Abstract
Objective
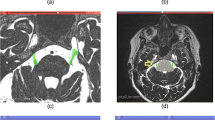
To evaluate the neurovascular compression (NVC) in patients with trigeminal neuralgia (TN) using T2 VISTA and FLAIR VISTA fusion imaging.
Methods
Sixty-six consecutive patients with TN who underwent MR imaging at 3-T between April 2008 and December 2010 were retrospectively reviewed. Multiplanar reconstructions (MPR) of T2 VISTA and FLAIR VISTA fusion imaging were used for image interpretation. The frequency of vascular contact, the segment of compression and the type of vessel were compared between the ipsilateral symptomatic side and the contralateral asymptomatic side.
Results
The frequency of vascular contact on the ipsilateral side and the contralateral side were 95.5% (63/66) and 74.2% (49/66), respectively. The frequency of indentation on the ipsilateral side and contralateral side were 74.2% (49/66) and 21.2% (14/66), and showed a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05). The sensitivity, specificity and odds ratio were 77.8%, 71.4% and 10.7, respectively. There were no significant differences in the involved segment or type of vessel between the ipsilateral side and contralateral side.
Conclusion
MPR of T2 VISTA and FLAIR VISTA fusion imaging is useful in the detection of NVC in patients with TN. Vascular indentation can predict the presence of symptoms in patients with TN.
Key Points
•Fusion MRI with multiplanar reconstruction can detect neurovascular compression in patients with trigeminal neuralgia
•Vascular indentation can predict the presence of symptoms in patients with trigeminal neuralgia
•In patients with trigeminal neuralgia, neurovascular indentation is commoner on the symptomatic side



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson VC, Berryhill PC, Sandquist MA, Ciaverella DP, Nesbit GM, Burchiel KJ (2006) High-resolution three-dimensional magnetic resonance angiography and three-dimensional spoiled gradient-recalled imaging in the evaluation of neurovascular compression in patients with trigeminal neuralgia: a double-blind pilot study. Neurosurgery 58:666–673, discussion 666–673
Love S, Coakham HB (2001) Trigeminal neuralgia: pathology and pathogenesis. Brain 124:2347–2360
Christiano LD, Singh R, Sukul V, Prestigiacomo CJ, Gandhi CD (2011) Microvascular Decompression for Trigeminal Neuralgia: Visualization of Results in a 3D Stereoscopic Virtual Reality Environment. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 54:12–15
Kabatas S, Karasu A, Civelek E, Sabanci AP, Hepgul KT, Teng YD (2009) Microvascular decompression as a surgical management for trigeminal neuralgia: long-term follow-up and review of the literature. Neurosurg Rev 32:87–93, discussion 93–84
Bowsher D, Miles JB, Haggett CE, Eldridge PR (1997) Trigeminal neuralgia: a quantitative sensory perception threshold study in patients who had not undergone previous invasive procedures. J Neurosurg 86:190–192
Jannetta PJ (1967) Arterial compression of the trigeminal nerve at the pons in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 26(Suppl):159–162
Burchiel KJ (2003) A new classification for facial pain. Neurosurgery 53:1164–1166, discussion 1166–1167
Miller J, Acar F, Hamilton B, Burchiel K (2008) Preoperative visualization of neurovascular anatomy in trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 108:477–482
Miller JP, Acar F, Hamilton BE, Burchiel KJ (2009) Radiographic evaluation of trigeminal neurovascular compression in patients with and without trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 110:627–632
Peker S, Dincer A, Necmettin Pamir M (2009) Vascular compression of the trigeminal nerve is a frequent finding in asymptomatic individuals: 3-T MR imaging of 200 trigeminal nerves using 3D CISS sequences. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 151:1081–1088
Yoshino N, Akimoto H, Yamada I et al (2003) Trigeminal neuralgia: evaluation of neuralgic manifestation and site of neurovascular compression with 3D CISS MR imaging and MR angiography. Radiology 228:539–545
Leal PR, Hermier M, Froment JC, Souza MA, Cristino-Filho G, Sindou M (2010) Preoperative demonstration of the neurovascular compression characteristics with special emphasis on the degree of compression, using high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging: a prospective study, with comparison to surgical findings, in 100 consecutive patients who underwent microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 152:817–825
Ueda F, Suzuki M, Fu**aga Y, Kadoya M, Takashima T (1999) In vivo anatomical analysis of arterial contact with trigeminal nerve: detection with three-dimensional spoiled grass imaging. Br J Radiol 72:838–845
Pamir MN, Zirh TA, Ozer AF, Keles GE, Baykan N (1995) Microvascular decompression in the surgical management of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurg Rev 18:163–167
Peker S, Kurtkaya O, Uzun I, Pamir MN (2006) Microanatomy of the central myelin-peripheral myelin transition zone of the trigeminal nerve. Neurosurgery 59:354–359, discussion 354–359
McLaughlin MR, Jannetta PJ, Clyde BL, Subach BR, Comey CH, Resnick DK (1999) Microvascular decompression of cranial nerves: lessons learned after 4400 operations. J Neurosurg 90:1–8
Sindou M, Howeidy T, Acevedo G (2002) Anatomical observations during microvascular decompression for idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia (with correlations between topography of pain and site of the neurovascular conflict). Prospective study in a series of 579 patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 144:1–12, discussion 12–13
Apfelbaum RI (2000) Neurovascular decompression: the procedure of choice? Clin Neurosurg 46:473–498
Sarlani E, Grace EG, Balciunas BA, Schwartz AH (2005) Trigeminal neuralgia in a patient with multiple sclerosis and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J Am Dent Assoc 136:469–476
Lang J (1982) Anatomy, length and blood vessel relations of “central” and “peripheral” paths of intracisternal cranial nerves. Zentralbl Neurochir 43:217–258
Haines SJ, Jannetta PJ, Zorub DS (1980) Microvascular relations of the trigeminal nerve. An anatomical study with clinical correlation. J Neurosurg 52:381–386
Hardy DG, Rhoton AL Jr (1978) Microsurgical relationships of the superior cerebellar artery and the trigeminal nerve. J Neurosurg 49:669–678
Ozsarlak O, Van Goethem JW, Maes M, Parizel PM (2004) MR angiography of the intracranial vessels: technical aspects and clinical applications. Neuroradiology 46:955–972
Zerris VA, Noren GC, Shucart WA, Rogg J, Friehs GM (2005) Targeting the cranial nerve: microradiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia with CISS and 3D-flash MR imaging sequences. J Neurosurg 102(Suppl):107–110
Satoh T, Omi M, Nabeshima M, Onoda K, Date I (2009) Severity analysis of neurovascular contact in patients with trigeminal neuralgia: assessment with the inner view of the 3D MR cisternogram and angiogram fusion imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:603–607
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cha, J., Kim, S.T., Kim, HJ. et al. Trigeminal neuralgia: Assessment with T2 VISTA and FLAIR VISTA fusion imaging. Eur Radiol 21, 2633–2639 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2216-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2216-1