Abstract
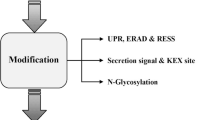
Filamentous fungi are widely used in food fermentation and therapeutic protein production due to their prominent protein secretion and post-translational modification system. Aspergillus nidulans is an important model strain of filamentous fungi, but not a fully developed cell factory for heterologous protein expression. One of the limitations is its relatively low capacity of protein secretion. To alleviate this limitation, in this study, the protein secretory pathway and mycelium morphology were stepwise modified. With eGFP as a reporter protein, protein secretion was significantly enhanced through reducing the degradation of heterologous proteins by endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation (ERAD) and vacuoles in the secretory pathway. Elimination of mycelial aggregation resulted in a 1.5-fold and 1.3-fold increase in secretory expression of eGFP in typical constitutive and inducible expression systems, respectively. Combined with these modifications, high secretory expression of human interleukin-6 (HuIL-6) was achieved. Consequently, a higher yield of secretory HuIL-6 was realized by further disruption of extracellular proteases. Overall, a superior chassis cell of A. nidulans suitable for efficient secretory expression of heterologous proteins was successfully obtained, providing a promising platform for biosynthesis using filamentous fungi as hosts.
Key points
• Elimination of mycelial aggregation and decreasing the degradation of heterologous protein are effective strategies for improving the heterologous protein expression.
• The work provides a high-performance chassis host △agsB-derA for heterologous protein secretory expression.
• Human interleukin-6 (HuIL-6) was expressed efficiently in the high-performance chassis host △agsB-derA.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Anyaogu DC, Hansen AH, Hoof JB, Majewska NI, Contesini FJ, Paul JT, Nielsen KF, Hobley TJ, Yang S, Zhang H, Betenbaugh M, Mortensen UH (2021) Glycoengineering of Aspergillus nidulans to produce precursors for humanized N-glycan structures. Metab Eng 67:153–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2021.06.001
Berger H, Pachlinger R, Morozov I, Goller S, Narendja F, Caddick M, Strauss J (2006) The GATA factor AreA regulates localization and in vivo binding site occupancy of the nitrate activator NirA. Mol Microbiol 59(2):433–446. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04957.x
Berger H, Basheer A, Böck S, Reyes-Dominguez Y, Dalik T, Altmann F, Strauss J (2008) Dissecting individual steps of nitrogen transcription factor cooperation in the Aspergillus nidulans nitrate cluster. Mol Microbiol 69(6):1385–1398. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06359.x
Besada-Lombana PB, Da Silva NA (2019) Engineering the early secretory pathway for increased protein secretion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 55:142–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2019.06.010
Cao H, Villatoro-Hernandez J, Weme RDO, Frenzel E, Kuipers OP (2018) Boosting heterologous protein production yield by adjusting global nitrogen and carbon metabolic regulatory networks in Bacillus subtilis. Metab Eng 49:143–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.08.001
Carvalho NDSP, Arentshorst M, Kooistra R, Stam H, Sagt CM, van den Hondel CAMJJ, Ram AFJ (2011) Effects of a defective ERAD pathway on growth and heterologous protein production in Aspergillus niger. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89(2):357–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2916-5
Chen X, Zhou J, Ding Q, Luo Q, Liu L (2019) Morphology engineering of Aspergillus oryzae for L-malate production. Biotechnol Bioeng 116(10):2662–2673. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.27089
Chen Y, Lin A, Liu P, Fan X, Wu C, Li N, Wei L, Wang W, Wei D (2021) Trichoderma reesei ACE4, a novel transcriptional activator involved in the regulation of cellulase genes during growth on cellulose. Appl Environ Microbiol 87(15):e00593-e621. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00593-21
Chiang Y-M, Oakley CE, Ahuja M, Entwistle R, Schultz A, Chang S-L, Sung CT, Wang CCC, Oakley BR (2013) An efficient system for heterologous expression of secondary metabolite genes in Aspergillus nidulans. J Am Chem Soc 135(20):7720–7731. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja401945a
Curran KA, Crook NC, Karim AS, Gupta A, Wagman AM, Alper HS (2014) Design of synthetic yeast promoters via tuning of nucleosome architecture. Nat Commun 5(1):4002. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5002
Dancourt J, Barlowe C (2010) Protein sorting receptors in the early secretory pathway. Annu Rev Biochem 79(1):777–802. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-061608-091319
Demain AL, Vaishnav P (2009) Production of recombinant proteins by microbes and higher organisms. Biotechnol Adv 27(3):297–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2009.01.008
Driouch H, Sommer B, Wittmann C (2010) Morphology engineering of Aspergillus niger for improved enzyme production. Biotechnol Bioeng 105(6):1058–1068. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.22614
Einhaus A, Baier T, Rosenstengel M, Freudenberg RA, Kruse O (2021) Rational promoter engineering enables robust terpene production in microalgae. ACS Synth Biol 10(4):847–856. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.0c00632
Fiedler MRM, Barthel L, Kubisch C, Nai C, Meyer V (2018) Construction of an improved Aspergillus niger platform for enhanced glucoamylase secretion. Microb Cell Fact 17(1):95. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-018-0941-8
Fregno I, Fasana E, Soldà T, Galli C, Molinari M (2021) N-Glycan processing selects ERAD-resistant misfolded proteins for ER-to-lysosome-associated degradation. EMBO 40(15):e107240. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2020107240
Gabriel R, Thieme N, Liu Q, Li F, Meyer LT, Harth S, Jecmenica M, Ramamurthy M, Gorman J, Simmons BA, McCluskey K, Baker SE, Tian C, Schuerg T, Singer SW, Fleißner A, Benz JP (2021) The F-box protein gene exo-1 is a target for reverse engineering enzyme hypersecretion in filamentous fungi. PNAS 118(26):e2025689118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2025689118
Guillemette T, van Peij NNME, Goosen T, Lanthaler K, Robson GD, van den Hondel CA, Stam H, Archer DB (2007) Genomic analysis of the secretion stress response in the enzyme-producing cell factory Aspergillus niger. BMC Genomics 8(1):158. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-8-158
Gupta A, Reizman IMB, Reisch CR, Prather KLJ (2017) Dynamic regulation of metabolic flux in engineered bacteria using a pathway-independent quorum-sensing circuit. Nat Biotechnol 35(3):273–279. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3796
Havlik D, Brandt U, Bohle K, Fleißner A (2017) Establishment of Neurospora crassa as a host for heterologous protein production using a human antibody fragment as a model product. Microb Cell Fact 16(1):128. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-017-0734-5
He X, Li S, Kaminskyj SGW (2018) Overexpression of Aspergillus nidulans α-1,3-glucan synthase increases cellular adhesion and causes cell wall defects. Med Mycol 56(5):645–648. https://doi.org/10.1093/mmy/myx090
Heimel K (2015) Unfolded protein response in filamentous fungi-implications in biotechnology. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(1):121–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6192-7
Hou J, Tyo K, Liu Z, Petranovic D, Nielsen J (2012) Engineering of vesicle trafficking improves heterologous protein secretion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 14(2):120–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2012.01.002
Jacobs DI, Olsthoorn MMA, Maillet I, Akeroyd M, Breestraat S, Donkers S, van der Hoeven RAM, van den Hondel CAMJJ, Kooistra R, Lapointe T, Menke H, Meulenberg R, Misset M, Müller WH, van Peij NNME, Ram A, Rodriguez S, Roelofs MS, Roubos JA, van Tilborg MWEM, Verkleij AJ, Pel HJ, Stam H, Sagt CMJ (2009) Effective lead selection for improved protein production in Aspergillus niger based on integrated genomics. Fungal Genet Biol 46:S141–S152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2008.08.012
Jiang S, Wang D, Wang R, Zhao C, Ma Q, Wu H, **e X (2021) Reconstructing a recycling and nonauxotroph biosynthetic pathway in Escherichia coli toward highly efficient production of L-citrulline. Metab Eng 68:220–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2021.10.009
Jiang X-R, Chen G-Q (2016) Morphology engineering of bacteria for bio-production. Biotechnol Adv 34(4):435–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.12.007
Katayama T, Nakamura H, Zhang Y, Pascal A, Fujii W, Maruyama J-i (2019) Forced recycling of an AMA1-based genome-editing plasmid allows for efficient multiple gene deletion/integration in the industrial filamentous fungus Aspergillus oryzae. Appl Environ Microbiol 85(3):e01896-e1918. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01896-18
Kruger NJ (1994) The Bradford method for protein quantitation. In: Walker JM (ed) Basic protein and peptide protocols, 1st edn. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, pp 9–15
Krull R, Wucherpfennig T, Esfandabadi ME, Walisko R, Melzer G, Hempel DC, Kampen I, Kwade A, Wittmann C (2013) Characterization and control of fungal morphology for improved production performance in biotechnology. J Biotechnol 163(2):112–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2012.06.024
Li ZJ, Shukla V, Fordyce AP, Pedersen AG, Wenger KS, Marten MR (2000) Fungal morphology and fragmentation behavior in a fed-batch Aspergillus oryzae fermentation at the production scale. Biotechnol Bioeng 70(3):300–312. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0290(20001105)70:3%3c300::AID-BIT7%3e3.0.CO;2-3
Liu D, Garrigues S, de Vries RP (2023) Heterologous protein production in filamentous fungi. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12660-8
Lubertozzi D, Keasling JD (2009) Develo** Aspergillus as a host for heterologous expression. Biotechnol Adv 27(1):53–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.09.001
Luo X, Li R, Feng J-X, Qin X (2022) Disruption of vacuolar protein sorting receptor gene Poxvps10 improves cellulolytic enzyme production by Penicillium oxalicum. Enzyme Microb Technol 160:110098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2022.110098
Madhavan A, Pandey A, Sukumaran RK (2017) Expression system for heterologous protein expression in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus unguis. Bioresour Technol 245:1334–1342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.140
Motoyama T, Fujiwara M, Kojima N, Horiuchi H, Ohta A, Takagi M (1997) The Aspergillus nidulans genes chsA and chsD encode chitin synthases which have redundant functions in conidia formation. Mol Gen Genet 253(4):520–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380050353
Ohsumi K, Matsuda Y, Nakajima H, Kitamoto K (2001) Cloning and characterization of the cpyA gene encoding intracellular carboxypeptidase from Aspergillus nidulans. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65(5):1175–1180. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.65.1175
Olsvik E, Kristiansen B (1994) Rheology of filamentous fermentations. Biotechnol Adv 12(1):1–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/0734-9750(94)90288-7
Pantazopoulou A, Peñalva MA (2011) Characterization of Aspergillus nidulans RabC/Rab6. Traffic 12(4):386–406. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01164.x
Papagianni M (2004) Fungal morphology and metabolite production in submerged mycelial processes. Biotechnol Adv 22(3):189–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2003.09.005
Punt PJ, Schuren FHJ, Lehmbeck J, Christensen T, Hjort C, van den Hondel CAMJJ (2008) Characterization of the Aspergillus niger prtT, a unique regulator of extracellular protease encoding genes. Fungal Genet Biol 45(12):1591–1599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2008.09.007
Rantasalo A, Landowski CP, Kuivanen J, Korppoo A, Reuter L, Koivistoinen O, Valkonen M, Penttilä M, Jäntti J, Mojzita D (2018) A universal gene expression system for fungi. NAR 46(18):e111–e111. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky558
Roux I, Chooi Y-H (2022) Cre/lox-mediated chromosomal integration of biosynthetic gene clusters for heterologous expression in Aspergillus nidulans. ACS Synth Biol 11(3):1186–1195. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.1c00458
Saloheimo M, Valkonen M, Penttilä M (2003) Activation mechanisms of the HACI-mediated unfolded protein response in filamentous fungi. Mol Microbiol 47(4):1149–1161. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03363.x
Steiger MG, Rassinger A, Mattanovich D, Sauer M (2019) Engineering of the citrate exporter protein enables high citric acid production in Aspergillus niger. Metab Eng 52:224–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.12.004
Tang H, Bao X, Shen Y, Song M, Wang S, Wang C, Hou J (2015) Engineering protein folding and translocation improves heterologous protein secretion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Bioeng 112(9):1872–1882. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.25596
te Biesebeke R, Record E, van Biezen N, Heerikhuisen M, Franken A, Punt PJ, van den Hondel CAMJJ (2005) Branching mutants of Aspergillus oryzae with improved amylase and protease production on solid substrates. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69(1):44–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-1968-4
Valkonen M, Ward M, Wang H, Penttilä M, Saloheimo M (2003) Improvement of foreign-protein production in Aspergillus niger var. awamori by constitutive induction of the unfolded-protein response. Appl Environ Microbiol. 69(12):6979–6986. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.12.6979-6986.2003
Vanegas KG, Jarczynska ZD, Strucko T, Mortensen UH (2019) Cpf1 enables fast and efficient genome editing in Aspergilli. Fungal Biol Biotechnol 6(1):6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40694-019-0069-6
vanKuyk PA, Cheetham BF, Katz ME (2000) Analysis of two Aspergillus nidulans genes encoding extracellular proteases. Fungal Genet Biol 29(3):201–210. https://doi.org/10.1006/fgbi.2000.1195
Virag A, Lee MP, Si H, Harris SD (2007) Regulation of hyphal morphogenesis by cdc42 and rac1 homologues in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Microbiol 66(6):1579–1596. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.06021.x
Wang Q, Zhong C, **ao H (2020) Genetic engineering of filamentous fungi for efficient protein expression and secretion. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:293. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00293
Ward M, Lin C, Victoria DC, Fox BP, Fox JA, Wong DL, Meerman HJ, Pucci JP, Fong RB, Heng MH, Tsurushita N, Gieswein C, Park M, Wang H (2004) Characterization of humanized antibodies secreted by Aspergillus niger. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(5):2567–2576. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.5.2567-2576.2004
Ward OP (2012) Production of recombinant proteins by filamentous fungi. Biotechnol Adv 30(5):1119–1139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.09.012
Wei L, Zhao J, Wang Y, Gao J, Du M, Zhang Y, Xu N, Du H, Ju J, Liu Q, Liu J (2022) Engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for high-level γ-aminobutyric acid production from glycerol by dynamic metabolic control. Metab Eng 69:134–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2021.11.010
Xu Y, Wang Y-h, Liu T-q, Zhang H, Zhang H, Li J (2018) The GlaA signal peptide substantially increases the expression and secretion of α-galactosidase in Aspergillus niger. BiotL 40(6):949–955. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-018-2540-5
Yoon J, Aishan T, Maruyama J-i, Kitamoto K (2010) Enhanced production and secretion of heterologous proteins by the filamentous fungus Aspergillus oryzae via disruption of vacuolar protein sorting receptor gene Aovps10. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(17):5718–5727. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03087-09
Yu T, Liu Q, Wang X, Liu X, Chen Y, Nielsen J (2022) Metabolic reconfiguration enables synthetic reductive metabolism in yeast. Nat Metab 4(11):1551–1559. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-022-00654-1
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32201034), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu (BK20210470), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M701461), the International S&T Innovation Cooperation programme (2017YFE0129600), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (no. 111–2-06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QY, LH, SZ, and ZZ conceived the project and wrote the paper. QY, LH, and ZL designed and performed all the experiments. QY and LH analyzed the results. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Q., Han, L., Liu, Z. et al. Stepwise genetic modification for efficient expression of heterologous proteins in Aspergillus nidulans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 6923–6935 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12755-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12755-2