Abstract
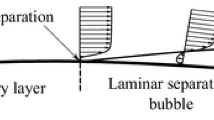
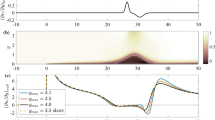
The unsteady dynamics of laminar separation bubble formation and bursting are studied on a NACA 0018 airfoil at an angle of attack of 6° using controlled ramp changes in freestream velocity between limiting Reynolds numbers of \(4.0\times 10^4\) and \(6.0\times 10^4\). Compared to the timescales associated with transition in the separated shear layer, the ramp changes are essentially quasi-steady with a duration of approximately 60 global convective timescales and a maximum non-dimensional acceleration of 0.015. Surface pressure and planar particle image velocimetry measurements are used to explore flow field development during laminar separation bubble formation and bursting transients. At the lower limiting Reynolds number, laminar separation occurs on the suction surface and the airfoil is stalled. At the higher limiting Reynolds number, transition to turbulence in the separated shear layer leads to reattachment in the mean sense and the formation of a short laminar separation bubble. During bubble formation, a steady-state condition is reached approximately 50 convective timescales after the initiation of the ramp change, with the most significant changes to the flow field occurring over a shorter period of time at the end of the transient. The duration of the bursting transient is 1.2 times longer than the formation transient, due to substantial oscillations in the position of the separated shear layer after cessation of reattachment that resemble the step response of a second-order under-damped system. During formation and bursting transients, the changes to the band of unstable frequencies and wavenumbers of the separated shear layer display a similar Reynolds number dependency to quasi-steady flows. Despite the quasi-steady nature of the imposed freestream accelerations, the movement of the separated shear layer exhibits substantial hysteresis.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Alam M, Sandham ND (2000) Direct numerical simulation of ‘short’ laminar separation bubbles with turbulent reattachment. J Fluid Mech 403:223–250. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112099007119
Alferez N, Mary I, Lamballais E (2013) Study of stall development around an airfoil by means of high fidelity large eddy simulation. Flow, Turbul Combust 91(3):623–641. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-013-9483-7
Amitay M, Glezer A (2002) Controlled transients of flow reattachment over stalled airfoils. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 23(5):690–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-727X(02)00165-0
Bastedo WG, Mueller TJ (1986) Spanwise variation of laminar separation bubbles on wings at low Reynolds number. J Aircr 23(9):687–694. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.45363
Boutilier MSH, Yarusevych S (2012) Parametric study of separation and transition characteristics over an airfoil at low Reynolds numbers. Exp Fluids 52(6):1491–1506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-012-1270-z
Boutilier MSH, Yarusevych S (2012) Separated shear layer transition over an airfoil at a low Reynolds number. Phys Fluids 24(8):084–105. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4744989
Brendel M, Mueller TJ (1988) Boundary-layer measurements on an airfoil at low Reynolds numbers. J Aircr 25(7):612–617. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.45631
Burgmann S, Schröder W (2008) Investigation of the vortex induced unsteadiness of a separation bubble via time-resolved and scanning PIV measurements. Exp Fluids 45(4):675–691. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-008-0548-7
Carmichael BH (1981) Low Reynolds Number Airfoil Survey. Tech. Rep. NASA CR-165803, Low Energy Transportation Systems, Capistrano Beach, CA
Dellacasagrande M, Barsi D, Lengani D et al. (2020) Response of a flat plate laminar separation bubble to Reynolds number, free-stream turbulence and adverse pressure gradient variation. Exp Fluids 61(6):128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-020-02958-y
Diwan S, Chetan S, Ramesh O (2006) On the bursting criterion for Laminar separation bubbles. Fluid Mech Appl 78:401–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-4159-4_57
Diwan SS, Ramesh ON (2009) On the origin of the inflectional instability of a laminar separation bubble. J Fluid Mech 629:263–298. https://doi.org/10.1017/S002211200900634X
Dovgal A, Kozlov V, Michalke A (1994) Laminar boundary layer separation: instability and associated phenomena. Prog Aerosp Sci 30(1):61–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/0376-0421(94)90003-5
Franklin GF, Powell JD, Emami-Naeini A (2014) Dynamic Response. In: Feedback Control of Dynamic Systems, 7th edn. Pearson, p 129
Gaster M (1967) The structure and behaviour of Laminar separation bubbles. Tech. Rep. Aeronautical Research Council Reports and Memoranda 3595, London
Hain R, Kähler CJ, Radespiel R (2009) Dynamics of laminar separation bubbles at low-Reynolds-number aerofoils. J Fluid Mech 630:129–153. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112009006661
Hodson HP, Howell RJ (2005) The role of transition in high-lift low-pressure turbines for aeroengines. Prog Aerosp Sci 41(6):419–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paerosci.2005.08.001
Horton HP (1968) Laminar separation bubbles in two and three dimensional incompressible flow. Ph.d. thesis, University of London, London
Hristov G, Ansell PJ (2018) Poststall hysteresis and flowfield unsteadiness on a NACA 0012 airfoil. AIAA J 56(7):2528–2539. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J056774
Jones AR, Cetiner O, Smith MJ (2021) Physics and modeling of large flow disturbances: discrete gust encounters for modern air vehicles. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 54:469–493. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-fluid-031621-085520
Kurelek JW (2016) Transition in a Laminar separation bubble and the effect of acoustic excitation. Master thesis, University of Waterloo
Kurelek JW, Yarusevych S, Kotsonis M (2019) Vortex merging in a laminar separation bubble under natural and forced conditions. Phys Rev Fluids 4(6):063–903. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevFluids.4.063903
Kurelek JW, Tuna BA, Yarusevych S et al. (2021) Three-dimensional development of coherent structures in a two-dimensional Laminar separation bubble. AIAA J 59(2):493–505. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J059700
Marchman JF, Abtahi A (1985) Aerodynamics of an aspect ratio 8 wing at low reynolds numbers. J Aircr 22(7):628–634. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.45176
Marxen O, Henningson DS (2011) The effect of small-amplitude convective disturbances on the size and bursting of a Laminar separation bubble. J Fluid Mech 671:1–33. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112010004957
Marxen O, Lang M, Rist U (2012) Discrete linear local eigenmodes in a separating laminar boundary layer. J Fluid Mech 711:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2012.263
Marxen O, Lang M, Rist U (2013) Vortex formation and vortex breakup in a laminar separation bubble. J Fluid Mech 728:58–90. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2013.222
Mitra A, Ramesh ON (2019) New correlation for the prediction of bursting of a Laminar separation bubble. AIAA J 57(4):1400–1408. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J057658
Mueller TJ (1985) The influence of laminar separation and transition on low Reynolds number airfoil hysteresis. J Aircr 22(9):763–770. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.45199
Nati A, de Kat R, Scarano F et al. (2015) Dynamic pitching effect on a laminar separation bubble. Exp Fluids 56(9):172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-015-2031-6
Ol M, McCauliffe B, Hanff E, et al. (2005) Comparison of Laminar separation bubble measurements on a low reynolds number airfoil in Three Facilities. In: 35th AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference and Exhibit. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Reston, Virigina, https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2005-5149
O’Meara MM, Mueller TJ (1987) Laminar separation bubble characteristics on an airfoil at low Reynolds numbers. AIAA J 25(8):1033–1041. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.9739
Serna J, Lazaro BJ (2015) On the bursting condition for transitional separation bubbles. Aerosp Sci Technol 44:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2014.10.010
Siauw W, Bonnet JP, Tensi J et al. (2010) Transient dynamics of the flow around a NACA 0015 airfoil using fluidic vortex generators. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 31(3):450–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2010.02.028
Simoni D, Lengani D, Ubaldi M et al. (2017) Inspection of the dynamic properties of laminar separation bubbles: free-stream turbulence intensity effects for different Reynolds numbers. Exp Fluids 58(6):66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-017-2353-7
Tani I (1964) Low-speed flows involving bubble separations. Prog Aerosp Sci 5:70–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/0376-0421(64)90004-1
Van Ingen JL (1991) Research on Laminar Separation Bubbles at Delft University of Technology. In: Separated Flows and Jets. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, p 537–556, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-84447-8_73
Welch P (1967) The use of fast Fourier transform for the estimation of power spectra: a method based on time averaging over short, modified periodograms. IEEE Trans Audio Electroacoustics 15(2):70–73. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAU.1967.1161901
Wieneke B (2015) PIV uncertainty quantification from correlation statistics. Meas Sci Technol 26(7):07400074002. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-0233/26/7/074002
Yarusevych S, Kotsonis M (2017) Steady and transient response of a laminar separation bubble to controlled disturbances. J Fluid Mech 813:955–990. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2016.848
Yarusevych S, Sullivan PE, Kawall JG (2009) On vortex shedding from an airfoil in low-Reynolds-number flows. J Fluid Mech 632:245–271. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112009007058
Funding
We acknowledge the support of the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CT and SY designed the experiment and wrote the manuscript. CT performed the experiment.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file 1 (mp4 1480 KB)
Supplementary file 2 (mp4 1602 KB)
Supplementary file 3 (mp4 371 KB)
Supplementary file 4 (mp4 445 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Top**s, C., Yarusevych, S. Transient dynamics of laminar separation bubble formation and bursting. Exp Fluids 64, 57 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-023-03590-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-023-03590-2