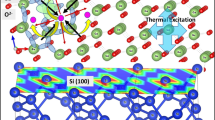
Abstract
In the present work, room temperature epitaxial growth of Zn-doped iron oxide films (Zn: FeOx) was achieved by pulsed laser deposition, on c-cut sapphire substrates without any high temperature thermal treatments before the growth. The nature of the oxide phases (wüstite and/or spinel) present in the films depends on the oxygen pressure during the laser ablation. At the residual vacuum (2 × 10− 7 mbar), the (111) wüstite (Zn: FeO) textures was obtained in the films, while oxygen pressures between 2 × 10− 5 to 2 × 10− 3 mbar led to the growth of the spinel (Zn: Fe3O4) phase on the c-cut sapphire substrate. Moreover, the species emitted by the target in the 2 × 10− 7 to 2 × 10− 5 mbar range, preserve their high kinetic energy which allows an easy crystallization of the film on the substrate at room temperature, leading to the epitaxial growth of the wustite and spinel phases. Magnetic properties through M(H) curves at 10 K and 300 K, of the wüstite-based film grown under 2 × 10− 7 mbar were studied, and an exchange bias due to the presence of Fe3+ cation in the film is observed. Finally, the possible mechanisms of the room temperature epitaxial growth of the oxide films on the substrate are presented and discussed.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
-D.P. Norton, Synthesis and properties of epitaxial electronic oxide thin film materials. Mat. Sci. Eng. R. 43, 139 (2004)
-J. Narayan, Recent progress in film epitaxy across the misfit scale. Acta Mater. 61, 2703 (2013)
-A. Roemer, E. Millon, B. Vincent, A. Boudrioua, O. Pons-Y-Moll, R.M. Defourneau, W. Seiler, Epitaxial PbTiO3 thin films grown on (100) MgO by pulsed-laser deposition for optical waveguiding properties. J. Appl. Phys. 95, 3041 (2004)
-S. Tricot, M. Nistor, E. Millon, C. Boulmer-Leborgne, N.B. Mandache, J. Perrière, W. Seiler, Epitaxial ZnO thin films grown by pulsed electron beam deposition. Surf. Sci. 604, 2024 (2010)
-D. Rasic, R. Sachan, M.F. Chisholm, J. Prater, J. Narayan, Room temperature growth of epitaxial titanium nitride by pulsed-laser deposition. Cryst. Growth. Des. 17, 6634 (2017)
-T. Kiyomura, M. Gomi, Structural and magnetic properties of spinel ferrite epitaxial films pulsed-laser-deposited at low temperature. Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 40, 118 (2001)
-V. Craciun, J. Perriere, N. Bassim, R.K. Singh, D. Craciun, J. Spear, Low temperature growth of epitaxial ZnO films on (001) sapphire by ultraviolet-assisted pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Phys. A 69, S531 (1999)
-M. Yoshimoto, K. Shimozono, T. Maeda, T. Onishi, M. Kumagai, T. Chikyow, O. Ishiyama, M. Shinohara, H. Koinuma, Room-temperature epitaxial growth of CeO2 thin films on Si (111) substrates for fabrication of sharp oxide/silicon interface. Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 34, L688 (1995)
-T. Onishi, M. Yoshimoto, G.H. Lee, T. Maeda, H. Koinuma, Unit cell layer-by-layer heteroepitaxy of BaO thin films at temperatures a low as 20°C. J. Vac Sci. Technol. A 15, 2469 (1997)
-Y.T. Ho, K.S. Chang, K.C. Liu, L.Z. Hsieh, M.H. Liang, Room temperature epitaxial growth of (001) CeO2 on (001) LaAlO3 by pulsed laser deposition. Cryst. Res. Technol. 48, 308 (2013)
-K. Shimomoto, A. Kobayashi, K. Mitamura, K. Ueno, J. Ohta, M. Oshima, H. Fujika, Characteristics of m-plane InN films grown on ZnO substrates at room temperature by pulsed laser deposition. Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 49, 080202 (2010)
-A. Matsuda, R. Yamauchi, D. Shiojiri, G. Tan, S. Kaneko, M. Yoshimoto, Room-temperature selective epitaxial growth of CoO (111) and Co3O4 (111) thin films with atomic steps by pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Suf Sci. 349, 78 (2015)
-X.B. Liu, H.B. Lu, M. He, K.J. **, G.Z. Yang, Room-temperature epitaxial growth of V2O3 films. Sci. China-Phys Mech. Astron. 57, 1866 (2014)
-Y. Kakehi, S. Nakao, K. Satoh, T. Kusaka, Room-temperature epitaxial growth of NiO (111) thin films by pulsed laser deposition. J. Cryst. Growth. 237–239, 591 (2002)
-T. Kiyomura, M. Gomi, Room-temperature epitaxial growth of Ni-Zn ferrite thin films by pulsed laser deposition in high vacuum. Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 36, L1000 (1997)
-A. Matsuda, S. Akiba, M. Kasahara, T. Watanabe, Y. Akita, Y. Kitamoto, T. Tojo, H. Kawaji, T. Atake, K. Koyama, M. Yoshimoto, Fabrication of ferromagnetic ni epitaxial thin film by way of hydrogen reduction of NiO. Thin Solid Films. 516, 3873 (2008)
-M. Yoshimoto, T. Maeda, T. Ohnishi, H. Koinuma, O. Ishiyama, M. Shinohara, M. Kubo, R. Miura, A. Piyamoto, Atomic-scale formation of ultrasmooth surfaces on sapphire substrates for high-quality thin film fabrication. Appl. Phys. Lett. 67, 2615 (1995)
-M. Yoshimoto, A. Sasaki, S. Akiba, Nanoscale epitaxial growth control of oxide thin films by laser molecular beam epitaxy – towards oxide nanoelectronics. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 5, 527 (2004)
-J.T. Gudmundson, A. Anders, A. von Kendell, Foundations of physical vapor deposition with plasma assistance. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 31, 083001 (2022)
-V. Trtik, A. Perez, J. Navarro, C. Ferrater, F. Sanchez, M. Varela, Influence of laser-ablation plume dynamics on the room-temperature epitaxial growth of CeO2 on silicon. Appl. Phys. A 69, S815 (1999)
-M. Yoshimoto, R. Yamauchi, D. Shiojiri, G. Tan, S. Kaneko, A. Matsuda, Room-temperature synthesis of epitaxial oxide thin films for development of unequilibrium structure and novel functionalization. J. Ceram. Soc. Japan. 121, 1 (2013)
-Y.K. Kim, M. Oliveria, Magnetic properties of reactively sputtered Fe1 – x O and Fe3O4 thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 75, 431 (1994)
-Y. Peng, C. Park, D.E. Laughlin, Fe3O4 thin films sputter deposited from iron oxide targets. J. Appl. Phys. 93, 7957 (2003)
-S. Tiwari, R. Prakash, R.J. Choudhary, D.M. Phase, Oriented growth of Fe3O4 thin film on crystalline and amorphous substrates by pulsed laser deposition. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40, 4943 (2007)
-X. Liu, H. Lu, M. He, L. Wang, H. Shi, K. **, C. Wanh, G. Yang, Room-temperature layer-by-layer epitaxial growth and characteristics of Fe3O4 ultrathin films. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 47, 105004 (2014)
-C.-E. Bejjit, V. Rogé, C. Cachoncinlle, C. Hebert, J. Perrière, E. Briand, E. Millon, Iron oxide thin films grown on (00l) sapphire substrate by pulsed-laser deposition. Thin Solid Films. 745, 139101 (2022)
-V. Demange, X. Portier, S. Ollivier, M. Pasturel, T. Roisnel, M. Guilloux-Viry, C. Hebert, M. Nistor, C. Cachoncinlle, E. Millon, J. Perrière, Room-temperature epitaxial growth of Zn-doped iron oxide films on c-, a-, and r-cut sapphire substrates. Cryst. Growth. Des. 23, 8534 (2023)
-Y. Thimont, J. Clatot, M. Nistor, C. Labrugere, A. Rougier, From ZnF2 to ZnO films using pulsed-laser deposition: Optical and electrical properties. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 107, 136–141 (2012)
-P. Atanasov, R.I. Tomov, J. Perrière, R. Eason, N. Vainos, A. Klimi, A. Zherikhin, E. Millon, Growth of nd:potassium gadolinium tungstate thin-film waveguides by pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 2490 (2000)
-J. Clatot, M. Nistor, A. Rougier, Influence of Si concentration on electrical and optical properties of room temperature ZnO:Si thin films. Thin Solid Films. 531, 197 (2013)
-C. Marechal, E. Lacaze, W. Seiler, J. Perrière, Growth mechanisms of laser deposited BiSrCaCuO films on MgO substrates. Phys. C : Superconductivity. 294, 23 (1998)
-E. Le Boulbar, E. Millon, J. Mathias, C. Boulmer-Leborgne, M. Nistor, F. Gherendi, N. Sbaï, J.B. Quoirin, Pure and Nb-doped TiO1.5 films grown by pulsed-laser deposition for transparent p-n homojunctions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 5380 (2011)
-N. Chaoui, E. Millon, J.F. Muller, P. Ecker, W. Bieck, H.N. Migeon, On the role of ambient oxygen in the formation of lead titanate pulsed laser deposition thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 138–139, 256 (1999)
-N. Chaoui, E. Millon, J.F. Muller, P. Ecker, W. Bieck, H.N. Migeon, Perovskite lead titanate PLD thin films: study of oxygen incorporation by O18 tracing techniques. Mat. Chem. Phys. 59, 114 (1999)
-M. Nistor, A. Petitmangin, C. Hebert, W. Seiler, Nanocomposite oxide thin films grown by pulsed energy beam deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 5337 (2011)
-R. Yamauchi, Y. Hamasaki, T. Shibuya, A. Saito, N. Tsuchimine, K. Koyama, A. Matsuda, M. Yoshimoto, Layer matching epitaxy of NiO thin films on atomically stepped sapphire (0001) substrates. Sci. Rep. 5, 14385 (2015)
-Y. Fuji, M. Hara, H. Yuasa, S. Murakami, H. Fukuzawa, Enhancement of magnetoresistance by ultra-thin zn wüstite layer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 132103 (2011)
-S.G. Bhat, P.S. Anil Kumar, Investigation on the origin of exchange bias in epitaxial, oriented and polycrystalline Fe3O4 thin films. AIP Adv. 5, 117123–117121 (2015)
-S. Moll, S.-U. Weber, K.-D. Becker, W. Mader, Solid Solutions in the System Fe1–xO/ZnO at low Oxygen partial pressure. Z. Anorg Allg Chem. 636, 1880 (2010)
-J. Perrière, C. Hebert, M. Nistor, E. Millon, J.J. Ganem, N. Jedrecy, Zn1 – xFexO films: from transparent Fe-diluted ZnO wurtzite to magnetic zn diluted Fe3O4 spinel. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 11239 (2015)
-P. Pant, J.D. Budai, R. Aggarwal, R. Narayan, J. Narayan, Thin film epitaxy and structure property correlations for non-colar ZnO films. Acta Mater. 57, 4426 (2009)
-J. Narayan, K. Dovidenko, A.K. Sharma, S. Oktyabrsky, Defects and interfaces in epitaxial ZnO/α-Al2O3 and AlN/ZnO/ α-Al2O3 heterostructures. J. Appl. Phys. 84, 2597 (1998)
-W. Seiler, M. Nistor, C. Hebert, J. Perrière, Epitaxial undoped indium oxide thin films: structural and physical properties, Solar En. Mat. Solar Cells. 116, 34 (2013)
-M. Nistor, E. Millon, C. Cachoncinlle, W. Seiler, N. Jedrecy, C. Hebert, J. Perrière, Transparent conductive Nd-doped ZnO thin films. J. Phys. D 48, 195103 (2015)
-C. Colliex, T. Manoubi, C. Ortiz, Electron-energy-loss-spectroscopy near-edge fine-structures in the iron-oxygen system. Phys. Rev. B 44, 11402 (1991)
-N. Jedrecy, C. Hebert, J. Perriere, M. Nistor, E. Millon, Magnetic and magneto-transport properties of ZnxFe3 – xO4 – y thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 116, 213903 (2014)
-U. Schwertman, R.M. Cornell, The iron oxides: structure, properties, reactions, occurrence and uses, VCH, Weinheim and New York, 1996. ISBN 3-527-28576-8
-D.V. Dimitrov, K. Unruh, G.C. Hadjipanayis, V. Papafthymiou, A. Simopoulos, Defect clusters in Fe1-xO and their ferrimagnetic properties. J. Appl. Phys. 87, 7022 (2000)
-Y.K. Kim, M. Olivetia, Magnetic properties of reactively sputtered Fe1 – x0 and Fe&, thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 75, 431 (1994)
-C.R.A. Catlow, B.E.F. Fender, Calculations of defect clustering in Fe1-xO. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 8, 3267 (1975)
-M. Gheisari, M. Mozaffari, M. Acet, J. Amighian, Preparation and investigation of magnetic properties of wüstite nanoparticles. J. Magnetism Magn. Mater. 320, 2618 (2008)
-M. Gheisari, M. Mozaffari, M. Niyaifar, J. Amighian, R. Soleimani, Observation of small exchange bias in defect wüstite (Fe0.93O). J. Superconductivity Novel Magnetism. 26, 237 (2013)
-P.V.M. Shameen, L. Mekala, S. Kumar, Structural and magnetic properties of non-stoichiometric Fe1 – xO, AIP Conf. Proc. 1942, 080077 (2018)
-S. Amoruso, B. Toftmann, J. Schou, Thermalization of a UV laser ablation plume in a background gas: from a directed to a diffusion like flow. Phys. Rev. E. 69, 056403 (2004)
-S. Amoruso, B. Toftmann, J. Schou, R. Velotta, X. Wang, Diagnostics of laser ablated plasma plumes. Thin Solid Films. 453–454, 562 (2003)
-T. Wijnands, E.P. Houwman, G. Koster, G. Rijnders, M. Huijben, Numerical modeling of the plasma plume propagation and oxidation during pulsed laser deposition of complex oxide thin films. Phys. Rev. Mat. 4, 103803 (2020)
-X. Portier, C. Hebert, E. Briand, J. Perrière, E. Millon, C. Cachoncinlle, M. Nistor, N. Jedrecy, Microstructure of nanocomposite wurtzite-spinel (fe:ZnO)-(Zn:Fe3O4) epitaxial films. Mat. Chem. Phys. 229, 130 (2019)
-P.B. Mozhaev, J.E. Mozhaeva, A.V. Khoryushin, J.B. Hansen, C.S. Jacobsen, I.K. Bdikin, I.M. Kotelyanskii, V.A. Luzanov, Three dimensional graphoepitaxial growth of oxide films by pulsed laser deposition. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2, 103401 (2018)
-Y-H, Chu, « Van Der Waals oxide heteroepitaxy ». NPJ Quantum Mater. 2, 67 (2017)
-S. Ke, J. **e, C. Chen, P. Lin, X. Zeng, L. Shu, L. Fei, Y. Wang, M. Ye, D. Wang, Van Der Waals epitaxy of Al-doped ZnO film on mica as a flexible transparent heater with ultrafast thermal response. Appl. Phys. Lett. 112, 031905 (2018)
Acknowledgements
XP is grateful to the ANR (Agence Nationale de la Recherche) organisation and the Normandie Region for their financial support in the acquisition of the EELS spectrometer and the FIB setup (ANR-11-EQPX-0020). He also thanks Franck LEMARIE for the preparation of the TEM samples. All the results reported in this manuscript fall within the scope of the research foundation IRMA (FR 3095). Pole figure measurements were performed on Osirix platform (ScanMAT, UAR 2025 University of Rennes-CNRS), which received a financial support from the European Union through the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF), the Département d’Ille et Vilaine, Rennes Métropole and Région Bretagne (2015–2020 CPER project SCANMAT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.P., E.M., and J.P. wrote the original draft of the manuscript. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript, read and approved the final manuscript. X.P. performed the TEM and EELS measurements, analyzed, and interpreted the corresponding data. E.M. analyzed and interpreted the data and managed the article. V.D. performed the XRD pole figure measurements, analyzed, and interpreted the corresponding data. S.O. performed the AFM measurements and analyzed the corresponding data. C.H. synthesized PLD films and performed the magnetic measurements and analyzed the corresponding data. M.N., C.C. and M.G. revised the manuscript. J.P. conceived and designed the project, synthesized PLD films, performed theta/2theta XRD and RBS measurement. He analyzed and interpreted the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Portier, X., Millon, E., Demange, V. et al. Growth and magnetic properties of iron-based oxide thin films deposited by pulsed laser deposition at room temperature. Appl. Phys. A 130, 502 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07674-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07674-6