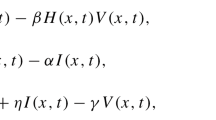Abstract
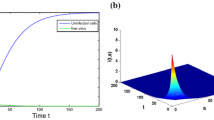
In this paper, we focus on the global dynamics of a multiscale hepatitis C virus model. The model takes into account the evolution of the virus in cells and RNA. For the model, we establish the globally asymptotical stability of both infection-free and infected equilibria. We first give the basic reproduction number \({\mathcal {R}}_0\) of the model, and then find that the system holds infected equilibrium when \({\mathcal {R}}_0>1\). Using eigenvalue analysis, Lyapunov functional, persistence theory and so on, it is proved that infection-free and infected equilibria are globally asymptotically stable when \({\mathcal {R}}_0<1\) and \({\mathcal {R}}_0>1\), respectively. Thus, extinction and persistence of viruses in cells are theoretically judged. Finally, we show our theoretical results by means of numerical simulation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arends J, van der Meer J, Posthouwer D, Kortmann W, Brinkman K, van Assen S, Smit C, van der Valk M, van der Ende M, Schinkel J et al (2015) Favourable svr12 rates with boceprevir or telaprevir triple therapy in hiv/hcv coinfected patients. Neth J Med 73(7):324–330
Avila-Vales E, Chan-Chí N, García-Almeida GE, Vargas-De-León C (2015) Stability and hopf bifurcation in a delayed viral infection model with mitosis transmission. Appl Math Comput 259:293–312
Birger R, Kouyos R, Dushoff J, Grenfell B (2015) Modeling the effect of hiv coinfection on clearance and sustained virologic response during treatment for hepatitis c virus. Epidemics 12:1–10
Chekroun A, Frioui MN, Kuniya T, Touaoula TM (2019) Global stability of an age-structured epidemic model with general lyapunov functional. Math Biosci Eng 16:1525–1553
Corson S, Greenhalgh D, Hutchinson S (2012) Mathematically modelling the spread of hepatitis c in injecting drug users. Math med biol: a j IMA 29(3):205–230
Elbasha EH (2013) Model for hepatitis c virus transmissions. Math Biosci & Eng 10(4):1045–1065
Frioui MN, Touaoula TM, Ainseba B (2020) Global dynamics of an age-structured model with relapse. Discret & Contin Dyn Sys-B 25(6):2245–2270
Guedj J, Dahari H, Rong L, Sansone ND, Nettles RE, Cotler SJ, Layden TJ, Uprichard SL, Perelson AS (2013) Modeling shows that the ns5a inhibitor daclatasvir has two modes of action and yields a shorter estimate of the hepatitis c virus half-life. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110(10):3991–3996
Kitagawa K, Kuniya T, Nakaoka S, Asai Y, Watashi K, Iwami S (2019) Mathematical analysis of a transformed ode from a pde multiscale model of hepatitis c virus infection. Bull Math Biol 81(5):1427–1441
Lavanchy D (2009) The global burden of hepatitis c. Liver Int 29:74–81
Li J, Wang K, Yang Y (2011) Dynamical behaviors of an hbv infection model with logistic hepatocyte growth. Math Comput Model 54(1–2):704–711
Magal P, McCluskey C, Webb G (2010) Lyapunov functional and global asymptotic stability for an infection-age model. Appl Anal 89(7):1109–1140
Magal P, Ruan S (2014) Susceptible-infectious-recovered models revisited: From the individual level to the population level. Math Biosci 250:26–40
Magal P, Ruan S (2018) Theory and applications of abstract semilinear Cauchy problems, vol 201. Springer, Switzerland
Martcheva M, Castillo-Chavez C (2003) Diseases with chronic stage in a population with varying size. Math Biosci 182(1):1–25
Neumann AU, Lam NP, Dahari H, Gretch DR, Wiley TE, Layden TJ, Perelson AS (1998) Hepatitis c viral dynamics in vivo and the antiviral efficacy of interferon-\(\alpha \) therapy. Sci 282(5386):103–107
Pinto CM, Carvalho A (2015) Effects of treatment, awareness and condom use in a coinfection model for hiv and hcv in msm. J Biol Syst 23(02):165–193
Rong L, Guedj J, Dahari H, Coffield DJ Jr, Levi M, Smith P, Perelson AS (2013) Analysis of hepatitis c virus decline during treatment with the protease inhibitor danoprevir using a multiscale model. PLoS Comput Biol 9(3):e1002959
Rong L, Perelson AS (2013) Mathematical analysis of multiscale models for hepatitis c virus dynamics under therapy with direct-acting antiviral agents. Math Biosci 245(1):22–30
Smith HL, Thieme HR (2011) Dynamical systems and population persistence, vol 118. American Mathematical Soc, Providence, Rhode Island
Soufiane B, Touaoula TM (2016) Global analysis of an infection age model with a class of nonlinear incidence rates. J Math Anal Appl 434(2):1211–1239
Sun C, Hsieh YH (2010) Global analysis of an seir model with varying population size and vaccination. Appl Math Model 34(10):2685–2697
Westbrook RH, Dusheiko G (2014) Natural history of hepatitis c. J Hepatol 61(1):S58–S68
Xu J, Zhou Y (2016) Bifurcation analysis of hiv-1 infection model with cell-to-cell transmission and immune response delay. Math biosci eng: MBE 13(2):343–367
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant numbers 11301263, 11701275, 11701306]; the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation [grant number 2018M630547]; the Talent introduction project of Shanghai Institute of Technology [grant number YJ2022-26] the Natural Science Fund Development Project by Nan**g Tech University; the Second Batch of High Level Demonstration Project for Sino-foreign Cooperative Education in Jiangsu; and the China Scholarship Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, Y., Li, Y. & Zheng, D. Global dynamics of an age-dependent multiscale hepatitis C virus model. J. Math. Biol. 85, 21 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-022-01773-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-022-01773-9