Abstract
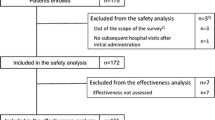
We aimed to obtain the effects of immunosuppressive doses on the QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus (QFT-Plus) test results in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) patients. Besides this, the impact of the TB2 tube in QFT-Plus test was also investigated. This study included RA patients registered to HURBIO and were screened via QFT-Plus test for latent tuberculosis between January 2018 and March 2021, before the initiation of treatment of biologic/targeted-synthetic disease modifying anti-rheumatismal drugs (b/ts-DMARDs). Patients using methotrexate ≥ 10 mg or leflunomide (any dose) or steroids (≥ 7.5 mg prednisolone) at the time of QFT-Plus test were classified as the “high dose” group and the rest of the patients constituted the “low dose” group. The study included 534 RA patients; 353 [66.1%] in the high-dose group and 181 [33.9%] in the low-dose group. While QFT-Plus test was positive in 10.5% (37/353) patients in the high-dose group, it was positive in 20.4% (37/181) patients in the low-dose group (p < 0.001). The percentage of QFT-Plus indeterminate results were similar (around 2%) in both groups. The contribution of the TB2 tube to QFT-Plus test positivity was 6.89%. During a median (inter-quartile range) follow-up period of 23 (7–38) months under treatment of b/ts-DMARDs, latent TB reactivation was not observed. Primer active tuberculosis disease developed in two patients. Positive test results of Interferon-Gamma Release Assays (IGRAs) could decrease as immunosuppressive treatment doses increase in patients with RA and addition of the TB2 tube could increase test sensitivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available on request due to privacy or other restrictions.
References
Dinser R, Fousse M, Sester U, Albrecht K, Singh M, Kohler H, Muller-Ladner U, Sester M (2008) Evaluation of latent tuberculosis infection in patients with inflammatory arthropathies before treatment with TNF-alpha blocking drugs using a novel flow-cytometric interferon-gamma release assay. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47(2):212–218. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kem351
Lee H, Park HY, Jeon K, Jeong BH, Hwang JW, Lee J, Cha HS, Koh EM, Kang ES, Koh WJ (2015) QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube assay for screening arthritis patients for latent tuberculosis infection before starting anti-tumor necrosis factor treatment. PLoS ONE 10(3):e0119260. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119260
Seyhoglu E, Uyaroglu OA, Erden A, Kilic L, Karadag O, Akdogan A, Bilgen SA, Ertenli I, Kiraz S, Kalyoncu U (2021) QuantiFERON(R)-TB Gold In-Tube test can be used for screening latent tuberculosis before biological treatment in a Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG)-vaccinated country: the HUR-BIO single-center real-life results. Clin Rheumatol 40(5):2027–2035. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05443-3
Carmona L, Gomez-Reino JJ, Rodriguez-Valverde V, Montero D, Pascual-Gomez E, Mola EM, Carreno L, Figueroa M, Group B (2005) Effectiveness of recommendations to prevent reactivation of latent tuberculosis infection in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor antagonists. Arthritis Rheum 52(6):1766–1772. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.21043
Fragoulis GE, Nikiphorou E, Dey M et al (2022) EULAR recommendations for screening and prophylaxis of chronic and opportunistic infections in adults with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases [published online ahead of print, 2022 Nov 3]. Ann Rheum Dis. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard-2022-223335
Farhat M, Greenaway C, Pai M, Menzies D (2006) False-positive tuberculin skin tests: what is the absolute effect of BCG and non-tuberculous mycobacteria? Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 10(11):1192–1204
Koydemir HC, Kulah H, Alp A, Uner AH, Hascelik G, Ozgen C (2014) A Fully microfabricated electrochemical sensor and its implementation for detection of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. IEEE Sens J 14(6):1844–1851. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2014.2305152
Barcellini L, Borroni E, Brown J, Brunetti E, Campisi D, Castellotti PF, Codecasa LR, Cugnata F, Di Serio C, Ferrarese M, Goletti D, Lipman M, Rancoita PM, Russo G, Tadolini M, Vanino E, Cirillo DM (2016) First evaluation of QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus performance in contact screening. Eur Respir J 48(5):1411–1419. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00510-2016
Allen NP, Swarbrick G, Cansler M, Null M, Salim H, Miyamasu M, Howard J, Boyle J, Lewinsohn D, Lewinsohn D (2018) Characterization of specific CD4 and CD8 T-cell responses in QuantiFERON TB Gold-Plus TB1 and TB2 tubes. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 113:239–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tube.2018.10.014
Nikiphorou E, Buch MH, Hyrich KL (2017) Biologics registers in RA: methodological aspects, current role and future applications. Nat Rev Rheumatol 13(8):503–510. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2017.81
Hong JY, Park SY, Kim A, Cho SN, Hur YG (2019) Comparison of QFT-Plus and QFT-GIT tests for diagnosis of M. tuberculosis infection in immunocompetent Korean subjects. J Thorac Dis 11(12):5210–5217. https://doi.org/10.21037/jtd.2019.12.11
QIAGEN (2016) QuantiFERON-TB Gold plus (QFT-Plus) ELISA Package Insert Rev. 04.
Brock I, Ruhwald M, Lundgren B, Westh H, Mathiesen LR, Ravn P (2006) Latent tuberculosis in HIV positive, diagnosed by the M. tuberculosis specific interferon-gamma test. Respir Res 7(1):56. https://doi.org/10.1186/1465-9921-7-56
Luetkemeyer AF, Charlebois ED, Flores LL, Bangsberg DR, Deeks SG, Martin JN, Havlir DV (2007) Comparison of an interferon-gamma release assay with tuberculin skin testing in HIV-infected individuals. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 175(7):737–742. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200608-1088OC
Ponce de Leon D, Acevedo-Vasquez E, Alvizuri S, Gutierrez C, Cucho M, Alfaro J, Perich R, Sanchez-Torres A, Pastor C, Sanchez-Schwartz C, Medina M, Gamboa R, Ugarte M (2008) Comparison of an interferon-gamma assay with tuberculin skin testing for detection of tuberculosis (TB) infection in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in a TB-endemic population. J Rheumatol 35(5):776–781
Igari H, Ishikawa S, Nakazawa T, Oya Y, Futami H, Tsuyuzaki M, Suzuki K, Matsumura R (2018) Lymphocyte subset analysis in QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus and T-Spot.TB for latent tuberculosis infection in rheumatoid arthritis. J Infect Chemother 24(2):110–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiac.2017.09.012
Martin J, Walsh C, Gibbs A, McDonnell T, Fearon U, Keane J, Codd MB, Dodd J, Veale D, Fitzgerald O, Bresnihan B (2010) Comparison of interferon gamma release assays and conventional screening tests before tumour necrosis factor alpha blockade in patients with inflammatory arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 69(1):181–185. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2008.101857
Matulis G, Juni P, Villiger PM, Gadola SD (2008) Detection of latent tuberculosis in immunosuppressed patients with autoimmune diseases: performance of a Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen-specific interferon gamma assay. Ann Rheum Dis 67(1):84–90. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2007.070789
Belard E, Semb S, Ruhwald M, Werlinrud AM, Soborg B, Jensen FK, Thomsen H, Brylov A, Hetland ML, Nordgaard-Lassen I, Ravn P (2011) Prednisolone treatment affects the performance of the QuantiFERON gold in-tube test and the tuberculin skin test in patients with autoimmune disorders screened for latent tuberculosis infection. Inflamm Bowel Dis 17(11):2340–2349. https://doi.org/10.1002/ibd.21605
Yu DT, Clements PJ, Paulus HE, Peter JB, Levy J, Barnett EV (1974) Human lymphocyte subpopulations. Effect of corticosteroids. J Clin Invest 53(2):565–571. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI107591
Kleinert S, Kurzai O, Elias J, Marten K, Engelke C, Feuchtenberger M, Sandstede J, Frosch M, Tony HP, Kneitz C (2010) Comparison of two interferon-gamma release assays and tuberculin skin test for detecting latent tuberculosis in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. Ann Rheum Dis 69(4):782–784. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.113829
Pieterman ED, Liqui Lung FG, Verbon A, Bax HI, Ang CW, Berkhout J, Blaauw G, Brandenburg A, van Burgel ND, Claessen A, van Dijk K, Heron M, Hooghiemstra M, Leussenkamp-Hummelink R, van Lochem E, van Loo IHM, Mulder B, Ott A, Pontesilli O, Reuwer A, Rombouts P, Saegeman V, Scholing M, Vainio S, de Steenwinkel JEM (2018) A multicentre verification study of the QuantiFERON((R))-TB Gold Plus assay. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 108:136–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tube.2017.11.014
Venkatappa TK, Punnoose R, Katz DJ, Higgins MP, Banaei N, Graviss EA, Belknap RW, Ho CS (2019) Comparing QuantiFERON-TB gold plus with other tests to diagnose Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J Clin Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00985-19
Funding
No specific funding was received from any bodies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors to carry out the work described in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the analysis: ZO, AO, ME, EB, LK, SK, ZS, BŞ, and OK. Collected the data: ZO, AO, ME, EB, LK, SK, ZS, BŞ, and OK. Contributed data or analysis tools: ZO, AO, ME, EB, LK, SK, ZS, BŞ, and OK. Performed the analysis: ZO, AO, ME, EB, LK, SK, ZS, BŞ, and OK. Wrote the paper: ZO, AO, ME, EB, LK, SK, ZS, BŞ, and OK. Other contribution: ZO, AO, ME, EB, LK, SK, ZS, BŞ, and OK.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
EB received honorary from AbbVie, Novartis, and UCB-Pharma. SK received honorary from AbbVie, Amgen, Johnson, and Johnson, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB-Pharma. OK received honorary from AbbVie, Aristea, Roche, Novartis, Viela-Bio, Zenas Biopharma, Abdi İbrahim, Celltrion, UCB-Pharma, and Menarini. All of the other authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval
Ethical approval was obtained from Hacettepe University Institutional Review Board (GO21/595, 04/05/2021).
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from each patient regarding the use of clinical data for research purposes. The study was in accordance with the 2013 amendment of the Helsinki declaration.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ozsoy, Z., Ozdemir, A., Ekici, M. et al. Do the drug doses of conventional synthetic DMARDs used for the treatment of biologic/targeted-synthetic DMARDs naive rheumatoid arthritis patients affect QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus test results?. Rheumatol Int 43, 1445–1451 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-023-05320-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-023-05320-7