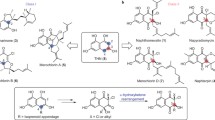
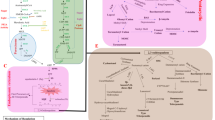
Abstract
Meroterpenoids are a class of terpenoid-containing hybrid natural products with impressive structural architectures and remarkable pharmacological activities. Remarkable advances in enzymology and synthetic biology have greatly contributed to the elucidation of the molecular basis for their biosynthesis. Here, we review structurally unique meroterpenoids catalyzed by novel enzymes and unusual enzymatic reactions over the period of last 5 years. We also discuss recent progress on the biomimetic synthesis of chrome meroterpenoids and synthetic biology-driven biomanufacturing of tropolone sesquiterpenoids, merochlorins, and plant-derived meroterpenoid cannabinoids. In particular, we focus on the novel enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of polyketide-terpenoids, nonribosomal peptide-terpenoids, terpenoid alkaloids, and meroterpenoid with unique structures. The biological activities of these meroterpenoids are also discussed. The information reviewed here might provide useful clues and lay the foundation for develo** new meroterpenoid-derived drugs.
Key points
• Meroterpenoids possess intriguing structural features and relevant biological activities.
• Novel enzymes are involved in the biosynthesis of meroterpenoids with unique structures.
• Biomimetic synthesis and synthetic biology enable the construction and manufacturing of complex meroterpenoids.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Hameed M, Bertrand RL, Piercey-Normore MD, Sorensen JL (2016) Identification of 6-hydroxymellein synthase and accessory genes in the lichen Cladonia uncialis. J Nat Prod 79(6):1645–1650. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00257
Ainsworth AM, Chicarelli-Robinson MI, Copp BR, Fauth U, Hylands PJ, Holloway JA, Latif M, O'Beirne GB, Porter N, Renno DV, Michelle R, Neil R (1995) Xenovulene A, a novel GABA-benzodiazepine receptor binding compound produced by Acremonium strictum. J Antibiot 48(7):568–573. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.48.568
Appendino G, Chianese G, Taglialatela-Scafati O (2011) Cannabinoids: occurrence and medicinal chemistry. Curr Med Chem 18(7):1085–1099. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986711794940888
Arico-Muendel C, Centrella PA, Contonio BD, Morgan BA, O’Donovan G, Paradise CL, Skinner SR, Sluboski B, Svendsen JL, White KF, Debnath A, Gut J, Wilson N, McKerrow JH, DeRisi JL, Rosenthal PJ, Chiang PK (2009) Antiparasitic activities of novel, orally available fumagillin analogs. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19(17):5128–5131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.07.029
Augustiniak H, Forche E, Reichenbach H, Wray V, Gräfe U, Höfle G (1991) Isolierung und Strukturaufklärung von Ergokonin A und B; zwei neue antifungische Sterol-Antibiotika aus Trichoderma koningii. Liebigs Ann Chem 1991(4):361–366. https://doi.org/10.1002/jlac.199119910163
Awakawa T, Zhang L, Wakimoto T, Hoshino S, Mori T, Ito T, Ishikawa J, Tanner ME, Abe I (2014) A methyltransferase initiates terpene cyclization in teleocidin B biosynthesis. J Am Chem Soc 136(28):9910–9913. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja505224r
Ayers S, Zink DL, Powell JS, Brown CM, Grund A, Bills GF, Platas G, Thompson D, Singh SB (2008) Noreupenifeldin, a tropolone from an unidentified ascomycete. J Nat Prod 71(3):457–459. https://doi.org/10.1021/np070513k
Bai T, Quan Z, Zhai R, Awakawa T, Matsuda Y, Abe I (2018) Elucidation and heterologous reconstitution of chrodrimanin B biosynthesis. Org Lett 20(23):7504–7508. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.8b03268
Bai T, Matsuda Y, Tao H, Mori T, Zhang Y, Abe I (2020) Structural diversification of andiconin-derived natural products by α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases. Org Lett 22(11):4311–4315. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.0c01358
Barra L, Abe I (2020) Chemistry of fungal meroterpenoid cyclases. Nat Prod Rep 38:566–585. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NP00056F
Baunach M, Franke J, Hertweck C (2015) Terpenoid biosynthesis off the beaten track: unconventional cyclases and their impact on biomimetic synthesis. Angew Chem Int Ed 54(9):2604–2626. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201910710
Beaudry CM, Malerich JP, Trauner D (2005) Biosynthetic and biomimetic electrocyclizations. Chem Rev 105(12):4757–4778. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr0406110
Brulíková L, Harrison A, Miller MJ, Hlaváč J (2016) Stereo-and regioselectivity of the hetero-Diels–Alder reaction of nitroso derivatives with conjugated dienes. Beilstein J Org Chem 12(1):1949–1980. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjoc.12.184
Bunyapaiboonsri T, Veeranondha S, Boonruangprapa T, Somrithipol S (2008) Ramiferin, a bisphenol-sesquiterpene from the fungus Kionochaeta ramifera BCC 7585. Phytochem Lett 1(4):204–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2008.09.008
Carvalho Â, Hansen EH, Kayser O, Carlsen S, Stehle F (2017) Designing microorganisms for heterologous biosynthesis of cannabinoids. FEMS Yeast Res 17(4). https://doi.org/10.1093/femsyr/fox037
Chen Q, Gao J, Jamieson C, Liu J, Ohashi M, Bai J, Yan D, Liu B, Che Y, Wang Y, Houk KN, Hu Y (2019) Enzymatic intermolecular hetero-Diels–Alder reaction in the biosynthesis of tropolonic sesquiterpenes. J Am Chem Soc 141(36):14052–14056. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b06592
Cheon Y, Kim J-S, Park J-B, Heo P, Lim JH, Jung GY, Seo J-H, Park JH, Koo HM, Cho KM, Park J-B, Ha S-J, Kweon D-H (2014) A biosynthetic pathway for hexanoic acid production in Kluyveromyces marxianus. J Biotechnol 182:30–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.04.010
Collado IG, Hanson JR, Macías-Sánchez AJ (1998) Recent advances in the chemistry of caryophyllene. Nat Prod Rep 15(2):187–204. https://doi.org/10.1039/A815187Y
Cravens A, Payne J, Smolke CD (2019) Synthetic biology strategies for microbial biosynthesis of plant natural products. Nat Commun 10(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09848-w
Day AJ, Sumby CJ, George JH (2019) Biomimetic synthetic studies on the bruceol Family of meroterpenoid natural products. J Organomet Chem 85(4):2103–2117. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.9b02862
de la Torre MC, Sierra MA (2004) Comments on recent achievements in biomimetic organic synthesis. Angew Chem Int Ed 43(2):160–181. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200200545
Dethe DH, Kumar V, Maiti R (2018) Biomimetic total syntheses of chromane meroterpenoids, guadials B and C, guapsidial A and psiguajadial D. Org Biomol Chem 16(26):4793–4796. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8OB01092G
Diaz-Marrero AR, Austin P, Van Soest R, Matainaho T, Roskelley CD, Roberge M, Andersen RJ (2006) Avinosol, a meroterpenoid-nucleoside conjugate with antiinvasion activity isolated from the marine sponge Dysidea sp. Org Lett 8(17):3749–3752. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol061333p
Didier PJ, Phillips JN, Kuebler DJ, Nasr M, Brindley PJ, Stovall ME, Bowers LC, Didier E (2006) Antimicrosporidial activities of fumagillin, TNP-470, ovalicin, and ovalicin derivatives in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50(6):2146–2155. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00020-06
Dillen JL, Horak RM, Maharaj VJ, Marais SF, Vleggaar R (1989) Absolute configuration and biosynthesis of the austalides, meroterpenoid metabolites of Aspergillus ustus: mode of cyclisation of the farnesyl moiety. J Chem Soc Chem Commun (7):393–394. https://doi.org/10.1039/C39890000393
Ding L, Münch J, Goerls H, Maier A, Fiebig H-H, Lin W-H, Hertweck C (2010) **amycin, a pentacyclic indolosesquiterpene with selective anti-HIV activity from a bacterial mangrove endophyte. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20(22):6685–6687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.09.010
Duffield A, Jefferies P, Maslen E, Rae A (1963) The structure of bruceol. Tetrahedron 19(4):593–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4020(01)98546-1
El-Elimat T, Raja HA, Ayers S, Kurina SJ, Burdette JE, Mattes Z, Sabatelle R, Bacon JW, Colby AH, Grinstaff MW, Pearce CJ, Oberlies NH (2019) Meroterpenoids from Neosetophoma sp.: a dioxa [4.3.3] propellane ring system, potent cytotoxicity, and prolific expression. Org Lett 21(2):529–534. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.8b03769
Fujiki H, Tanaka Y, Miyake R, Kikkawa U, Nishizuka Y, Sugimura T (1984) Activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase (protein kinase C) by new classes of tumor promoters: teleocidin and debromoaplysiatoxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 120(2):339–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291X(84)91259-2
García-Gutiérrez MS, Navarrete F, Gasparyan A, Austrich-Olivares A, Sala F, Manzanares J (2020) Cannabidiol: a potential new alternative for the treatment of anxiety, depression, and psychotic disorders. Biomolecules 10(11):1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111575
Geris R, Simpson TJ (2009) Meroterpenoids produced by fungi. Nat Prod Rep 26(8):1063–1094. https://doi.org/10.1039/B820413F
Ghisalberti EL (1998) Phytochemistry of the Australian rutaceae: Boronia, Eriostemon and Phebalium species. Phytochemistry 47(2):163–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(97)00571-2
Gozari M, Alborz M, El-Seedi HR, Jassbi AR (2020) Chemistry, biosynthesis and biological activity of terpenoids and meroterpenoids in bacteria and fungi isolated from different marine habitats. Eur J Med Chem 210:112957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112957
Guo C, Knox BP, Chiang Y-M, Lo H-C, Sanchez JF, Lee K-H, Oakley BR, Bruno KS, Wang CC (2012) Molecular genetic characterization of a cluster in A. terreus for biosynthesis of the meroterpenoid terretonin. Org Lett 14(22):5684–5687. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol302682z
Gutiérrez RMP, Mitchell S, Solis RV (2008) Psidium guajava: a review of its traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology. J Ethnopharmacol 117(1):1–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2008.01.025
Han J, Zhang J, Song Z, Zhu G, Liu M, Dai H, Hsiang T, Liu X, Zhang L, Quinn RJ, Feng Y (2020) Genome-based mining of new antimicrobial meroterpenoids from the phytopathogenic fungus Bipolaris sorokiniana strain 11134. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10522-1
Hashimoto T, Kuzuyama T (2016) Mechanistic insights into Diels-Alder reactions in natural product biosynthesis. Curr Opin Chem Biol 35:117–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2016.09.015
Heravi MM, Ahmadi T, Ghavidel M, Heidari B, Hamidi H (2015) Recent applications of the hetero Diels–Alder reaction in the total synthesis of natural products. RSC Adv 5(123):101999–102075. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA17488K
Hou J-Q, Guo C, Zhao J-J, Dong Y-Y, Hu X-L, He Q-W, Zhang B-B, Yan M, Wang H (2017a) Anti-inflammatory meroterpenoids from Baeckea frutescens. J Nat Prod 80(8):2204–2214. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.7b00042
Hou J-Q, Guo C, Zhao J-J, He Q-W, Zhang B-B, Wang H (2017b) Frutescone A–G, tasmanone-based meroterpenoids from the aerial parts of Baeckea frutescens. J Organomet Chem 82(3):1448–1457. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.6b02643
Hou J-Q, Wang B-L, Han C, Xu J, Wang Z, He Q-W, Zhang P-L, Zhao S-M, Pei X, Wang H (2018) Atropisomeric meroterpenoids with rare triketone-phloroglucinol-terpene hybrids from Baeckea frutescens. Org Biomol Chem 16(44):8513–8524. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8OB02433B
Hou J-Q, Yu J-H, Zhao H, Dong Y-Y, Peng Q-S, Zhang B-B, Wang H (2020) Biomimetic total syntheses of baefrutones A–D, baeckenon B, and frutescones A, D–F. Org Biomol Chem 18(6):1135–1139. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9OB02490E
Itoh T, Tokunaga K, Matsuda Y, Fujii I, Abe I, Ebizuka Y, Kushiro T (2010) Reconstitution of a fungal meroterpenoid biosynthesis reveals the involvement of a novel family of terpene cyclases. Nat Chem 2(10):858–864. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.764
Jeon B, Wang S-A, Ruszczycky MW, H-w L (2017) Natural [4 + 2]-cyclases. Chem Rev 117(8):5367–5388. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00578
Jiao W, Cheng B, Shi G, Chen G, Gu B, Zhou Y, Hong L, Yang F, Liu Z, Qiu S, Liu Z, Yang P, Lin H (2017) Dysivillosins A–D, unusual anti-allergic meroterpenoids from the marine sponge Dysidea villosa. Sci Rep 7(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04021-z
Jiao W, Li J, Zhang M, Cui J, Gui Y, Zhang Y, Li J, Liu K, Lin H (2019) Frondoplysins A and B, unprecedented terpene-alkaloid bioconjugates from Dysidea frondosa. Org Lett 21(16):6190–6193. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.9b01754
Kahlert L, Bassiony EF, Cox RJ, Skellam EJ (2020) Diels–Alder reactions during the biosynthesis of sorbicillinoids. Angew Chem Int Ed 59(14):5816–5822. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201915486
Kaysser L, Bernhardt P, Nam S-J, Loesgen S, Ruby JG, Skewes-Cox P, Jensen PR, Fenical W, Moore BS (2012) Merochlorins A–D, cyclic meroterpenoid antibiotics biosynthesized in divergent pathways with vanadium-dependent chloroperoxidases. J Am Chem Soc 134(29):11988–11991. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja305665f
Kikuchi H, Sakurai K, Oshima Y (2014) Development of diversity-enhanced extracts of Curcuma zedoaria and their new sesquiterpene-like compounds. Org Lett 16(7):1916–1919. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol5004324
Kikuchi H, Ichinohe K, Kida S, Murase S, Yamada O, Oshima Y (2016) Monoterpene indole alkaloid-like compounds based on diversity-enhanced extracts of iridoid-containing plants and their immune checkpoint inhibitory activity. Org Lett 18(22):5948–5951. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.6b03057
Kikuchi H, Kawai K, Nakashiro Y, Yonezawa T, Kawaji K, Kodama EN, Oshima Y (2019) Construction of a meroterpenoid-like compounds library based on diversity-enhanced extracts. Chem Eur J 25(4):1106–1112. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201805417
Kim HJ, Ruszczycky MW, Liu H-W (2012) Current developments and challenges in the search for a naturally selected Diels-Alderase. Curr Opin Chem Biol 16(1–2):124–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2011.12.017
Lawrence AL, Adlington RM, Baldwin JE, Lee V, Kershaw JA, Thompson AL (2010) A short biomimetic synthesis of the meroterpenoids guajadial and psidial A. Org Lett 12(8):1676–1679. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol100138k
Lee C, Chen L, Chiang C, Lai C, Lin H (2019) The biosynthesis of norsesquiterpene aculenes requires three cytochrome P450 enzymes to catalyze a stepwise demethylation process. Angew Chem Int Ed 58(51):18414–18418. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201910200
Li H, Zhang Q, Li S, Zhu Y, Zhang G, Zhang H, Tian X, Zhang S, Ju J, Zhang C (2012) Identification and characterization of xiamycin A and oxiamycin gene cluster reveals an oxidative cyclization strategy tailoring indolosesquiterpene biosynthesis. J Am Chem Soc 134(21):8996–9005. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja303004g
Li Y, Wu C, Liu D, Proksch P, Guo P, Lin W (2014) Chartarlactams A–P, phenylspirodrimanes from the sponge-associated fungus Stachybotrys chartarum with antihyperlipidemic activities. J Nat Prod 77(1):138–147. https://doi.org/10.1021/np400824u
Li H, Sun Y, Zhang Q, Zhu Y, Li S-M, Li A, Zhang C (2015) Elucidating the cyclization cascades in xiamycin biosynthesis by substrate synthesis and enzyme characterizations. Org Lett 17(2):306–309. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol503399b
Li H, Feng W, Li X, Kang X, Yan S, Chao M, Mo S, Sun W, Lu Y, Chen C, Wang J, Zhu H, Zhang Y (2020a) Terreuspyridine: an unexpected pyridine-fused meroterpenoid alkaloid with a tetracyclic 6/6/6/6 skeleton from Aspergillus terreus. Org Lett 22(17):7041–7046. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.0c02641
Li H, Zhang R, Cao F, Wang J, Hu Z, Zhang Y (2020b) Proversilins A–E, drimane-type sesquiterpenoids from the endophytic Aspergillus versicolor. J Nat Prod 83(7):2200–2206. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c00298
Li J, Li F, King-Smith E, Renata H (2020c) Merging chemoenzymatic and radical-based retrosynthetic logic for rapid and modular synthesis of oxidized meroterpenoids. Nat Chem 12(2):173–179. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-019-0407-6
Lin H-C, Chooi Y-H, Dhingra S, Xu W, Calvo AM, Tang Y (2013) The fumagillin biosynthetic gene cluster in Aspergillus fumigatus encodes a cryptic terpene cyclase involved in the formation of β-trans-bergamotene. J Am Chem Soc 135(12):4616–4619. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja312503y
Lin H-C, Tsunematsu Y, Dhingra S, Xu W, Fukutomi M, Chooi Y-H, Cane DE, Calvo AM, Watanabe K, Tang Y (2014) Generation of complexity in fungal terpene biosynthesis: discovery of a multifunctional cytochrome P450 in the fumagillin pathway. J Am Chem Soc 136(11):4426–4436. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja500881e
Liu D, Li Y, Guo X, Ji W, Lin W (2020) Chartarlactams Q–T, dimeric phenylspirodrimanes with antibacterial and antiviral activities. Chem Biodivers 17(6):e2000170. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.202000170
Long Y, Tang T, Wang L-Y, He B, Gao K (2019) Absolute configuration and biological activities of meroterpenoids from an endophytic fungus of Lycium barbarum. J Nat Prod 82(8):2229–2237. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b00288
Luo X, Reiter MA, d’Espaux L, Wong J, Denby CM, Lechner A, Zhang Y, Grzybowski AT, Harth S, Lin W, Lee H, Yu C, Shin J, Deng K, Benites VT, Wang G, Baidoo EEK, Chen Y, Dev I, Petzold CJ, Keasling JD (2019) Complete biosynthesis of cannabinoids and their unnatural analogues in yeast. Nature 567(7746):123–126. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-0978-9
Lv J, Gao Y, Zhao H, Awakawa T, Liu L, Chen G, Yao X, Hu D, Abe I, Gao H (2020) Biosynthesis of biscognienyne B involving an unprecedented cytochrome P450-dependent alkynylation. Angew Chem 132(32):13633–13638. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.202004364
Ma T-K, Elliott DC, Reid S, White AJ, Parsons PJ, Barrett AG (2018) Meroterpenoid synthesis via sequential polyketide aromatization and cationic polyene cyclization: total syntheses of (+)-hongoquercin A and B and related meroterpenoids. J Organomet Chem 83(21):13276–13286. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.8b02095
Ma T-K, Parsons PJ, Barrett AG (2019) Meroterpenoid synthesis via sequential polyketide aromatization and radical anion cascade triene cyclization: biomimetic total syntheses of austalide natural products. J Organomet Chem 84(9):4961–4970. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.9b00142
Macias FA, Carrera C, Galindo JC (2014) Brevianes revisited. Chem Rev 114(5):2717–2732. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr300048m
Matsuda Y, Abe I (2016) Biosynthesis of fungal meroterpenoids. Nat Prod Rep 33(1):26–53. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NP00090D
Matsuda Y, Awakawa T, Itoh T, Wakimoto T, Kushiro T, Fujii I, Ebizuka Y, Abe I (2012) Terretonin biosynthesis requires methylation as essential step for cyclization. ChemBioChem 13(12):1738–1741. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201200369
Matsuda Y, Wakimoto T, Mori T, Awakawa T, Abe I (2014) Complete biosynthetic pathway of anditomin: nature’s sophisticated synthetic route to a complex fungal meroterpenoid. J Am Chem Soc 136(43):15326–15336. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja508127q
Matsuda Y, Iwabuchi T, Wakimoto T, Awakawa T, Abe I (2015) Uncovering the unusual D-ring construction in terretonin biosynthesis by collaboration of a multifunctional cytochrome P450 and a unique isomerase. J Am Chem Soc 137(9):3393–3401. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b00570
Matsuda Y, Awakawa T, Mori T, Abe I (2016) Unusual chemistries in fungal meroterpenoid biosynthesis. Curr Opin Chem Biol 31:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2015.11.001
Matsuda Y, Bai T, Phippen CB, Nødvig CS, Kjærbølling I, Vesth TC, Andersen MR, Mortensen UH, Gotfredsen CH, Abe I, Larsen TO (2018) Novofumigatonin biosynthesis involves a non-heme iron-dependent endoperoxide isomerase for orthoester formation. Nat Commun 9(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04983-2
Mayerl F, Gao Q, Huang S, Klohr SE, Matson JA, Gustavson DR, Pirnik DM, Berry RL, Fairchild C, Rose WC (1993) Eupenifeldin, a novel cytotoxic bistropolone from Eupenicillium brefeldianum. J Antibiot 46(7):1082–1088. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.46.1082
McCowen MC, Callender ME, Lawlis JF Jr (1951) Fumagillin (H-3), a new antibiotic with amebicidal properties. Science (Washington):202–203
Minagawa N, Yabu Y, Kita K, Nagai K, Ohta N, Meguro K, Sakajo S, Yoshimoto A (1996) An antibiotic, ascofuranone, specifically inhibits respiration and in vitro growth of long slender bloodstream forms of Trypanosoma brucei brucei. Mol Biochem Parasitol 81(2):127–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-6851(96)02665-5
Mitsuhashi T, Barra L, Powers Z, Kojasoy V, Cheng A, Yang F, Taniguchi Y, Kikuchi T, Fujita M, Tantillo DJ, Porco JA, Abe I (2020) Exploiting the potential of meroterpenoid cyclases to expand the chemical space of fungal meroterpenoids. Angew Chem 132(52):23980–23989. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.202011171
Mori T, Iwabuchi T, Hoshino S, Wang H, Matsuda Y, Abe I (2017) Molecular basis for the unusual ring reconstruction in fungal meroterpenoid biogenesis. Nat Chem Biol 13(10):1066–1073. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2443
Murray LA, McKinnie SM, Moore BS, George JH (2020) Meroterpenoid natural products from Streptomyces bacteria—the evolution of chemoenzymatic syntheses. Nat Prod Rep 37:1334–1366. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NP00018C
Nagamitsu T, Sunazuka T, Obata R, Tomoda H, Tanaka H, Harigaya Y, Omura S, Smith AB III (1995) Total synthesis of (+)-pyripyropene A, a potent, orally bioavailable inhibitor of acyl-CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase. J Organomet Chem 60(25):8126–8127. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo00130a005
Nevoigt E (2008) Progress in metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 72(3):379–412. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.00025-07
Newman DJ, Cragg GM (2016) Natural products as sources of new drugs from 1981 to 2014. J Nat Prod 79(3):629–661. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b01055
Ning S, Liu Z, Wang Z, Liao M, **e Z (2019) Biomimetic synthesis of psiguajdianone guided discovery of the meroterpenoids from Psidium guajava. Org Lett 21(21):8700–8704. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.9b03299
Oikawa H (2016) Nature’s strategy for catalyzing Diels-Alder reaction. Cell Chem Biol 23(4):429–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2016.04.002
Peng X-R, Liu J-Q, Wan L-S, Li X-N, Yan Y-X, Qiu M-H (2014) Four new polycyclic meroterpenoids from Ganoderma cochlear. Org Lett 16(20):5262–5265. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol5023189
Peng X, Liu J, Wang C, Han Z, Shu Y, Li X, Zhou L, Qiu M (2015) Unusual prenylated phenols with antioxidant activities from Ganoderma cochlear. Food Chem 171:251–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.08.127
Petersen LM, Hoeck C, Frisvad JC, Gotfredsen CH, Larsen TO (2014) Dereplication guided discovery of secondary metabolites of mixed biosynthetic origin from Aspergillus aculeatus. Molecules 19(8):10898–10921. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190810898
Picoul W, Bedel O, Haudrechy A, Langlois Y (2003) Progress in fumagillin synthesis. Pure Appl Chem 75(2–3):235–249. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac200375020235
Powers Z, Scharf A, Cheng A, Yang F, Himmelbauer M, Mitsuhashi T, Barra L, Taniguchi Y, Kikuchi T, Fujita M (2019) Biomimetic synthesis of meroterpenoids by dearomatization-driven polycyclization. Angew Chem Int Ed 58(45):16141–16146. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201910710
Prompanya C, Dethoup T, Bessa LJ, Pinto MM, Gales L, Costa PM, Silva A, Kijjoa A (2014) New isocoumarin derivatives and meroterpenoids from the marine sponge-associated fungus Aspergillus similanensis sp. nov. KUFA 0013. Mar Drugs 12(10):5160–5173. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12105160
Qin X-J, Yu Q, Yan H, Khan A, Feng M-Y, Li P-P, Hao X-J, An L-K, Liu H-Y (2017) Meroterpenoids with antitumor activities from guava (Psidium guajava). J Agric Food Chem 65(24):4993–4999. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b01762
Raggatt ME, Simpson TJ, Chicarelli-Robinson MI (1997) Biosynthesis of Xenovulene A®: formation of a cyclopentenone via a unique ring expansion–ring contraction mechanism. ChemComm (22):2245–2247. https://doi.org/10.1039/A704864E
Ro D-K, Paradise EM, Ouellet M, Fisher KJ, Newman KL, Ndungu JM, Ho KA, Eachus RA, Ham TS, Kirby J, Chang MCY, Withers ST, Shiba Y, Sarpong R, Keasling JD (2006) Production of the antimalarial drug precursor artemisinic acid in engineered yeast. Nature 440(7086):940–943
Robinson R (1917) LXIII.—A synthesis of tropinone. J Chem Soc Trans 111:762–768
Sakoulas G, Nam S-J, Loesgen S, Fenical W, Jensen PR, Nizet V, Hensler M (2012) Novel bacterial metabolite merochlorin A demonstrates in vitro activity against multi-drug resistant methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS One 7(1):e29439. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0029439
Schmidt-Dannert C (2014) Biosynthesis of terpenoid natural products in fungi. Biotechnology of Isoprenoids. Springer:19–61
Schor R, Schotte C, Wibberg D, Kalinowski J, Cox RJ (2018) Three previously unrecognised classes of biosynthetic enzymes revealed during the production of xenovulene A. Nat Commun 9(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04364-9
Schotte C, Li L, Wibberg D, Kalinowski J, Cox RJ (2020) Synthetic biology driven biosynthesis of unnatural tropolone sesquiterpenoids. Angew Chem Int Ed 59(52):23870–23878. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202009914
Shao H, Gao X, Wang ZT, Gao Z, Zhao YM (2020) Divergent biomimetic total syntheses of ganocins A–C, ganocochlearins C and D, and cochlearol T. Angew Chem 132(19):7489–7494. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.202000677
Sin N, Meng L, Wang MQ, Wen JJ, Bornmann WG, Crews CM (1997) The anti-angiogenic agent fumagillin covalently binds and inhibits the methionine aminopeptidase, MetAP-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94(12):6099–6103. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.94.12.6099
Sintchak MD, Fleming MA, Futer O, Raybuck SA, Chambers SP, Caron PR, Murcko MA, Wilson KP (1996) Structure and mechanism of inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase in complex with the immunosuppressant mycophenolic acid. Cell 85(6):921–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81275-1
Smith AB III, Kinsho T, Sunazuka T, Ōmura S (1996) Biomimetic total synthesis of the ACAT inhibitor (+)-pyripyropene E. Tetrahedron Lett 37(36):6461–6464. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-4039(96)01439-6
Springer JP, Dorner JW, Cole RJ, Cox RH (1979) Terretonin, a toxic compound from Aspergillus terreus. J Organomet Chem 44(26):4852–4854. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo00394a023
Stierle AA, Stierle DB (2014) Bioactive secondary metabolites from acid mine waste extremophiles. Nat Prod Commun 9(7):1037–1044. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578X1400900738
Stierle DB, Stierle AA, Patacini B (2007) The berkeleyacetals, three meroterpenes from a deep water acid mine waste Penicillium. J Nat Prod 70(11):1820–1823. https://doi.org/10.1021/np070329z
Sunazuka T, Ōmura S (2005) Total synthesis of α-pyrone meroterpenoids, novel bioactive microbial metabolites. Chem Rev 105(12):4559–4580. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr040628i
Takashima M, Sakai H (1960) A new toxic substance, teleocidin, produced by Streptomyces. Part I. Production, isolation and chemical studies Part II. Biological studies of teleocidin. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 24(7):647–655. https://doi.org/10.1080/03758397.1960.10857741
Teufel R, Kaysser L, Villaume MT, Diethelm S, Carbullido MK, Baran PS, Moore BS (2014) One-pot enzymatic synthesis of merochlorin A and B. Angew Chem Int Ed 53(41):11019–11022. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201405694
Thomas F, Schmidt C, Kayser O (2020) Bioengineering studies and pathway modeling of the heterologous biosynthesis of tetrahydrocannabinolic acid in yeast. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10798-3
Tomoda H, Nishida H, Kim YK, Obata R, Sunazuka T, Omura S, Bordner J, Guadliana M, Dormer PG, Smith AB III (1994) Relative and absolute stereochemistry of pyripyropene A, a potent, bioavailable inhibitor of acyl-CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT). J Am Chem Soc 116(26):12097–12098. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00105a078
Tsukada K, Shinki S, Kaneko A, Murakami K, Irie K, Murai M, Miyoshi H, Dan S, Kawaji K, Hayashi H, Kodama EN, Hori A, Salim E, Kuraishi T, Hirata N, Kanda Y, Asai T (2020) Synthetic biology based construction of biological activity-related library of fungal decalin-containing diterpenoid pyrones. Nat Commun 11(1):1–12, 1830.
Ubillas R, Barnes CL, Gracz H, Rottinghaus GE, Tempesta MS (1989) X-ray crystal structure of oxalicine A, a novel alkaloid from Penicillium oxalicum. J Chem Soc, Chem Commun(21):1618–1619. https://doi.org/10.1039/C39890001618
Vicente M, Cabello A, Platas G, Basilio A, Diez M, Dreikorn S, Giacobbe R, Onishi J, Meinz M, Kurtz M, Rosenbach M, Thompson J, Abruzzo G, Flattery A, Kong L, Tsipouras A, Wilson K, Peláez F (2001) Antimicrobial activity of ergokonin A from Trichoderma longibrachiatum. J Appl Microbiol 91(5):806–813. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2672.2001.01447.x
Wang W, Du L, Sheng S, Li A, Li Y, Cheng G, Li G, Sun G, Hu Q, Matsuda Y (2019a) Genome mining for fungal polyketide-diterpenoid hybrids: discovery of key terpene cyclases and multifunctional P450s for structural diversification. Org Chem Front 6(5):571–578. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8QO01124A
Wang W, Lee J, Kim K-J, Sung Y, Park K-H, Oh E, Park C, Son Y-J, Kang H (2019b) Austalides, osteoclast differentiation inhibitors from a marine-derived strain of the fungus Penicillium rudallense. J Nat Prod 82(11):3083–3088. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b00690
Wang H, Li R, Li J, He J, Cao Z, Kurtán T, Mándi A, Zheng G, Zhang W (2020) Alternarin A, a drimane meroterpenoid, suppresses neuronal excitability from the coral-associated fungi Alternaria sp. ZH-15. Org Lett 22(8):2995–2998. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.0c00746
Wolfender J-L, Queiroz EF (2012) Chemical diversity of natural resources and the bioactivity of their constituents. CHIMIA Int J Chem 66(5):324–329. https://doi.org/10.2533/chimia.2012.324
Yaegashi J, Romsdahl J, Chiang Y-M, Wang CC (2015) Genome mining and molecular characterization of the biosynthetic gene cluster of a diterpenic meroterpenoid, 15-deoxyoxalicine B, in Penicillium canescens. Chem Sci 6(11):6537–6544. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC01965F
Yamazaki H, Nakayama W, Takahashi O, Kirikoshi R, Izumikawa Y, Iwasaki K, Toraiwa K, Ukai K, Rotinsulu H, Wewengkang DS, Sumilat DA, Mangindaan REP, Namikoshi M (2015) Verruculides A and B, two new protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors from an Indonesian ascidian-derived Penicillium verruculosum. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 25(16):3087–3090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.06.026
Yee DA, Kakule TB, Cheng W, Chen M, Chong CT, Hai Y, Hang LF, Hung Y-S, Liu N, Ohashi M, Okorafor IC, Song Y, Tang M, Zhang Z, Tang Y (2019) Genome mining of alkaloidal terpenoids from a hybrid terpene and nonribosomal peptide biosynthetic pathway. J Am Chem Soc 142(2):710–714. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b13046
Yu F, Li M, Xu C, Sun B, Zhou H, Wang Z, Xu Q, **e M, Zuo G, Huang P, Guo H, Wang Q, He J (2016) Crystal structure and enantioselectivity of terpene cyclization in SAM-dependent methyltransferase TleD. Biochem J 473(23):4385–4397. https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20160695
Zaehle C, Gressler M, Shelest E, Geib E, Hertweck C, Brock M (2014) Terrein biosynthesis in Aspergillus terreus and its impact on phytotoxicity. Chem Biol 21(6):719–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2014.03.010
Zhai Y, Li Y, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Ren F, Zhang X, Liu G, Liu X, Che Y (2019) Identification of the gene cluster for bistropolone-humulene meroterpenoid biosynthesis in Phoma sp. Fungal Genet Biol 129:7–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2019.04.004
Zhang T, Wan J, Zhan Z, Bai J, Liu B, Hu Y (2018a) Activation of an unconventional meroterpenoid gene cluster in Neosartorya glabra leads to the production of new berkeleyacetals. Acta Pharm Sin B 8(3):478–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2017.12.005
Zhang X, Wang T, Xu Q, **ong Y, Zhang L, Han H, Xu K, Guo W, Xu Q, Tan R (2018b) Genome mining and comparative biosynthesis of meroterpenoids from two phylogenetically distinct fungi. Angew Chem 130(27):8316–8320. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201804317
Zhao H, Chen G-D, Zou J, He R-R, Qin S-Y, Hu D, Li G-Q, Guo L-D, Yao X-S, Gao H (2017) Dimericbiscognienyne A: a meroterpenoid dimer from Biscogniauxia sp. with new skeleton and its activity. Org Lett 19(1):38–41. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.6b03264
Zhou Y, Mándi A, Debbab A, Wray V, Schulz B, Müller WE, Lin W, Proksch P, Kurtán T, Aly AH (2011) New austalides from the sponge-associated fungus Aspergillus sp. Eur J Org Chem 2011(30):6009–6019. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.201100670
Funding
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21907031 and 21977029). J. Han thanks Griffith University for the provision of the Ph.D. scholarships (GUPRS and GUIPRS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.F. and R.Q. conceived and designed research. J.H., L.J., and X.L. wrote the manuscript. Y.F., X.L., R.Q., and L.Z. reviewed and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 637 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, J., Jiang, L., Zhang, L. et al. Peculiarities of meroterpenoids and their bioproduction. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105, 3987–4003 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11312-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11312-z