Abstract
Key message
The nuclear Factor YB of Carthamus tinctorius L. increased the content of unsaturated fatty acids by regulating the expression of genes involved in fatty acid synthesis and oil accumulation.
Abstract
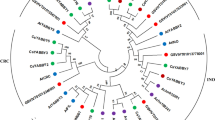
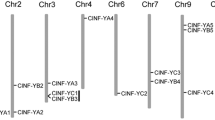
Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) seed oil is rich in linoleic acid and is widely used in food and medicine. Therefore, key genes regulating oil synthesis were mined through genetic engineering to provide genetic resources for improving oil content. Based on the conserved domain of the NF-YB, we screened and identified 14 CtNF-YB transcription factors in the safflower genome and divided them into three subfamilies through phylogenetic analysis. Regulatory motif analysis of the CtNF-YB promoter revealed specific cis-regulatory elements related to abiotic stress, growth, and development. Expression analysis of CtNF-YB family genes showed that non-Leafy Cotyledon 1(non-LEC1) genes were highly expressed in roots, leaves, and flowers; Leafy Cotyledon 1(LEC1) genes were highly expressed during early seed development; and Dr1-like genes were highly expressed in roots, stems, and leaves. CtNF-YB12 was identified as a LEC1 transcription factor based on phylogeny and BLAST alignment. Heterologous CtNF-YB12 expression in Arabidopsis thaliana increased seed pod length and seed size. Moreover, CtNF-YB12 overexpression increased the oil content of seeds, upregulated genes involved in fatty acid biosynthesis and glycolysis, and altered the content of unsaturated fatty acids, including oleic acid (C18:1), linoleic acid (C18:2), and linolenic acid (C18:3), as well as of sucrose, fructose, and glucose. CtNF-YB12 may increase the oil content by regulating key enzyme genes of oil synthesis, so it can be used as a reliable target.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data associated with manuscript is included in this paper and its supplementary materials. The whole-genome sequence of Carthamus tinctorius is derived from NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov), accession number PRJNA399628.
Abbreviations
- FA:
-
Fatty acids
- TAG:
-
Triacylglycerol
- LEC1:
-
Leafy cotyledon 1
- FUS3:
-
FUSCA3
- ABI3:
-
Abscisic acid insensitive 3
- WRI1:
-
WRINKLE1
- RPKM:
-
Reads per kilobase per million mapped reads
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
- GRAVY:
-
Grand average of hydropathicity
- Rc:
-
Ricinus communis
- Ha:
-
Helianthus annuus
- Os:
-
Oryza sativa
- BP:
-
Biological process
- MF:
-
Molecular function
- CC:
-
Cellular component
- DPA:
-
Days post-anthesis
- Kda:
-
Kilo dalton
- WT:
-
Wild type
- NF-Y:
-
Nuclear factor-F
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- At:
-
Arabidopsis thaliana
- Ah:
-
Arachis hypogaea
- Ct:
-
Carthamus tinctorius L.
References
Baud S, Mendoza MS, To A, Harscoët E, Lepiniec L, Dubreucq B (2007) WRINKLED1 specifies the regulatory action of LEAFY COTYLEDON2 towards fatty acid metabolism during seed maturation in Arabidopsis. Plant J 50(5):825–838. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03092.x
Boulard C, Fatihi A, Lepiniec L (1860) Dubreucq B (2017) regulation and evolution of the interaction of the seed B3 transcription factors with NF-Y subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech 10:1069–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2017.08.008
Cai X, Ballif J, Endo S, Davis E, Liang M, Chen D, DeWald D, Kreps J, Zhu T, Wu Y (2007) A putative CCAAT-binding transcription factor is a regulator of flowering timing in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 145(1):98–105. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.102079
Cernac A, Benning C (2004) WRINKLED1 encodes an AP2/EREB domain protein involved in the control of storage compound biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 40(4):575–585. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02235.x
Chakradhari S, Perkons I, Miina I, Sipeniece E, Górna P (2020) Profiling of the bioactive components of safflower seeds and seed oil: cultivated (carthamus tinctorius L.) vs. wild (carthamus oxyacantha m. bieb). Eur Food Res Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-019-03414-w
Chen W, Cheng Z, Liu L, Wang M, You X, Wang J, Zhang F, Zhou C, Zhang Z, Zhang H, You S, Wang Y, Luo S, Zhang J, Wang J, Wang J, Zhao Z, Guo X, Lei C, Zhang X, Lin Q, Ren Y, Zhu S, Wan J (2019) Small Grain and Dwarf 2, encoding an HD-Zip II family transcription factor, regulates plant development by modulating gibberellin biosynthesis in rice. Plant Sci 288:110208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2019.110208
Chen B, Zhang G, Li P, Yang J, Guo L, Benning C, Wang X, Zhao J (2020) Multiple GmWRI1s are redundantly involved in seed filling and nodulation by regulating plastidic glycolysis, lipid biosynthesis and hormone signalling in soybean (Glycine max). Plant Biotechnol J 18(1):155–171. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13183
Dai JH, Hu AQ, Zhang JS, Liao WH, Ma HY, Wu JZ, Yu Y, Cao SJ (2021) NF-YB-mediated active responses of plant growth under salt and temperature stress in Eucalyptus grandis. Plants (basel) 10(6):1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10061107
Das S, Parida SK, Agarwal P, Tyagi AK (2019) Transcription factor OsNF-YB9 regulates reproductive growth and development in rice. Planta 250(6):1849–1865. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-019-03268-2
Den Hartigh LJ (2019) Conjugated linoleic acid effects on cancer, obesity, and atherosclerosis: a review of pre-clinical and human trials with current perspectives. Nutrients 11(2):370. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11020370
Devic M, Roscoe T (2016) Seed maturation: simplification of control networks in plants. Plant Sci 252:335–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2016.08.012
Ding Y, Yang L, Zhang S, Wang Y, Du Y, Pu J, Peng G, Chen Y, Zhang H, Yu J, Hang H, Wu P, Yang F, Yang H, Steinbüchel A, Liu P (2012) Identification of the major functional proteins of prokaryotic lipid droplets. J Lipid Res 53(3):399–411. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M021899
Ding X, Zeng J, Huang L, Li X, Song S, Pei Y (2019) Senescence-induced expression of ZmSUT1 in cotton delays leaf senescence while the seed coat-specific expression increases yield. Plant Cell Rep 38(8):991–1000. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-019-02421-1
Dolfini D, Gatta R, Mantovani R (2012) NF-Y and the transcriptional activation of CCAAT promoters. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 47(1):29–49. https://doi.org/10.3109/10409238.2011.628970
Elahi N, Duncan RW, Stasolla C (2016) Modification of oil and glucosinolate content in canola seeds with altered expression of Brassica napus LEAFY COTYLEDON1. Plant Physiol Biochem 100:52–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.12.022
Elhiti M, Yang C, Chan A, Durnin DC, Belmonte MF, Ayele BT, Tahir M, Stasolla C (2012) Altered seed oil and glucosinolate levels in transgenic plants overexpressing the Brassica napus SHOOTMERISTEMLESS gene. J Exp Bot 63(12):4447–4461. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ers125
Grimberg Å (2009) Carbon partitioning between starch and oil in Avena sativa (oat) and Arabidopsis thaliana. Acta Universitatis Agriculturae Sueciae. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ern266
Hill LM, Rawsthorne S (2000) Carbon supply for storage-product synthesis in develo** seeds of oilseed rape. Biochem Soc Trans 28(6):667–669
Hiromitsu K, Toshiki I, Toshiaki M, Shin K, Maki Y, Jun-ichi O (2014) Arabidopsis glycerol-3-phosphate permease 4 is localized in the plastids and involved in the accumulation of seed oil. Plant Bio 31(159):165. https://doi.org/10.5511/plantbiotechnology.14.0222a
Huang KL, Tian J, Wang H, Fu YF, Li Y, Zheng Y, Li XB (2021) Fatty acid export protein BnFAX6 functions in lipid synthesis and axillary bud growth in Brassica napus. Plant Physiol 186(4):2064–2077. https://doi.org/10.1093/plphys/kiab229
Hwang YH, Kim SK, Lee KC, Chung YS, Lee JH, Kim JK (2016) Functional conservation of rice OsNF-YB/YC and Arabidopsis AtNF-YB/YC proteins in the regulation of flowering time. Plant Cell Rep 35(4):857–865. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-015-1927-1
Jako C, Kumar A, Wei Y, Zou J, Barton DL, Giblin EM, Covello PS, Taylor DC (2001) Seed-specific over-expression of an Arabidopsis cdna encoding a diacylglycerol acyltransferase enhances seed oil content and seed weight. Plant Physiol 126(2):861–874. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.126.2.861
**g G, Tang D, Yao Y, Su Y, Shen Y, Bai Y, **g W, Zhang Q, Lin F, Guo D, Zhang W (2021) Seed specifically over-expressing DGAT2A enhances oil and linoleic acid contents in soybean seeds. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 568:143–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.06.087
Kong Q, Yang Y, Guo L, Yuan L, Ma W (2020) Molecular basis of plant oil biosynthesis: insights gained from studying the WRINKLED1 transcription factor. Front Plant Sci 11:24. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00024
Lepiniec L, Devic M, Roscoe TJ, Bouyer D, Zhou DX, Boulard C, Baud S, Dubreucq B (2018) Molecular and epigenetic regulations and functions of the LAFL transcriptional regulators that control seed development. Plant Reprod 31(3):291–307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-018-0337-2
Li N, Zhang S, Zhao Y, Li B, Zhang J (2011) Over-expression of AGPase genes enhances seed weight and starch content in transgenic maize. Planta 233(2):241–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1296-5
Li D, Yu J, Wang Q, Hu B, Chen C, Hou K, Wu W (2019a) Sequence variations and expression analysis of FAD2 gene among safflower materials with different linoleic acid content in seed oil. Acta Physiol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-019-2928-4
Li M, Li G, Liu W, Dong X, Zhang A (2019b) Genome-wide analysis of the NF-Y gene family in peach (Prunus persica L.). BMC Genomics 20(1):612. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-5968-7
Liu X, Zhang D, Zhang J, Chen Y, Liu X, Fan C, Wang RR, Hou Y, Hu Z (2021a) Overexpression of the transcription factor AtLEC1 significantly improved the lipid content of chlorella ellipsoidea. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 9:626162. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021a.626162
Liu Z, Li Y, Zhu J, Ma W, Li Z, Bi Z, Sun C, Bai J, Zhang J, Liu Y (2021b) Genome-wide identification and analysis of the NF-Y gene family in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Front Genet 12:739989. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.739989
Lu Y, Chi M, Li L, Li H, Noman M, Yang Y, Ji K, Lan X, Qiang W, Du L, Li H, Yang J (2018) Genome-wide identification, expression profiling, and functional validation of Oleosin gene family in Carthamus tinctorius L. Front Plant Sci 9:1393. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01393
Manan S, Ahmad MZ, Zhang G, Chen B, Haq BU, Yang J, Zhao J (2017) Soybean LEC2 regulates subsets of genes involved in controlling the biosynthesis and catabolism of seed storage substances and seed development. Front Plant Sci 8:1604. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01604
Quach TN, Nguyen HT, Valliyodan B, Joshi T, Xu D, Nguyen HT (2015) Genome-wide expression analysis of soybean NF-Y genes reveals potential function in development and drought response. Mol Genet Genom 290(3):1095–1115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-014-0978-2
Ruuska SA, Girke T, Benning C, Ohlrogge JB (2002) Contrapuntal networks of gene expression during Arabidopsis seed filling. Plant Cell 14(6):1191–1206. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.000877
Saidi A, Hajibarat Z (2019) Characterization of cis-elements in hormonal stress-responsive genes in Oryza sativa. Asia Pac J Mol Biol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.35118/apjmbb.2019.027.1.10
Salimonti A, Carbone F, Romano E, Pellegrino M, Benincasa C, Micali S, Tondelli A, Conforti FL, Perri E, Ienco A, Zelasco S (2020) Association study of the 5’UTR intron of the FAD2–2 gene with oleic and linoleic acid content in Olea europaea L. Front Plant Sci 11:66. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00066
Sato H, Suzuki T, Takahashi F, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2019) NF-YB2 and NF-YB3 have functionally diverged and differentially induce drought and heat stress-specific genes. Plant Physiol 180(3):1677–1690. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.19.00391
Shao J, Haider I, **ong L, Zhu X, Hussain RMF, Övernäs E, Meijer AH, Zhang G, Wang M, Bouwmeester HJ, Ouwerkerk PBF (2018) Functional analysis of the HD-Zip transcription factor genes Oshox12 and Oshox14 in rice. PLoS ONE 13(7):e0199248. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0199248
Shen B, Allen WB, Zheng P, Li C, Glassman K, Ranch J, Nubel D, Tarczynski MC (2010) Expression of ZmLEC1 and ZmWRI1 increases seed oil production in maize. Plant Physiol 153(3):980–987. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.157537
Sun J, Cui X, Teng S, Kunnong Z, Wang Y, Chen Z, Sun X, Wu J, Ai P, Quick WP, Lu T, Zhang Z (2020) HD-ZIP IV gene Roc8 regulates the size of bulliform cells and lignin content in rice. Plant Biotechnol J 18(12):2559–2572. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13435
Tan H, Yang X, Zhang F, Zheng X, Qu C, Mu J, Fu F, Li J, Guan R, Zhang H, Wang G, Zuo J (2011) Enhanced seed oil production in canola by conditional expression of Brassica napus LEAFY COTYLEDON1 and LEC1-LIKE in develo** seeds. Plant Physiol 156(3):1577–1588. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.175000
Tang G, Xu P, Ma W, Wang F, Liu Z, Wan S, Shan L (2018) Seed-specific expression of AtLEC1 increased oil content and altered fatty acid composition in seeds of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Front Plant Sci 9:260. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00260
Thirumurugan T, Ito Y, Kubo T, Serizawa A, Kurata N (2008) Identification, characterization and interaction of HAP family genes in rice. Mol Genet Genom 279(3):279–289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-007-0312-3
Weselake RJ, Taylor DC, Rahman MH, Shah S, Laroche A, McVetty PBE, Harwood JL (2009) Increasing the flow of carbon into seed oil. Biotechnol Adv 27(6):866–878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2009.07.001
Wood CC, Okada S, Taylor MC, Menon A, Mathew A, Cullerne D, Stephen SJ, Allen RS, Zhou XR, Liu Q (2018) Seed-specific RNAi in safflower generates a superhigh oleic oil with extended oxidative stability. Plant Biotechnol J 16:1788–1796. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12915
**ong Y, Ren Y, Li W, Wu F, Yang W, Huang X, Yao J (2019) NF-YC12 is a key multi-functional regulator of accumulation of seed storage substances in rice. J Exp Bot 70(15):3765–3780. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erz168
Xu Y, Holic R, Li D, Pan X, Mietkiewska E, Chen G, Ozga J, Weselake RJ (2018) Substrate preferences of long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase and diacylglycerol acyltransferase contribute to enrichment of flax seed oil with α-linolenic acid. Biochem J 475(8):1473–1489. https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20170910
Yang W, Lu Z, **ong Y, Yao J (2017) Genome-wide identification and co-expression network analysis of the os nf-y gene family in rice. Crop J. 1(5):23–33
Zhao H, Wu D, Kong F, Lin K, Zhang H, Li G (2017) The Arabidopsis thaliana nuclear factor Y transcription factors. Front Plant Sci 7:2045. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.02045
Zheng P, Allen WB, Roesler K, Williams ME, Zhang S, Li J, Glassman K, Ranch J, Nubel D, Solawetz W, Bhattramakki D, Llaca V, Deschamps S, Zhong GY, Tarczynski MC, Shen B (2008) A phenylalanine in DGAT is a key determinant of oil content and composition in maize. Nat Genet 40(3):367–372. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.85
Zhu YX, Yang L, Liu N, Yang J, Zhou XK, **a YC, He Y, He YQ, Gong HJ, Ma DF, Yin JL (2019) Genome-wide identification, structure characterization, and expression pattern profiling of aquaporin gene family in cucumber. BMC Plant Biol 19(1):345. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1953-1
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the great experimental support of the Public Platform of Bioreactor and Drug Development Research Center, College of Life Sciences, Jilin Agricultural University.
Funding
This work was funded by National Outstanding Youth Science Fund Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (31801396) and Education Department of Jilin Province (JJKH20200319KJ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JY conceived and designed the experiments. SND conducted most of the experiments and wrote the manuscript. RNW, CLT, LXL, SW, CJ, YLL, RD, and LND participated in experiments and data collection. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Amit Dhingra.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, S., Wang, R., Tao, C. et al. Genome-wide analysis of CtNF-YB and lipid synthesis regulation of CtNF-YB12 in Carthamus tinctorius L.. Plant Cell Rep 42, 57–72 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-022-02936-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-022-02936-0