Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the effectiveness of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in reflecting histopathologic changes after radiofrequency ablation (RFA) to the lung and to assess accurately the extent of tissue necrosis for evaluating untreated lesions.
Methods
Percutaneous RFA was performed on 72 lung regions in 12 pigs under computed tomographic guidance. After performing MRI, the animals were divided into three experimental phases: in the acute phase, 4 pigs were killed immediately after the procedure; in the subacute phase, 4 pigs were killed at 1 week; and in the chronic phases, 2 pigs were killed at 4 and 8 weeks after the procedure, respectively. MRI–histopathologic correlation was performed.
Results
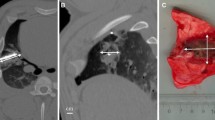
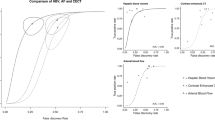
In the acute phase, the inner zone showed hypointensity on T2-weighted images and isointensity on T1-weighted images, with a lack of enhancement on contrast-enhanced T1-weighted images, representing early changes in coagulative necrosis on histopathologic examination. The outer zone showed hyperintensity on T2-weighted images and isointensity on T1-weighted images, with ring-like enhancement on contrast-enhanced T1-weighted images. The histopathologic section showed alveolar fluid collections and congestion. In the subacute phase the MR zone pattern was essentially similar to that of the acute phase, but the ablated lesion showed extensive coagulative necrosis with a fibrovascular rim on histopathologic examination. In the chronic phase, there was no change in the zone pattern on MRI. The lesions showed gradual resorption of coagulative necrosis. The area of coagulative necrosis correlated closely with the histopathologic size (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
MRI effectively visualized the histopathologic changes after RFA and accurately determined the extent of the necrotic lesion. MRI is potentially a useful modality for evaluating therapeutic efficacy after RFA to the lung.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
SN Goldberg GS Gazelle L Solbiati et al. (1998) ArticleTitleAblation of liver tumors using percutaneous RF therapy AJR Am J Roentgenol 170 1023–1028 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c7ptFSrtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9530053
S Rossi E Buscarini F Garbagnati et al. (1998) ArticleTitlePercutaneous treatment of small hepatic tumors by an expandable RF needle electrode AJR Am J Roentgenol 170 1015–1022 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c7ptFSrsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9530052
BJ Wood JR Ramkaransingh T Fojo et al. (2002) ArticleTitlePercutaneous tumor ablation with radiofrequency Cancer 94 443–451
L Solbiati T Livraghi SN Goldberg et al. (2001) ArticleTitlePercutaneous radio-frequency ablation of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer: Long-term results in 117 patients Radiology 221 159–166
R Lencioni D Cioni C Bartolozzi (2001) ArticleTitlePercutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation of liver malignancies: Techniques, indications, imaging findings, and clinical results Abdom Imaging 26 345–360 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002610000194 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38%2FhvVShsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11441546
SA Curley F Izzo LM Ellis et al. (2000) ArticleTitleRadiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular cancer in 110 patients with cirrhosis Ann Surg 232 381–391 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3cvktFKltw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10973388
SA Curley F Izzo P Delrio et al. (1999) ArticleTitleRadiofrequency ablation of unresectable primary and metastatic hepatic malignancies: Results in 123 patients Ann Surg 230 1–8 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00000658-199907000-00001 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1MzisFKitA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10400029
T Livraghi SN Goldberg S Lazzaroni et al. (1999) ArticleTitleSmall hepatocellular carcinoma: Treatment with radio-frequency ablation versus ethanol injection Radiology 210 655–661 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3itlyksw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10207464
WE Burak SuffixJr DM Agnese SP Povoski et al. (2003) ArticleTitleRadiofrequency ablation of invasive breast carcinoma followed by delayed surgical excision Cancer 98 1369–1376
BJ Wood J Abraham JL Hvizda et al. (2003) ArticleTitleRadiofrequency ablation of adrenal tumors and adrenocortical carcinoma metastases Cancer 97 554–560
MA Farrell WJ Charboneau DS DiMarco et al. (2003) ArticleTitleImaging-guided radiofrequency ablation of solid renal tumors AJR Am J Roentgenol 180 1509–1513 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3s3jvVOgsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle12760910
DI Rosenthal FJ Hornicek M Torriani et al. (2003) ArticleTitleOsteoid osteoma: Percutaneous treatment with radiofrequency energy Radiology 229 171–175
DE Dupuy RJ Zagoria W Akerley et al. (2000) ArticleTitlePercutaneous radiofrequency ablation of malignancies in the lung AJR Am J Roentgenol 174 57–59 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c%2Fpt1Sgtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10628454
RD Suh AB Wallace RE Sheehan et al. (2003) ArticleTitleUnresectable pulmonary malignancies: CT-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation-preliminary results Radiology 229 821–829 Occurrence Handle14657317
LJ Herrera HC Fernando Y Perry et al. (2003) ArticleTitleRadiofrequency ablation of pulmonary malignant tumors in nonsurgical candidates J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 125 929–937 Occurrence Handle10.1067/mtc.2003.18 Occurrence Handle12698158
K Steinke JM Habicht S Thomsen et al. (2002) ArticleTitleCT-guided radiofrequency ablation of a pulmonary metastasis followed by surgical resection Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 25 543–546 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00270-002-2646-x Occurrence Handle12391518
TS Kim HK Lim KS Lee et al. (2003) ArticleTitleImaging-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of pulmonary metastatic nodules caused by hepatocellular carcinoma: Preliminary experience AJR Am J Roentgenol 181 491–494 Occurrence Handle12876032
M Toyoshima T Matsuoka T Ohkuma et al. (2002) ArticleTitleRadiofrequency ablation of pulmonary malignancies Nippon igaku Hoshasen Gakkai Zasshi 62 836–838 Occurrence Handle12607954
T Nishida K Inoue Y Kawata et al. (2002) ArticleTitlePercutaneous radiofrequency ablation of lung neoplasms: A minimally invasive strategy for inoperable patients J Am Coll Surg 195 426–430 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1072-7515(02)01281-4 Occurrence Handle12229953
M Toyoshima T Matsuoka S Tanaka et al. (2001) ArticleTitlePercutaneous radiofrequency ablation for metastatic lung tumors: A case report Gan to Kagaku Ryoho 28 1604–1606 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3Mnmt1Ojtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11707990
K Steinke J King D Glenn et al. (2003) ArticleTitleRadiologic appearance and complications of percutaneous computed tomography-guided radiofrequency-ablated pulmonary metastases from colorectal carcinoma J Comput Assist Tomogr 27 750–757 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00004728-200309000-00012 Occurrence Handle14501366
S Sironi T Livraghi F Meloni et al. (1999) ArticleTitleSmall hepatocellular carcinoma treated with percutaneous RF ablation: MR imaging follow-up AJR Am J Roentgenol 173 1225–1229 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c%2FgslWjtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10541093
TL Boaz JS Lewin YC Chung et al. (1998) ArticleTitleMR monitoring of MR-guided radiofrequency thermal ablation of normal liver in an animal model J Magn Reson Imaging 8 64–69 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c7lvFyqug%3D%3D
M Tsuda H Rikimaru K Majima et al. (2003) ArticleTitleTime-related changes of radiofrequency ablation lesion in the normal rabbit liver: Findings of magnetic resonance imaging and histopathology Invest Radiol 38 525–531 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00004424-200308000-00007 Occurrence Handle12874519
B Markarian ET Dailey (1993) Preparation of inflated lung specimens. Heitzman’s The Lung EditionNumber3 St Louis Mosby-Year Book 4–12
SN Goldberg GS Gazelle CC Compton et al. (1995) ArticleTitleRadiofrequency tissue ablation in the rabbit lung: Efficacy and complications Acad Radiol 2 776–784 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2FotV2juw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9419639
SN Goldberg GS Gazelle CC Compton et al. (1996) ArticleTitleRadio-frequency tissue ablation of VX2 tumor nodules in the rabbit lung Acad Radiol 3 929–935 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiC3MfjtVQ%3D Occurrence Handle8959183
E Unger J Littlefield M Gado (1988) ArticleTitleWater content and water structure in CT and MR signal changes: Possible influence in detection of early stroke AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 9 687–691 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BieB1M3gvFE%3D Occurrence Handle3135715
A Darkazanili K Hynynen E Unger et al. (1993) ArticleTitleOn-line monitoring of ultrasonic surgery with MR imaging J Magn Reson Imaging 3 509–514 Occurrence Handle8324310
JP McGahan JM Brock H Tesluk et al. (1992) ArticleTitleHepatic ablation with use of radio-frequency electrocautery in the animal model J Vasc Interv Radiol 3 291–297 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2A3s%2FgvVU%3D Occurrence Handle1627876
D Ulrich EM Noah D Heimburg Particlevon et al. (2003) ArticleTitleTIMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-9, and PIIINP as serum markers for skin fibrosis in patients following severe burn trauma Plast Reconstr Surg 111 1423–1431 Occurrence Handle10.1097/01.PRS.0000049450.95669.07 Occurrence Handle12618601
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oyama, Y., Nakamura, K., Matsuoka, T. et al. Radiofrequency Ablated Lesion in the Normal Porcine Lung: Long-Term Follow-Up with MRI and Pathology. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 28, 346–353 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-004-0156-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-004-0156-8