Abstract
Il-MnP1, a short-type manganese peroxidase from Irpex lacteus F17, can oxidize some substrates in the absence of Mn2+, but the catalysis was much lower than in the presence of Mn2+. Here, we report a mutant R70V/E166A of Il-MnP1 with some unique properties, which possessed clearly higher catalysis for the decolorization of anthraquinone and azo dyes in the absence of Mn2+ than that of Il-MnP1. Importantly, the optimum pH of R70V/E166A for decolorization of anthraquinone dyes (Reactive Blue 19, RB19) was 6.5, and the mutant achieved high decolorization activities in the range of pH 4.0–7.0, whereas Il-MnP1 only showed decolorization for RB19 at pH 3.5–4.0. In addition, the optimum H2O2 concentration of R70V/E166A for RB19 decolorization was eight times that of Il-MnP1 and the H2O2 stability has improved 1.4 times compared with Il-MnP1. Furthermore, Mn2+ competitively inhibited the oxidation of RB19 by R70V/E166A, explaining the higher catalytic activity of the mutant R70V/E166A in the absence of Mn2+. Molecular docking results suggested that RB19 binds to the distal side of the heme plane in mutant R70V/E166A, which extended from the heme δ-side to the heme γ-side, and close to the mutated residues of R70V and E166A, whereas RB19 could not access the heme pocket of Il-MnP1 due to the steric hindrance of the side-chain group of Arg 70. Thus, this study constructed a useful mutant R70V/E166A and analyzed its higher Mn2+-independent activity, which is very important for better understanding the Mn2+-independent catalytic mechanism for short manganese peroxidases.
Key points
• The mutant R70V/E166A of atypical MnP1 of I. lacteus F17 shows unique catalytic properties.
• At pH 6.5, the R70V/E166A had a strong ability to decolorize anthraquinone dyes in the absence of Mn 2+ .
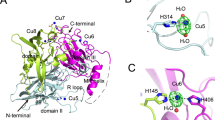
• The binding sites of Reactive Blue 19 in mutant R70V/E166A were elucidated.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and supplementary materials.
References
Aboelnga MM (2022) Mechanistic insights into the chemistry of compound I formation in heme peroxidases: quantum chemical investigations of cytochrome c peroxidase. RSC Adv 12(24):15543–15554. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ra01073a
Battistuzzi G, Bellei M, Bortolotti CA, Sola M (2010) Redox properties of heme peroxidases. Arch Biochem Biophys 500(1):21–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2010.03.002
Bilal M, Asgher M, Iqbal HMN, Hu H, Zhang X (2017) Delignification and fruit juice clarification properties of alginate-chitosan-immobilized ligninolytic cocktail. Lwt 80:348–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2017.02.040
Case DA, Cheatham TE, Darden T, Gohlke H, Luo R, Merz KM, Onufriev A, Simmerling C, Wang B, Woods RJ (2005) The Amber biomolecular simulation programs. J Comput Chem 26(16):1668–1688. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20290
Catucci G, Valetti F, Sadeghi SJ, Gilardi G (2020) Biochemical features of dye-decolorizing peroxidases: current impact on lignin degradation. Biotechnol Appl Bioc 67(5):751–759. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.2015
Chang Y, Yang D, Li R, Wang T, Zhu Y (2021) Textile dye biodecolorization by manganese peroxidase: a review. Molecules 26(15):4403. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154403
Chen W, Zheng L, Jia R, Wang N (2015) Cloning and expression of a new manganese peroxidase from Irpex lacteus F17 and its application in decolorization of reactive black 5. Process Biochem 50(11):1748–1759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2015.07.009
Chowdhary P, Shukla G, Raj G, Ferreira LFR, Bharagava RN (2019) Microbial manganese peroxidase: a ligninolytic enzyme and its ample opportunities in research. SN Appl Sci 1(1):45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-018-0046-3
Ding Y, Cui K, Guo Z, Cui M, Chen Y (2021) Manganese peroxidase mediated oxidation of sulfamethoxazole: Integrating the computational analysis to reveal the reaction kinetics, mechanistic insights, and oxidation pathway. J Hazard Mater 415:125719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125719
Fernández-Fueyo E, Acebes S, Ruiz-Dueñas FJ, Martínez MJ, Romero A, Medrano FJ, Guallar V, Martínez AT (2014a) Structural implications of the C-terminal tail in the catalytic and stability properties of manganese peroxidases from ligninolytic fungi. Acta Cryst D70(Pt 12):3253–3265. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1399004714022755
Fernández-Fueyo E, Ruiz-Dueñas FJ, Martínez MJ, Romero A, Hammel KE, Medrano FJ, Martínez AT (2014b) Ligninolytic peroxidase genes in the oyster mushroom genome: heterologous expression, molecular structure, catalytic and stability properties, and lignin-degrading ability. Biotechnol Biofuels 7(1):2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-7-2
George SJ, Kvaratskhelia M, Dilworth MJ, Thorneley RNF (1999) Reversible alkaline inactivation of lignin peroxidase involves the release of both the distal and proximal site calcium ions and bishistidine co-ordination of the haem. Biochem J 344(Pt 1):237–237. https://doi.org/10.1042/0264-6021:3440237
Giardina P, Palmieri G, Fontanella B, Rivieccio V, Sannia G (2000) Manganese peroxidase isoenzymes produced by Pleurotus ostreatus grown on wood sawdust. Arch Biochem Biophys 376(1):171–179. https://doi.org/10.1006/abbi.1999.1691
Gumiero A, Murphy EJ, Metcalfe CL, Moody PCE, Raven EL (2010) An analysis of substrate binding interactions in the heme peroxidase enzymes: a structural perspective. Arch Biochem Biophys 500(1):13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2010.02.015
Heering HA, Smith AT, Smulevich G (2002) Spectroscopic characterization of mutations at the Phe41 position in the distal haem pocket of horseradish peroxidase C: structural and functional consequences. Biochem J 363(3):571–579. https://doi.org/10.1042/0264-6021:3630571
Henriksen A, Smith AT, Gajhede M (1999) The structures of the horseradish peroxidase C-ferulic acid complex and the ternary complex with cyanide suggest how peroxidases oxidize small phenolic substrates. J Biol Chem 274(49):35005–35011. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.49.35005
Hofbauer S, Pfanzagl V, Michlits H, Schmidt D, Obinger C, Furtmüller PG (2021) Understanding molecular enzymology of porphyrin-binding α + β barrel proteins - one fold, multiple functions. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom 1869(1):140536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2020.140536
Ivancich A, Jouve HM, Sartor B, Gaillard J (1997) EPR investigation of compound I in Proteus mirabilis and bovine liver catalases: formation of porphyrin and tyrosyl radical intermediates. Biochemistry 36(31):9356–9364. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi970886s
Ivancich A, Mazza G, Desbois A (2001) Comparative electron paramagnetic resonance study of radical intermediates in turnip peroxidase isozymes. Biochemistry 40(23):6860–6866. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi002826j
Kishi K, Hildebrand DP, Someren MK, Gettemy J, Mauk AG, Gold MH (1997) Site-directed mutations at phenylalanine-190 of manganese peroxidase: effects on stability, function, and coordination. Biochemistry 36(14):4268–4277. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi962627t
Kuan IC, Tien M (1993) Stimulation of Mn peroxidase activity: a possible role for oxalate in lignin biodegradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(4):1242–1246. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.90.4.1242
Li L, Liu B, Yang J, Zhang Q, He C, Jia R (2019) Catalytic properties of a short manganese peroxidase from Irpex lacteus F17 and the role of Glu166 in the Mn2+-independent activity. Int J Biol Macromol 136:859–869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.06.065
Lundell T, Bentley E, Hildén K, Rytioja J, Kuuskeri J, Ufot UF, Nousiainen P, Hofrichter M, Wahlsten M, Doyle W, Smith AT (2016) Engineering towards catalytic use of fungal class-II peroxidases for dye-decolorizing and conversion of lignin model compounds. Curr Biotechnol 6(2):116–127. https://doi.org/10.2174/2211550105666160520120101
Lundell TK, Mäkelä MR, Hildén K (2010) Lignin-modifying enzymes in filamentous basidiomycetes-ecological, functional and phylogenetic review. J Basic Microbiol 50(1):5–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.200900338
Martínez MJ, Ruiz-Dueñas FJ, Guillén F, Martínez AT (1996) Purification and catalytic properties of two manganese peroxidase isoenzymes from Pleurotus eryngii. Eur J Biochem 237(2):424–432. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.0424k.x
Mino Y, Wariishi H, Blackburn NJ, Loehr TM, Gold MH (1988) Spectral characterization of manganese peroxidase, an extracellular heme enzyme from the lignin-degrading basidiomycete, Phanerochaete chrysosporium. J Biol Chem 263(15):7029–7036. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9258(18)68599-0
Miyazaki-Imamura C, Oohira K, Kitagawa R, Nakano H, Yamane T, Takahashi H (2003) Improvement of H2O2 stability of manganese peroxidase by combinatorial mutagenesis and high-throughput screening using in vitro expression with protein disulfide isomerase. Protein Eng Des Sel 16(6):423–428. https://doi.org/10.1093/protein/gzg054
Moffet DA, Foley J, Hecht MH (2003) Midpoint reduction potentials and heme binding stoichiometries of de novo proteins from designed combinatorial libraries. Biophys Chem 105(2-3):231–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0301-4622(03)00072-3
Ngo ACR, Conrad C, Gómez Baraibar Á, Matura A, van Pée KH, Tischler D (2021) Characterization of two hydrogen peroxide resistant peroxidases from Rhodococcus opacus 1CP. Appl Sci 11(17):7941. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11177941
Palma C, Martı́nez AT, Lema JM, Martı́nez MJ (2000) Different fungal manganese-oxidizing peroxidases: a comparison between Bjerkandera sp. and Phanerochaete chrysosporium. J Biotechnol 77(2–3):235–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-1656(99)00218-7
Pfanzagl V, Nys K, Bellei M, Michlits H, Mlynek G, Battistuzzi G, D**ovic-Carugo K, Van Doorslaer S, Furtmüller PG, Hofbauer S, Obinger C (2018) Roles of distal aspartate and arginine of B-class dye-decolorizing peroxidase in heterolytic hydrogen peroxide cleavage. J Biol Chem 293(38):14823–14838. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.004773
Rodríguez-López JN, Lowe DJ, Hernández-Ruiz J, Hiner ANP, García-Cánovas F, Thorneley RNF (2001) Mechanism of reaction of hydrogen peroxide with horseradish peroxidase: identification of intermediates in the catalytic cycle. J Am Chem Soc 123(48):11838. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja011853+
Rodriguez-Lopez JN, Smith AT, Thorneley RNF (1996a) Role of arginine 38 in horseradish peroxidase. a critical residue for substrate binding and catalysis. J Biol Chem 271(8):4023–4030. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.271.8.4023
Rodriguez-Lopez JN, Smith AT, Thorneley RNF (1996b) Recombinant horseradish peroxidase isoenzyme C: the effect of distal haem cavity mutations (His42→Leu and Arg38→Leu) on compound I formation and substrate binding. J Biol Inorg Chem 1:136–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007750050032
Sellami K, Couvert A, Nasrallah N, Maachi R, Abouseoud M, Amrane A (2022) Peroxidase enzymes as green catalysts for bioremediation and biotechnological applications: a review. Sci Total Environ 806(Pt 2):150500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150500
Singh AK, Bilal M, Iqbal HMN, Meyer AS, Raj A (2021) Bioremediation of lignin derivatives and phenolics in wastewater with lignin modifying enzymes: status, opportunities and challenges. Sci Total Environ 777:145988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145988
Sundaramoorthy M, Gold MH, Poulos TL (2010) Ultrahigh (0.93Å) resolution structure of manganese peroxidase from Phanerochaete chrysosporium: implications for the catalytic mechanism. J Inorg Biochem 104(6):683–690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.**orgbio.2010.02.011
Sundaramoorthy M, Kishi K, Gold MH, Poulos TL (1994) The crystal structure of manganese peroxidase from Phanerochaete chrysosporium at 2.06-Å resolution. J Biol Chem 269(52):32759–32767. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9258(20)30056-9
Sundaramoorthy M, Terner J, Poulos TL (1995) The crystal structure of chloroperoxidase: a heme peroxidase--cytochrome P450 functional hybrid. Structure 3(12):1367–1377. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00274-x
Sutherland GRJ, Zapanta LS, Tien M, Aust SD (1997) Role of calcium in maintaining the heme environment of manganese peroxidase. Biochemistry 36(12):3654–3662. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi962195m
Uchida T, Omura I, Umetsu S, Ishimori K (2021) Radical transfer but not heme distal residues is essential for pH dependence of dye-decolorizing activity of peroxidase from Vibrio cholerae. J Inorg Biochem 219:111422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.**orgbio.2021.111422
Urzúa U, Larrondo LF, Lobos S, Larraín J, Vicuña R (1995) Oxidation reactions catalyzed by manganese peroxidase isoenzymes from Ceriporiopsis subvermispora. FEBS Lett 371(2):132–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(95)00874-9
Veitch NC (2004) Structural determinants of plant peroxidase function. Phytochem Rev 3:3–18. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PHYT.0000047799.17604.94
Vilar S, Cozza G, Moro S (2008) Medicinal chemistry and the molecular operating environment (MOE): application of QSAR and molecular docking to drug discovery. Curr Top Med Chem 8(18):1555–1572. https://doi.org/10.2174/156802608786786624
Wang N, Ren K, Jia R, Chen W, Sun R (2016) Expression of a fungal manganese peroxidase in Escherichia coli: a comparison between the soluble and refolded enzymes. BMC Biotechnol 16(1):87. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-016-0317-2
Weiner PK, Kollman PA (1981) AMBER: Assisted model building with energy refinement. A general program for modeling molecules and their interactions. J Comput Chem 2(3):287–303. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.540020311
Welinder KG (1992) Superfamily of plant, fungal and bacterial peroxidases. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2(3):388–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/0959-440X(92)90230-5
Wong DWS (2009) Structure and action mechanism of ligninolytic enzymes. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 157(2):174–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8279-z
Yang S, Yang J, Wang T, Li L, Yu S, Jia R, Chen P (2020) Construction of a combined enzyme system of graphene oxide and manganese peroxidase for efficient oxidation of aromatic compounds. Nanoscale 12(14):7976–7985. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0nr00408a
Acknowledgments
A portion of this work was performed on the Steady High Magnetic Field Facilities, High Magnetic Field Laboratory, CAS. Molecular Docking simulation was supported by WECOMPUT Technology Co. (Bei**g, China).
Founding
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31970100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RJ designed the research; JY constructed the mutant R70V/E166A; JLW conducted the biochemistry experiments and analyzed the results; WHH and WTH conducted part of this work. RJ and JLW co-wrote the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent for publication
All authors agree to publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Yang, J., Huang, W. et al. A mutant R70V/E166A of short manganese peroxidase showing Mn2+-independent dye decolorization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 2303–2319 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12438-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12438-y