Abstract
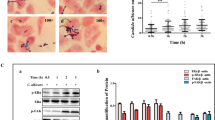
Staphylococcus aureus, a major opportunistic pathogen in aerobic vaginitis (AV), can potentially invade the host and occasionally cause infections. Estrogen is associated with an altered immune response of vaginal epithelial cells and prevention of certain vaginal infectious diseases. However, the molecular mechanisms involving estrogen and S. aureus adhesion to vaginal epithelial cells remain unclear. Thus, here, VK2/E6E7 vaginal epithelial cells were infected with S. aureus, and the role of the estrogen receptor α-associated signaling pathway (ERα/FAK/Src/iNOS axis) in S. aureus adhesion was evaluated. The estrogen-associated phosphorylation status of ERα, FAK, and Src and the protein level of iNOS were assessed by western blotting. We used a specific ERα inhibitor to validate the involvement of the ERα-associated signaling pathway. The results showed that with exposure to 1 nM estrogen for 24 h, transient ERα-associated pathway activation was observed, and the protein expression upregulation was accompanied by a dose-dependent increase in 17-β-estradiol (E2) content and increased S. aureus adherence to vaginal epithelial cells. Estrogen-induced activation of the ERα/FAK/Src/iNOS axis was notably inhibited by the specific ERα inhibitor (ICI 182780). Simultaneously, a significant decrease in the number of adherent S. aureus was observed. However, this inhibitory effect diminished after inhibitor treatment for 24 h. Our findings suggested that the ERα-associated signaling pathway might be involved in S. aureus adherence to vaginal epithelial cells, which appeared to be linked to enhanced cell adhesion leading to AV.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data sets supporting the results of this article are included within the article.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Deng L, Schilcher K, Burcham LR, Kwiecinski JM, Johnson PM, Head SR, Heinrichs DE, Horswill AR, Doran KS (2019) Identification of key determinants of Staphylococcus aureus vaginal colonization. MBio 10(6):e02321-19. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.02321-19
Bertuccini L, Russo R, Iosi F, Superti F (2017) Effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus acidophilus on bacterial vaginal pathogens. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol l 30(2):163–167. https://doi.org/10.1177/0394632017697987
Schlievert PM, Cahill MP, Hostager BS, Brosnahan AJ, Klingelhutz AJ, Gourronc FA, Bishop GA, Leung DYM (2019) Staphylococcal superantigens stimulate epithelial cells through CD40 to produce chemokines. MBio 10(2):e00214-19. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00214-19
Pierson JD, Hansmann MA, Davis CC, Forney LJ (2018) The effect of vaginal microbial communities on colonization by Staphylococcus aureus with the gene for toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1): a case-control study. Pathog Dis. https://doi.org/10.1093/femspd/fty015
MacPhee RA, Miller WL, Gloor GB, McCormick JK, Hammond JA, Burton JP, Reid G (2013) Influence of the vaginal microbiota on toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 production by Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(6):1835–1842. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02908-12
Sun X, Qiu H, ** Y (2017) Highly efficient treatment of aerobic vaginitis with simple acidic buffered gels: the importance of pH and buffers on the microenvironment of vaginas. Int J Pharm 525(1):175–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.04.026
Yan L, Luan T, Hua Q, Gu Y, Fu Z, Liu X, Li M, Liu C, Li P, Zeng X (2018) Peptidomic analysis of female reproductive tract secretion to identify putative anti-infection peptides in the female genital system via nanotechnologies. J Biomed Nanotechnol 14(1):215–226. https://doi.org/10.1166/jbn.2018.2500
Brotman RM, Ravel J, Bavoil PM, Gravitt PE, Ghanem KG (2014) Microbiome, sex hormones, and immune responses in the reproductive tract: challenges for vaccine development against sexually transmitted infections. Vaccine 32(14):1543–1552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.10.010
Wilson JD, Lee RA, Balen AH, Rutherford AJ (2007) Bacterial vaginal flora in relation to changing oestrogen levels. Int J STD AIDS 18(5):308–311. https://doi.org/10.1258/095646207780749583
Mudarris A, Peck EJ (1987) Human anti-estrogen receptor antibodies: assay, characterization, and age- and sex-related differences. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 64(2):246–254. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem-64-2-246
Young HE, Ward WE (2020) The relationship between polycystic ovarian syndrome, periodontal disease, and osteoporosis. Reprod Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43032-020-00310-7
Watanabe Y, Makino E, Tajiki-Nishino R, Koyama A, Tajima H, Ishimota M, Fukuyama T (2018) Involvement of estrogen receptor alpha in pro-pruritic and pro-inflammatory responses in a mouse model of allergic dermatitis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 355:226–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2018.07.008
Medina-Estrada I, Lopez-Meza JE, Ochoa-Zarzosa A (2016) Anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects of estradiol in bovine mammary epithelial cells during Staphylococcus aureus internalization. Mediators Inflamm. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6120509
Murphy LC, Skliris GP, Rowan BG, Al-Dhaheri M, Williams C, Penner C, Troup S, Begic S, Parisien M, Watson PH (2009) The relevance of phosphorylated forms of estrogen receptor in human breast cancer in vivo. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 114(1–2):90–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2009.01.017
Cole JN, Barnett TC, Nizet V, Walker MJ (2011) Molecular insight into invasive group A streptococcal disease. Nat Rev Microbiol 9(10):724–736. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2648
Kalo A, Segal E (1988) Interaction of Candida albicans with genital mucosa: effect of sex hormones on adherence of yeasts in vitro. Can J Microbiol 34(3):224–228. https://doi.org/10.1139/m88-042
Liu X, Luan T, Zhou W, Yan L, Qian H, Mao P, Jiang L, Liu J, Rui C, Wang X, Li P, Zeng X (2021) The role of 17β-estrogen in Escherichia coli adhesion on human vaginal epithelial cells via FAK phosphorylation. Infect Immun 89(11):e00219-21. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00219-21
Goni GM, Epifano C, Boskovic J, Camacho-Artacho M, Zhou J, Bronowska A, Martín MT, Eck MJ, Kremer L, Gräter F, Gervasio FL, Perez-Moreno M, Lietha D (2014) Phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-bisphosphate triggers activation of focal adhesion kinase by inducing clustering and conformational changes. PNAS 111:E3177–E3186. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1317022111
Ji Z, Su J, Hou Y, Yao Z, Yu B, Zhang X (2020) EGFR/FAK and c-Src signalling pathways mediate the internalisation of Staphylococcus aureus by osteoblasts. Cell Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/cmi.13240
Taheri M, Shoorei H, Dinger ME, Ghafouri-Fard S (2020) Perspectives on the role of non-coding RNAs in the regulation of expression and function of the estrogen receptor. Cancers (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082162
Yu L, Wang L, Kim JE, Mao C (1867) Shapiro DJ (2020) Src couples estrogen receptor to the anticipatory unfolded protein response and regulates cancer cell fate under stress. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 10:118765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2020.118765
Chiu JH, Wen CS, Wang JY, Hsu CY, Tsai YF, Hung SC, Tseng LM, Shyr YM (2017) Role of estrogen receptors and Src signaling in mechanisms of bone metastasis by estrogen receptor positive breast cancers. J Transl Med. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-017-1192-x
Bogavac M, Karaman M, Janjusevic L, Sudji J, Radovanovic B, Novakovic Z, Simeunovic J, Bozin B (2015) Alternative treatment of vaginal infections—in vitro antimicrobial and toxic effects of Coriandrum sativum L. and Thymus vulgaris L. essential oils. J Appl Microbiol 119(3):697–710. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.12883
Ceresa C, Hutton S, Lajarin-Cuesta M, Heaton R, Hargreaves I, Fracchia L, De Rienzo MAD (2020) Production of mannosylerythritol lipids (MELs) to be used as antimicrobial agents against S. aureus ATCC 6538. Curr Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-01927-2
Luan SX, Chen XH (2017) The glucocorticoid inhibits neutrophils formed extracellular traps (NETs) and suppresses the inflammation caused by fallopian tube staphylococcal infection. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 21(4):855–860
Zhou K, Li C, Chen D, Pan Y, Tao Y, Qu W, Liu Z, Wang X, **e S (2018) A review on nanosystems as an effective approach against infections of Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Nanomed 13:7333–7347. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S169935
Hillier SL, Lau RJ (1997) Vaginal microflora in postmenopausal women who have not received estrogen replacement therapy. Clin Infect Dis 25(Suppl 2):S123–S126. https://doi.org/10.1086/516221
Trevino LS, Gorelick DA (2021) The interface of nuclear and membrane steroid signaling. Endocrinology 162(8):bqab107. https://doi.org/10.1210/endocr/bqab107
Flamini MI, Sanchez AM, Genazzani AR, Simoncini T (2011) Estrogen regulates endometrial cell cytoskeletal remodeling and motility via focal adhesion kinase. Fertil Steril 95(2):722–726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2010.08.039
Yuan C, Gou X, Deng J, Dong Z, Ye P, Hu Z (2018) FAK and BMP-9 synergistically trigger osteogenic differentiation and bone formation of adipose derived stem cells through enhancing Wnt-beta-catenin signaling. Biomed Pharmacother 105:753–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.185
Kochi S, Yamashiro K, Hongo S, Yamamoto T, Ugawa Y, Shimoe M, Kawamura M (2017) Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans regulates the expression of integrins and reduces cell adhesion via integrin alpha5 in human gingival epithelial cells. Mol Cell Biochem 436(1–2):39–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3076-z
Hofstee MI, Heider A, Hackel S, Constant C, Riool M, Richards RG, Moriarty TF, Zaat SAJ (2021) In vitro 3D Staphylococcus aureus abscess communities induce bone marrow cells to expand into myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Pathogens. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111446
Kang HK, Park J, Seo CH, Park Y (2021) PEP27-2, a Potent antimicrobial cell-penetrating peptide, reduces skin abscess formation during Staphylococcus aureus infections in mouse when used in combination with antibiotics. ACS Infect Dis. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00894
Natarajan K, Abraham P, Kota R, Isaac B (2018) NF-kappaB-iNOS-COX2-TNF alpha inflammatory signaling pathway plays an important role in methotrexate induced small intestinal injury in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 118:766–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.06.040
Acknowledgements
We thank the medicine research center of Women's Hospital of Nan**g Medical University for technical, and equipment supports. We are also grateful to Nan**g Medical University for financial supports and excellent technical assistance.
Funding
This research was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (82071602, 81671410), Jiangsu provincial key research and development program BE2021613, and science and technology fund of Nan**g medical university (NMUB2018070).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PL, XW and XZ conceived and designed this study, and are corresponding authors. LY, XL, and TL carried out the experiments. LJ, ZD, QW and AW performed data collection and analysis. LY, CR, and BZ wrote and edited the manuscript, and they contributed equally to this study. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript and, therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, L., Rui, C., Zhuang, B. et al. 17β-Estradiol Mediates Staphylococcus aureus Adhesion in Vaginal Epithelial Cells via Estrogen Receptor α-Associated Signaling Pathway. Curr Microbiol 80, 391 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-023-03488-6
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-023-03488-6