Abstract
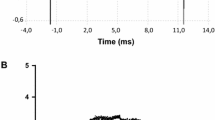
The pulsed electric field (PEF) of μs duration can induce electroporation by causing permanent damage to the membrane, leading to cell death. The microbe was treated by a homemade PEF generator instrument. The sterilization effect of PEF on the Rhizoctonia solani was observed by scanning electron microscope (SEM) and transmission electron microscope (TEM), and the leakage of the intracellular contents was measured with a conductometer and an ultraviolet spectrophotometer. The increases in the electrical conductivity and the optical density (OD) value indicated that the cell membrane was damaged, and the intracellular contents overflowed. As a result, according to our experimental conditions, the optimum condition was the high-pulsed electric voltage of 26 kV, and the treatment time was 4 min. It could be concluded that the PEF could damage the cell membrane, and the ratio of electroporation reached 100%, which provides a new method of killing R. solani efficiently.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to privacy reasons but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Manabe Y, Nakagawa R, Su Z, Maetani M, Teranishi K, Shimomura N et al (2011) Influences of pulsed electric fields on the gene expression of pathogenic bacteria. Pulsed Power Conference 99(3):38–45
Castro A, Barbosa-Cánovas G, Swanson B (2010) Microbial internation of foods by pulsed electric fields. J Food Process Pres 17:47–73
Corovic S, Lackovic I, Sustaric P, Sustar T, Rodic T, Miklavcic D (2013) Modeling of electric field distribution in tissues during electroporation. Biomed Eng Online 12(1):16
Guo F, Yao C, Li C, Mi Y, Peng Q, Tang J (2014) In vivo evidences of nanosecond pulsed electric fields for melanoma malignancy treatment on tumor-bearing BALB/c nude mice. Technol Cancer Res Treat 13:337–344
Wu S, Guo J, Wei W, Zhang J, Fang J, Beebe SJ (2014) Enhanced breast cancer therapy with nsPEFs and low concentrations of gemcitabine. Cancer Cell Int 14:1–12
Wu S, Wang Y, Guo J, Chen Q, Zhang J, Fang J (2014) Nanosecond pulsed electric fields as a novel drug free therapy for breast cancer: an in vivo study. Cancer Lett 343:268–274
Zhu B, Su H, Fang Z, Wu G, Wei X (2023) Development of a high-voltage pulsed electric field sterilization power supply using a new topology circuit. Energies 16:2741. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16062741
Szwarc D, Głowacka K (2021) Increasing the biogas potential of rapeseed straw using pulsed electric field pre-treatment. Energies 14:8307. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14248307
Sumathy P, Navamani JD, Lavanya A, Sathik J, Zahira R, Essa FA (2023) PV powered high voltage pulse converter with switching cells for food processing application. Energies 16:1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16021010
Timmermans R, Nierop Groot M, Nederhoff A, Van Boekel M, Matser A, Mastwijk H (2014) Pulsed electric field processing of different fruit juices: impact of pH and temperature on inactivation of spoilage and pathogenic micro-organisms. Int J Food Microbiol 173:105–111
Coustets M, Ganeva V, Galutzov B, Teissie J (2015) Millisecond duration pulses for flow through electro-induced protein extraction from E. coli and associated eradication. Bioelectrochemistry 103:82–91
Tao X, Jian C, Li L, Zhao L, Meng Z, Sun A (2015) Influence of pulsed electric field on Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Int J Food Prop 18:1416–1427
Huang J, Yang M, Zhou E, Qi P (2002) Research progress of Trichoderma. J Zhongkai Univ Agric Eng 15:61–67
Feng X, Chen Z, Peng D, Zhang J, Yin W (2018) Design and optimization of gas spark switch for the suppression of Rhizoctonia solani. Int Agric Eng J 27:270–277
Su M (2005) The Permeable Mechanism and Research of Cell Membrane under Pulsed Electrical Field. Tian** University of Technology. p.30.
Zhang H (2004) Cell-Wall degrading enzymes produced by Rhizoctonia solani and their pathogenicity to rice plants. Yangzhou University. p.35.
Michael E, Yeshayahu N, Langzam Y, Luboshits G, Cahan R (2016) Effect of toluene on P. stutzeri morphology: plasmolysis, cell size and outer membrane vesicles formation. Can J Microbiol 62:682–691
Yao C, Lv Y, Gong L, Dong S, Zhao Y, Tang L et al (2017) Targeted cell membrane damage by bipolar high repeated frequency pulses. IEEE Trans Dielect Electr Insul 24:3270–3282
Novickij V, Švedienė J, Paškevičius A, Markovskaja S, Girkontaitė I, Zinkevičienė A, et al (2017) Pulsed electric field-assisted sensitization of multidrug-resistant Candida albicans to antifungal drugs. Future. Microbiology. Published Online.
Evrendilek G, Tok F, Soylu E, Soylu S (2008) Inactivation of Penicillum expansum in sour cherry juice, peach and apricot nectars by pulsed electric fields. Food Microbiol 25:662–667
**ao D, Yao C, Liu H, Li C, Cheng J, Guo F et al (2013) Irreversible electroporation and apoptosis in human liver cancer cells induced by nanosecond electric pulses. Bioelectromagnetics 34:512–520
Guionet A, Joubert-Durigneux V, Packan D, Cheype D, Garnier J, David F et al (2014) Effect of nanosecond pulsed electric field on Escherichia coli in water: inactivation and impact on protein changes. J Appl Microbiol 117:721–728
Saulis G (2010) Electroporation of cell membranes: the fundamental effects of pulsed electric fields in food processing. Food Eng Rev 2:52–73
Timmermans RAH, Mastwijk HC, Berendsen LBJM, Nederhoff AL, Matser AM, Van Boekel MAJS, Nierop Groot MN (2019) Moderate intensity Pulsed Electric Fields (PEF) as alternative mild preservation technology for fruit juice. Int J Food Microbiol 298:63–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2019.02.015
Funding
His research was funded by the Central Universities (KJQN201623) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China(2017YFD0700800).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by XZ, MZ, YQ, and HL. The first draft of the manuscript was written by XF and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical Approval
This declaration is “not applicable.”
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, X., Zhu, X., Zhu, M. et al. Effects of Voltage and Treatment Time of Pulsed Electric Field on Electroporation in Rhizoctonia solani. Curr Microbiol 81, 58 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-023-03564-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-023-03564-x