novel Multi-granularity Attention in Attention (MGAiA) network to satisfy the raised demands for the aerial-based re-ID. Specifically, a novel multi-granularity attention (MGA) module is designed to supply the feature extraction model with a global awareness to explore the discriminative knowledge within scale variations. Subsequently, an Attention in Attention (AiA) mechanism is proposed to generate attention scores for measuring the importance of the different granularity, thereby proactively reducing the negative efforts caused by occlusions. We carry out comprehensive experiments on two large-scale UAV-based datasets including PRAI-1581 and P-DESTRE, as well as the transfer learning from three popular ground-based re-ID datasets CUHK03, Market-1501, and CUHK-SYSU to quantify the effectiveness of the proposed method.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets that support the findings of this study are available in the following public resources: [PRAI-1581], [P-DESTRE], [CUHK03], [Market-1501]. The dataset [CUHK-SYSU] are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Zheng, L., Yang, Y., Hauptmann, A.G.: Person re-identification: past, present and future. ar**v preprint ar**v:1610.02984 (2016)
Chen, G., Lu, J., Yang, M., Zhou, J.: Spatial-temporal attention-aware learning for video-based person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(9), 4192–4205 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2019.2908062
**e, J., Ge, Y., Zhang, J., Huang, S., Wang, H.: Low-resolution assisted three-stream network for person re-identification. Vis. Comput. 10, 1–11 (2021)
Sun, Y., Zheng, L., Yang, Y., Tian, Q., Wang, S.: Beyond part models: Person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline). In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 480–496 (2018)
Wang, P., Wang, M., He, D.: Multi-scale feature pyramid and multi-branch neural network for person re-identification. Vis. Comput. 1–13 (2022)
Jia, Z., Li, Y., Tan, Z., Wang, W., Wang, Z., Yin, G.: Domain-invariant feature extraction and fusion for cross-domain person re-identification. Vis. Comput. 1–12 (2022)
Zhou, P., Ni, B., Geng, C., Hu, J., Xu, Y.: Scale-transferrable object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 528–537 (2018)
Zhang, Y., Bai, Y., Ding, M., Li, Y., Ghanem, B.: W2f: A weakly-supervised to fully-supervised framework for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 928–936 (2018)
**ang, Y., Song, C., Mottaghi, R., Savarese, S.: Monocular multiview object tracking with 3d aspect parts. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 220–235. Springer (2014)
Zhang, S., Zhang, Q., Yang, Y., Wei, X., Wang, P., Jiao, B., Zhang, Y.: Person re-identification in aerial imagery. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 23, 281–291 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2020.2977528
Kumar, S.V.A., Yaghoubi, E., Das, A., Harish, B.S., Proença, H.: The p-destre: a fully annotated dataset for pedestrian detection, tracking, and short/long-term re-identification from aerial devices. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 16, 1696–1708 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2020.3040881
Zheng, Z., Zheng, L., Yang, Y.: A discriminatively learned CNN embedding for person reidentification. ACM Trans. Multimedia Comput. Commun. Appl. (TOMM) 14(1), 1–20 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1145/3159171
Xu, S., Luo, L., Hu, S.: Attention-based model with attribute classification for cross-domain person re-identification. In: 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), pp. 9149–9155. IEEE (2021)
Xu, S., Luo, L., Hu, J., Yang, B., Hu, S.: Semantic driven attention network with attribute learning for unsupervised person re-identification. Knowl.-Based Syst. 252, 109354 (2022)
Pervaiz, N., Fraz, M.M., Shahzad, M.: Per-former: rethinking person re-identification using transformer augmented with self-attention and contextual map**. Vis. Comput. 1–16 (2022)
Wang, G., Lai, J., Huang, P., **e, X.: Spatial-temporal person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 33, pp. 8933–8940 (2019)
Zhuo, J., Chen, Z., Lai, J., Wang, G.: Occluded person re-identification. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2018)
Wang, G., Wang, G., Zhang, X., Lai, J., Yu, Z., Lin, L.: Weakly supervised person re-id: differentiable graphical learning and a new benchmark. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 32(5), 2142–2156 (2020)
Layne, R., Hospedales, T.M., Gong, S.: Investigating open-world person re-identification using a drone. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 225–240 (2014)
Schumann, A., Schuchert, T.: Deep person re-identification in aerial images. In: Optics and Photonics for Counterterrorism, Crime Fighting, and Defence XII, vol. 9995, pp. 174–182. SPIE (2016)
Schumann, A., Metzler, J.: Person re-identification across aerial and ground-based cameras by deep feature fusion. In: Automatic Target Recognition XXVII, vol. 10202, pp. 56–67. SPIE (2017)
Mueller, M., Smith, N., Ghanem, B.: A benchmark and simulator for UAV tracking. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 445–461. Springer (2016)
Grigorev, A., Tian, Z., Rho, S., **ong, J., Liu, S., Jiang, F.: Deep person re-identification in UAV images. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2019(1), 1–10 (2019)
Wan, W., Zhong, Y., Li, T., Chen, J.: Rethinking feature distribution for loss functions in image classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 9117–9126 (2018)
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A.N., Kaiser, Ł., Polosukhin, I.: Attention is all you need. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 5998–6008 (2017)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7132–7141 (2018)
Pervaiz, N., Fraz, M., Shahzad, M.: Per-former: rethinking person re-identification using transformer augmented with self-attention and contextual map**. Vis. Comput. 1–16 (2022)
Zhou, Z., Huang, Y., Wang, W., Wang, L., Tan, T.: See the forest for the trees: joint spatial and temporal recurrent neural networks for video-based person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2017)
Wang, X., Girshick, R., Gupta, A., He, K.: Non-local neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7794–7803 (2018)
Chen, D., Li, H., **ao, T., Yi, S., Wang, X.: Video person re-identification with competitive snippet-similarity aggregation and co-attentive snippet embedding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1169–1178 (2018)
Liu, C.-T., Wu, C.-W., Wang, Y.-C.F., Chien, S.-Y.: Spatially and temporally efficient non-local attention network for video-based person re-identification. ar**v preprint ar**v:1908.01683 (2019)
Li, W., Zhu, X., Gong, S.: Harmonious attention network for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2285–2294 (2018)
Chen, T., Ding, S., **e, J., Yuan, Y., Chen, W., Yang, Y., Ren, Z., Wang, Z.: Abd-net: attentive but diverse person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 8351–8361 (2019)
Luo, L., Chen, L., Hu, S., Lu, Y., Wang, X.: Discriminative and geometry-aware unsupervised domain adaptation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 50(9), 3914–3927 (2020)
Luo, L., Chen, L., Hu, S.: Attention regularized Laplace graph for domain adaptation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. (2022)
Li, Y.-J., Yang, F.-E., Liu, Y.-C., Yeh, Y.-Y., Du, X., Frank Wang, Y.-C.: Adaptation and re-identification network: an unsupervised deep transfer learning approach to person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 172–178 (2018)
Huang, Y., Peng, P., **, Y., **ng, J., Lang, C., Feng, S.: Domain adaptive attention model for unsupervised cross-domain person re-identification. ar**v preprint ar**v:1905.10529 (2019)
Zhu, J.-Y., Park, T., Isola, P., Efros, A.A.: Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2223–2232 (2017)
Song, L., Wang, C., Zhang, L., Du, B., Zhang, Q., Huang, C., Wang, X.: Unsupervised domain adaptive re-identification: theory and practice. Pattern Recognit. 102, 107173 (2020)
Luo, L., Chen, L., Hu, S.: Discriminative noise robust sparse orthogonal label regression-based domain adaptation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. (2023)
Zhang, M., Wang, N., Li, Y., Gao, X.: Neural probabilistic graphical model for face sketch synthesis. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31(7), 2623–2637 (2019)
Zhang, M., Li, J., Wang, N., Gao, X.: Compositional model-based sketch generator in facial entertainment. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 48(3), 904–915 (2017)
Zhang, M., Wang, N., Li, Y., Gao, X.: Deep latent low-rank representation for face sketch synthesis. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 30(10), 3109–3123 (2019)
Zhang, M., **n, J., Zhang, J., Tao, D., Gao, X.: Curvature consistent network for microscope chip image super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2022)
Zhang, M., Wu, Q., Zhang, J., Gao, X., Guo, J., Tao, D.: Fluid micelle network for image super-resolution reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 53(1), 578–591 (2022)
Zhang, M., Wu, Q., Guo, J., Li, Y., Gao, X.: Heat transfer-inspired network for image super-resolution reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2022)
Yan, H., Ding, Y., Li, P., Wang, Q., Xu, Y., Zuo, W.: Mind the class weight bias: Weighted maximum mean discrepancy for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2272–2281 (2017)
Long, M., Cao, Y., Wang, J., Jordan, M.: Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 97–105. PMLR (2015)
Gretton, A., Borgwardt, K., Rasch, M., Schölkopf, B., Smola, A.: A kernel method for the two-sample-problem. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 19, 513–520 (2006)
Rubner, Y., Tomasi, C., Guibas, L.J.: The Earth Mover’s Distance as a Metric for Image Retrieval (2000)
Deng, W., Zheng, L., Ye, Q., Kang, G., Yang, Y., Jiao, J.: Image-image domain adaptation with preserved self-similarity and domain-dissimilarity for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 994–1003 (2018)
Fan, X., Jiang, W., Luo, H., Mao, W.: Modality-transfer generative adversarial network and dual-level unified latent representation for visible thermal person re-identification. Vis. Comput. 1–16 (2022)
Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., Bengio, Y.: Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 27 (2014)
Liang, W., Wang, G., Lai, J., Zhu, J.: M2m-gan: Many-to-many generative adversarial transfer learning for person re-identification. ar**: a simple unsupervised cross domain adaptation approach for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 6112–6121 (2019)
Yang, F., Li, K., Zhong, Z., Luo, Z., Sun, X., Cheng, H., Guo, X., Huang, F., Ji, R., Li, S.: Asymmetric co-teaching for unsupervised cross-domain person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 12597–12604 (2020)
Wang, G., Lai, J.-H., Liang, W., Wang, G.: Smoothing adversarial domain attack and p-memory reconsolidation for cross-domain person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10568–10577 (2020)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.-J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 248–255. IEEE (2009)
Hermans, A., Beyer, L., Leibe, B.: In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification. ar**v preprint ar**v:1703.07737 (2017)
Ding, S., Lin, L., Wang, G., Chao, H.: Deep feature learning with relative distance comparison for person re-identification. Pattern Recognit. 48(10), 2993–3003 (2015)
Wang, G., Lai, J., **e, X.: P2snet: Can an image match a video for person re-identification in an end-to-end way? IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 28(10), 2777–2787 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2017.2748698
Li, W., Zhao, R., **ao, T., Wang, X.: Deepreid: Deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 152–159 (2014)
Zheng, L., Shen, L., Tian, L., Wang, S., Wang, J., Tian, Q.: Scalable person re-identification: a benchmark. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1116–1124 (2015)
**ao, T., Li, S., Wang, B., Lin, L., Wang, X.: End-to-end deep learning for person search. ar**v preprint ar**v:1604.01850 2(2), 4 (2016)
Moritz, L., Specker, A., Schumann, A.: A study of person re-identification design characteristics for aerial data. In: Pattern Recognition and Tracking XXXII, vol. 11735, pp. 161–175. SPIE (2021)
Sommer, L., Specker, A., Schumann, A.: Deep learning based person search in aerial imagery. In: Automatic Target Recognition XXXI, vol. 11729, pp. 207–220. SPIE (2021)
Felzenszwalb, P.F., Girshick, R.B., McAllester, D., Ramanan, D.: Object detection with discriminatively trained part-based models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 32(9), 1627–1645 (2010)
Ustinova, E., Ganin, Y., Lempitsky, V.: Multi-region bilinear convolutional neural networks for person re-identification. In: 2017 14th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2017)
Zheng, Z., Zheng, L., Yang, Y.: Unlabeled samples generated by GAN improve the person re-identification baseline in vitro. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3754–3762 (2017)
Zhao, L., Li, X., Zhuang, Y., Wang, J.: Deeply-learned part-aligned representations for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3219–3228 (2017)
Sun, Y., Zheng, L., Deng, W., Wang, S.: Svdnet for pedestrian retrieval. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3800–3808 (2017)
Zhang, X., Luo, H., Fan, X., **ang, W., Sun, Y., **ao, Q., Jiang, W., Zhang, C., Sun, J.: Alignedreid: Surpassing human-level performance in person re-identification. ar**v preprint ar**v:1711.08184 (2017)
Wang, G., Yuan, Y., Chen, X., Li, J., Zhou, X.: Learning discriminative features with multiple granularities for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 274–282 (2018)
Zhou, K., Yang, Y., Cavallaro, A., **ang, T.: Omni-scale feature learning for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3702–3712 (2019)
He, L., Liang, J., Li, H., Sun, Z.: Deep spatial feature reconstruction for partial person re-identification: Alignment-free approach. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7073–7082 (2018)
Chung, D., Tahboub, K., Delp, E.J.: A two stream siamese convolutional neural network for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1983–1991 (2017)
Rao, S., Rahman, T., Rochan, M., Wang, Y.: Video-based person re-identification using spatial-temporal attention networks. ar**v preprint ar**v:1810.11261 (2018)
Li, S., Bak, S., Carr, P., Wang, X.: Diversity regularized spatiotemporal attention for video-based person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 369–378 (2018)
Li, J., Wang, J., Tian, Q., Gao, W., Zhang, S.: Global-local temporal representations for video person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3958–3967 (2019)
Gu, X., Ma, B., Chang, H., Shan, S., Chen, X.: Temporal knowledge propagation for image-to-video person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 9647–9656 (2019)
Liu, Y., Yuan, Z., Zhou, W., Li, H.: Spatial and temporal mutual promotion for video-based person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 33, pp. 8786–8793 (2019)
Subramaniam, A., Nambiar, A., Mittal, A.: Co-segmentation inspired attention networks for video-based person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 562–572 (2019)
Fu, H., Zhang, K., Li, H., Wang, J., Wang, Z.: Spatial temporal and channel aware network for video-based person re-identification. Image Vis. Comput. 118, 104356 (2022)
Han, C., Jiang, B., Tang, J.: Multi-granularity cross attention network for person re-identification. Multimedia Tools Appl. 82(10), 14755–14773 (2023)
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J.-Y., Kweon, I.S.: Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 3–19 (2018)
Selvaraju, R.R., Cogswell, M., Das, A., Vedantam, R., Parikh, D., Batra, D.: Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 618–626 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61773262, 62006152), and the China Aviation Science Foundation (2022Z071057002, 20142057006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, S., Luo, L., Hong, H. et al. Multi-granularity attention in attention for person re-identification in aerial images. Vis Comput 40, 4149–4166 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-03074-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-023-03074-8