Abstract
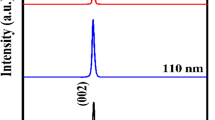
Co-doped ZnO epilayer films were grown by pulsed laser deposition (PLD) on vicinal cut silicon and sapphire substrates. Changes in deposition time were observed as a moderate effect on the quality of the films, and the influence of the thickness on thermoelectric signals from Zn0.9Co0.1O thin films were discussed. The effect of one of the main deposition parameters, the deposition time, on the crystallinity and electron mobility properties of the Zn0.9Co0.1O thin films grown on sapphire was investigated by means of X-ray diffraction (XRD) and laser-induced voltage (LIV) effect. It shown that the XRD rocking curve full-width half-maximun (FWHM) decreased as time increasing, and the LIV signals were observed along the tilting angle of the substrate orientation when the pulsed KrF excimer laser of 248 nm were irradiated on the films. When the films illuminated in pulse lasers, the highest signals occurred in the films with best crystalline quality, and the signals were higher in the films grown on sapphire than those on silicon substrates. It suggested that the electrical resistivity and electron mobility have close relations with not only the crystallinity but also with the interface of the thin films.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Lengfellner, S. Zeuner, W. Prettl, K.F. Renk, Europhys. Lett. 25, 375 (1994)
P.X. Zhang, H.-U. Habermeier, J. Nanomater. 329601 (2008)
X.F. Zhou, Z.M. Jiang, J.H. Lin, X.D. Tang, P.X. Zhang, J. Phys. D, Appl. Phys. 42, 225303 (2009)
K. Wang, Z. Ding, S. Yao, H. Zhang, S. Tan, F. **ong, P.X. Zhang, Mater. Res. Bull. 43, 3327 (2008)
P.X. Zhang, W.K. Lee, G.Y. Zhang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 4026 (2002)
P.X. Zhang, G.Y. Zhang, H.J. Wu, C. Wang, J.B. Peng, L.P. Li, H.-U. Habermeier, Trans. Mater. Res. Soc. Jpn. 29, 1423 (2004)
X.F. Zhou, H. Zhang, Y. Li, X.D. Tang, P.X. Zhang, Chin. Phys. Lett. 27, 018101 (2010)
S. Tripathi, R.J. Choudhary, A. Tripathi, in Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, vol. 266 (2008), pp. 1533–1536
X.F. Zhou, H. Zhang, J. Shang, P.X. Zhang, Thin Solid Films 519, 3026–3028 (2011)
X.H. Li, H.-U. Habermeier, P.X. Zhang, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 211, 232 (2000)
G.M. Gross, F.S. Razavi, R.B. Praus, H.-U. Habermeier, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 211, 22 (2000)
Th. Zahner, R. Stierstorfer, S. Reindl, T. Schauer, A. Penzkofer, H. Lengfellner, Physica C 313, 37 (1999)
T. Olorunyolemi, A. Birnboim, Y. Carmel, O.C. Wilson, I.K. Lloyd, S. Smith, R. Campbell, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 85, 1249 (2004)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the support of this research by the foundation of Shanxi Province University Science and technology research and development project (2010128).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X.F., Lu, M.H., Zhang, H. et al. Effects of crystallinity on laser-induced voltage effect from Zn0.9Co0.1O thin film. Appl. Phys. A 113, 509–513 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-013-7559-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-013-7559-9