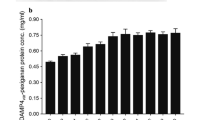
Abstract
Small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) tag is widely used to promote soluble expression of exogenous proteins, which can then be cleaved by ubiquitin-like protease 1 (Ulp1) to obtain interested protein. But the application of Ulp1 in large-scale recombinant protein production is limited by complicated purification procedures and high cost. In this study, we describe an efficient and simple method of extracellular production of Ulp1403-621 using a leaky Escherichia coli BL21(DE3), engineered by deleting the peptidoglycan-associated outer membrane lipoprotein (pal) gene. Ulp1403-621 was successfully leaked into extracellular supernatant by the BL21(DE3)-Δpal strain after IPTG induction. The addition of 1% glycine increased the extracellular production of Ulp1403-621 approximately four fold. Moreover, extracellular Ulp1403-621 without purification had high activities for cleaving SUMO fusion proteins, and antimicrobial peptide pBD2 obtained after cleavage can inhibit the growth of Staphylococcus aureus. The specific activity of extracellular Ulp1403-621 containing 1 mM EDTA and 8 mM DTT reached 2.0 × 106 U/L. Another commonly used protease, human rhinovirus 3C protease, was also successfully secreted by leaky E. coli strains. In conclusion, extracellular production of tool enzymes is an attractive way for producing large-scale active recombinant proteins at a lower cost for pharmaceutical, industrial, and biotechnological applications.
Key points
• First report of extracellular production of Ulp1 403-621 in leaky Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) strain.
• One percent glycine addition into cultivation medium increased the extracellular production of Ulp1 403-621 approximately four fold.
• The specific activity of extracellular Ulp1 403-621 produced in this study reached 2.0 × 10 6 U/L.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Abdelkader EH, Otting G (2021) NT*-HRV3CP: an optimized construct of human rhinovirus 14 3C protease for high-yield expression and fast affinity-tag cleavage. J Biotechnol 325:145–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2020.11.005
Babbal A, Mohanty S, Khasa YP (2019) Bioprocess optimization for the overproduction of catalytic domain of ubiquitin-like protease 1 (Ulp1) from S. cerevisiae in E. coli fed-batch culture. Enzym Microb Technol 120:98–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2018.10.008
Cascales E, Bernadac A, Gavioli M, Lazzaroni JC, Lloubes R (2002) Pal lipoprotein of Escherichia coli plays a major role in outer membrane integrity. J Bacteriol 184(3):754–759. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.184.3.754-759.2002
Chen ZY, Cao J, **e L, Li XF, Yu ZH, Tong WY (2014) Construction of leaky strains and extracellular production of exogenous proteins in recombinant Escherichia coli. Microb Biotechnol 7(4):360–370. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12127
Datsenko KA, Wanner BL (2000) One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(12):6640–6645. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.120163297
Ding N, Ruan Y, Fu X, Lin Y, Yu HY, Han LC, Fu CZ, Zhang JN, Hu XJ (2019) Improving production of N-glycosylated recombinant proteins by leaky Escherichia coli. 3 Biotech 9(8):302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1830-5
Duan XG, Zou C, Wu J (2015) Triton X-100 enhances the solubility and secretion ratio of aggregation-prone pullulanase produced in Escherichia coli. Bioresour Technol 194:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.07.024
Gao CY, Xu TT, Zhao QJ, Li CL (2015) Codon optimization enhances the expression of porcine β-defensin-2 in Escherichia coli. Genet Mol Res 14(2):4978–4988. https://doi.org/10.4238/2015.May.12.1
Garelnabi M, Younis A (2015) Paraoxonase-1 enzyme activity assay for clinical samples: Validation and correlation studies. Med Sci Monit 21:902–908. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.892668
Haitjema CH, Boock JT, Natarajan A, Dominguez MA, Gardner JG, Keating DH, Withers ST, Delisa MP (2014) Universal genetic assay for engineering extracellular protein expression. ACS Synth Biol 3(2):74–82. https://doi.org/10.1021/sb400142b
Hammes W, Schleifer KH, Kandler O (1973) Mode of action of glycine on the biosynthesis of peptidoglycan. J Bacteriol 116(2):1029–1053. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.116.2.1029-1053.1973
Hancock RE, Sahl HG (2006) Antimicrobial and host-defense peptides as new anti-infective therapeutic strategies. Nat Biotechnol 24(12):1551–1557. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1267
Hou HH, Yan WL, Du KX, Ye YJ, Cao QQ, Ren WH (2013) Construction and expression of an antimicrobial peptide scolopin 1 from the centipede venoms of Scolopendra subspinipes mutilans in Escherichia coli using SUMO fusion partner. Protein Expr Purif 92(2):230–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2013.10.004
Hu JY, Lu X, Wang HK, Wang FX, Zhao Y, Shen W, Yang HQ, Chen XZ (2019) Enhancing extracellular protein production in Escherichia coli by deleting the d-alanyl-d-alanine carboxypeptidase gene dacC. Eng Life Sci 19(4):270–278. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.201800199
Imler JL, Bulet P (2005) Antimicrobial peptides in Drosophila: structures, activities and gene regulation. Chem Immunol Allergy 86:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1159/000086648
Ingham AB, Moore RJ (2007) Recombinant production of antimicrobial peptides in heterologous microbial systems. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 47(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1042/BA20060207
Jang KH, Seo JW, Song KB, Kim CH, Rhee SK (1999) Extracellular secretion of levansucrase from Zymomonas mobilis in Escherichia coli. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 21:453–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00009084
Kim DS, Kim SW, Song JM, Kim SY, Kwon KC (2019) A new prokaryotic expression vector for the expression of antimicrobial peptide abaecin using SUMO fusion tag. BMC Biotechnol 19(1):13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-019-0506-x
Kotzsch A, Vernet E, Hammarstrom M, Berthelsen J, Weigelt J, Graslund S, Sundstrom M (2011) A secretory system for bacterial production of high-profile protein targets. Protein Sci 20(3):597–609. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.593
Lejeune A, Sakaguchi K, Imanaka T (1989) A spectrophotometric assay for the cyclization activity of cyclomaltohexaose (α-cyclodextrin) glucanotransferase. Anal Biochem 181(1):6–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(89)90385-0
Li B, Wang Lei SuLQ, Chen S, Li ZF, Chen J, Wu J (2012) Glycine and triton X-100 enhanced secretion of recombinant α-CGTase mediated by OmpA signal peptide in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioproc E 17:1128–1134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-011-0601-x
Li JF, Zhang J, Song R, Zhang JX, Shen Y, Zhang SQ (2009) Production of a cytotoxic cationic antibacterial peptide in Escherichia coli using SUMO fusion partner. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84(2):383–388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2109-2
Li YF (2009) Carrier proteins for fusion expression of antimicrobial peptides in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 54(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1042/BA20090087
Li YF (2011) Recombinant production of antimicrobial peptides in Escherichia coli: a review. Protein Expr Purif 80(2):260–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2011.08.001
Li ZF, Gu ZB, Wang M, Du GC, Wu J, Chen J (2010) Delayed supplementation of glycine enhances extracellular secretion of the recombinant α-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85(3):553–561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2157-7
Linova MY, Risør MW, Jørgensen SE, Mansour Z, Kaya J, Sigurdarson JJ, Enghild JJ, Karring H (2019) A novel approach for production of an active N-terminally truncated Ulp1 (SUMO protease 1) catalytic domain from Escherichia coli inclusion bodies. Protein Expr Purif 166:105507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2019.105507
Liu PT, Wu B, Chen M, Dai YH, Song C, Sun LL, Huang YH, Li SH, Hu GQ, He MX (2022) Enhancing secretion of endoglucanase in Zymomonas mobilis by disturbing peptidoglycan synthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol 88(3):e0216121. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02161-21
Loh B, Grant C, Hancock REW (1984) Use of the fluorescent probe 1-n-phenylnaphthylamine to study the interactions of aminoglycoside antibiotics with the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 26(4):546–551. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.26.4.546
Malakhov MP, Mattern MR, Malakhova OA, Drinker M, Weeks SD, Butt TR (2004) SUMO fusions and SUMO-specific protease for efficient expression and purification of proteins. J Struct Funct Genom 5(1–2):75–86. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JSFG.0000029237.70316.52
Malik A (2016) Protein fusion tags for efficient expression and purification of recombinant proteins in the periplasmic space of E coli. 3 Biotech 6(1):44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0397-7
Miksch G, Ryu S, Risse J, Flaschel E (2008) Factors that influence the extracellular expression of streptavidin in Escherichia coli using a bacteriocin release protein. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81(2):319–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1673-1
Naika GS, Tiku PK (2011) Influence of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) on the structural stability of endoglucanase from Aspergillus aculeatus. J Agric Food Chem 59:7341–7345. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf103889m
Shin HD, Chen RR (2008) Extracellular recombinant protein production from an Escherichia coli lpp deletion mutant. Biotechnol Bioeng 101(6):1288–1296. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.22013
Su L, Jiang Q, Yu L, Wu J (2017) Enhanced extracellular production of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli by co-expression with Bacillus cereus phospholipase C. Microb Cell Factories 16(1):24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-017-0639-3
Suzuki Y, Suzuki T, Awai K, Shioi Y (2019) Isolation and characterization of a tandem-repeated cysteine protease from the symbiotic dinoflagellate Symbiodinium sp. KB8. PLoS One 14(1):e0211534. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0211534
Tulsani NJ, Mishra P, Jakhesara SJ, Srivastava S, Jyotsana B, Dafale NA, Patil NV, Purohit HJ, Joshi CG (2021) Isolation, purification and characterization of a novel esterase from camel rumen metagenome. Protein Expr Purif 187:105941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2021.105941
Wang TN, Zhao M (2017) A simple strategy for extracellular production of CotA laccase in Escherichia coli and decolorization of simulated textile effluent by recombinant laccase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(2):685–696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7897-6
Wang XH, Liu HF, Liu YW, Li YT, Yan L, Yuan XH, Zhang YF, Wu Y, Liu JT, Zhang CL, Chu YH (2016) A novel strategy for the preparation of codon-optimized truncated Ulp1 and its simplified application to cleavage the SUMO fusion protein. Protein J 35(2):115–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-016-9654-1
Yang HQ, Lu X, Hu JY, Chen Y, Shen W, Liu L (2018) Boosting secretion of extracellular protein by Escherichia coli via cell wall perturbation. Appl Environ Microbiol 84(20):e01382-e1418. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01382-18
Yang J, Moyana T, MacKenzie S, **a Q, **ang J (1998) One hundred seventy-fold increase in excretion of an FV fragment-tumor necrosis factor alpha fusion protein (sFV/TNF-α) from Escherichia coli caused by the synergistic effects of glycine and Triton X-100. Appl Environ Microbiol 64(8):2869–2874. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.64.8.2869-2874.1998
Yu HL, Li HR, Gao DF, Gao CJ, Qi QS (2015) Secretory production of antimicrobial peptides in Escherichia coli using the catalytic domain of a cellulase as fusion partner. J Biotechnol 214:77–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2015.09.012
Yu HT, Ding XL, Li N, Zhang XY, Zeng XZ, Wang S, Liu HB, Wang YM, Jia HM, Qiao SY (2017) Dietary supplemented antimicrobial peptide microcin J25 improves the growth performance, apparent total tract digestibility, fecal microbiota, and intestinal barrier function of weaned pigs. J Anim Sci 95(11):5064–5076. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas2017.1494
Zhang YL, Li ZC, Li L, Rao B, Ma LX, Wang YP (2021) A method for rapid screening, expression, and purification of anti-microbial peptides. Microorganisms 9(9):1858. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091858
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grants number 32172754).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LF and ND conceived and designed research. LF, MS, and WW conducted experiments. ND and DL contributed new reagents or analytical tools. LF analyzed data. LF wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, L., Sun, M., Wen, W. et al. Extracellular production of Ulp1403-621 in leaky E. coli and its application in antimicrobial peptide production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 106, 7805–7817 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12235-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12235-z