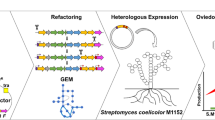
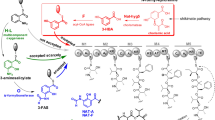
Abstract
Nargenicin A1, an antibacterial produced by Nocardia sp. CS682 (KCTC 11297BP), demonstrates effective activity against various Gram-positive bacteria. Hence, we attempted to enhance nargenicin A1 production by utilizing the cumulative effect of synthetic biology, metabolic engineering and statistical media optimization strategies. To facilitate the modular assembly of multiple genes for genetic engineering in Nocardia sp. CS682, we constructed a set of multi-monocistronic vectors, pNV18L1 and pNV18L2 containing hybrid promoter (derived from ermE* and promoter region of neo r ), ribosome binding sites (RBS), and restriction sites for cloning, so that each cloned gene was under its own promoter and RBS. The multi-monocistronic vector, pNV18L2 containing transcriptional terminator showed better efficiency in reporter gene assay. Thus, multiple genes involved in the biogenesis of pyrrole moiety (ngnN2, ngnN3, ngnN4, and ngnN5 from Nocardia sp. CS682), glucose utilization (glf and glk from Zymomonas mobilis), and malonyl-CoA synthesis (accA2 and accBE from Streptomyces coelicolor A3 (2)), were cloned in pNV18L2. Further statistical optimization of specific precursors (proline and glucose) and their feeding time led to ~84.9 mg/L nargenicin from Nocardia sp. GAP, which is ~24-fold higher than Nocardia sp. CS682 (without feeding). Furthermore, pikC from Streptomyces venezuelae was expressed to generate Nocardia sp. PikC. Nargenicin A1 acid was characterized as novel derivative of nargenicin A1 produced from Nocardia sp. PikC by mass spectrometry (MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analyses. We also performed comparative analysis of the anticancer and antibacterial activities of nargenicin A1 and nargenicin A1 acid, which showed a reduction in antibacterial potential for nargenicin A1 acid. Thus, the development of an efficient synthetic biological platform provided new avenues for enhancing or structurally diversifying nargenicin A1 by means of pathway designing and engineering.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson J, Dueber JE, Leguia M, Wu GC, Goler JA, Arkin AP, Keasling JD (2010) BglBricks: a flexible standard for biological part assembly. J Biol Eng 4:1. doi:10.1186/1754-1611-4-1
Arul Jose P, Jebakumar SR (2014) Successive nonstatistical and statistical approaches for the improved antibiotic activity of rare actinomycete Nonomuraea sp. JAJ18. Biomed Res Int 2014 . doi:10.1155/2014/906097906097
Bezerra MA, Santelli RE, Oliveira EP, Villar LS, Escaleira LA (2008) Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta 76:965–977. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2008.05.019
Bibb MJ, Janssen GR, Ward JM (1985) Cloning and analysis of the promoter region of the erythromycin resistance gene (ermE) of Streptomyces erythraeus. Gene 38:215–226. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(86)90122-8
Bierman M, Logan R, O’brien K, Seno ET, Rao RN, Schoner BE (1992) Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene 116:43–49. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(92)90627-2
Bilyk O, Luzhetskyy A (2016) Metabolic engineering of natural product biosynthesis in actinobacteria. Curr Opin Biotechnol 42:98–107. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2016.03.008
Chandran SS, Yi J, Draths KM, Daeniken RV, Weber W, Frost JW (2003) Phosphoenolpyruvate availability and the biosynthesis of shikimic acid. Biotechnol Prog 3:808–814
Chaudhary AK, Dhakal D, Sohng JK (2013a) An insight into the “-omics” based engineering of streptomycetes for secondary metabolite overproduction. Biomed Res Int 2013 . doi:10.1155/2013/968518968518
Chaudhary AK, Park JW, Yoon YJ, Kim BG, Sohng JK (2013b) Re-engineering of genetic circuit for 2-deoxystreptamine (2-DOS) biosynthesis in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3). Biotechnol Lett 35:285–293. doi:10.1007/s10529-012-1077-2
Chiba K, Hoshino Y, Ishino K, Kogure T, Mikami Y, Uehara Y, Ishikawa J (2007) Construction of a pair of practical Nocardia-Escherichia coli shuttle vectors. Jpn J Infect Dis 60:45–47
Clark BR, Murphy CD (2009) Biosynthesis of pyrrolyl polyenes in Auxarthron umbrinum. Org Biomol Chem 7:111–116. doi:10.1039/b813236d
Dhakal D, Jha AK, Pokhrel A, Shrestha A, Sohng JK (2016) Genetic manipulation of Nocardia species. Curr Protoc Microbiol 40. doi:10.1002/9780471729259.mc10f02s4010F.2.1-10F.2.18
Dhakal D, Le TT, Pandey RP, Jha AK, Gurung R, Parajuli P, Pokhrel AR, Yoo JC, Sohng JK (2015) Enhanced production of nargenicin A1 and generation of novel glycosylated derivatives. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175:2934–2949. doi:10.1007/s12010-014-1472-3
Dhakal D, Sohng JK (2015a) Commentary: toward a new focus in antibiotic and drug discovery from the Streptomyces arsenal. Front Microbiol 6:727. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.00727
Dhakal D, Sohng JK (2015b) Laboratory maintenance of Nocardia species. Curr Protoc Microbiol 39:1 . doi:10.1002/9780471729259.mc10f01s39 0F.1.1-8
Fan Y, Zhao M, Wei L, Hu F, Imanaka T, Bai L, Hua Q (2015) Enhancement of UDPG synthetic pathway improves ansamitocin production in Actinosynnem pretiosum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:2651–2662. doi:10.1007/s00253-015-7148-2
Gerth K, Steinmetz H, Höflel G, Reichenbach H (2002) Studies on the biosynthesis of epothilones: hydroxylation of Epo A and B to epothilones E and F. J Antibiot 55:41–45. doi.10.7164/antibiotics.55.41
Gibson DG, Young L, Chuang RY, Venter JC, Hutchison CA, Smith HO (2009) Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nat Methods 6:343–345. doi:10.1038/nmeth.1318
Harvey AL, Edrada-Ebel R, Quinn RJ (2015) The re-emergence of natural products for drug discovery in the genomics era. Nat Rev Drug Discov 14:111–129. doi:10.1038/nrd4510
Jha AK, Dhakal D, Van PT, Pokhrel AR, Yamaguchi T, Jung HJ, Yoon YJ, Sohng JK (2015) Structural modification of herboxidiene by substrate-flexible cytochrome P450 and glycosyltransferase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:3421–3431. doi:10.1007/s00253-015-6431-6
Keasling JD (2012) Synthetic biology and the development of tools for metabolic engineering. Metab Eng 14:189–195. doi:10.1016/j.ymben.2012.01.004
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Butter MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Kim SH, Yoo JC, Kim TS (2009) Nargenicin enhances 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3- and all-trans retinoic acid-induced leukemia cell differentiation via PKCβI/MAPK pathways. Biochem Pharmacol 77:1694–1701. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2009.03.004
Koju D, Maharjan S, Dhakal D, Yoo JC, Sohng JK (2012) Effect of different biosynthetic precursors on the production of nargenicin A1 from metabolically engineered Nocardia sp. CS682. J Microbiol Biotechnol 22:1127–1132
Lee SY, Kim HU, Park JH, Park JM, Kim TY (2009) Metabolic engineering of microorganisms: general strategies and drug production. Drug Discov Today 14:78–88. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2008.08.004
Maharjan S, Aryal N, Bhattarai S, Koju D, Lamichhane J, Sohng JK (2012a) Biosynthesis of the nargenicin A1 pyrrole moiety from Nocardia sp. CS682. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:687–696. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3567-x
Maharjan S, Koju D, Lee HC, Yoo JC, Sohng JK (2012b) Metabolic engineering of Nocardia sp. CS682 for enhanced production of nargenicin A1. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166:805–817. doi:10.1007/s12010-011-9470-1.
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Na D, Kim TY, Lee SY (2010) Construction and optimization of synthetic pathways in metabolic engineering. Curr Opin Microbiol 13:363–370. doi:10.1016/j.mib.2010.02.004
Newman DJ, Cragg GM (2012) Natural products as sources of new drugs over the 30 years from 1981 to 2010. J Nat Prod 75:311–335. doi:10.1021/np200906s
Nielsen J, Keasling JD (2011) Synergies between synthetic biology and metabolic engineering. Nat Biotechnol 29:693–695. doi:10.1038/nbt.1937
Olano C, Méndez C, Salas JA (2011) Molecular insights on the biosynthesis of antitumour compounds by actinomycetes. Microb Biotechnol 4:144–164. doi:10.1111/j.1751-7915.2010.00231.x
Painter RE, Adam GC, Arocho M, DiNunzio E, Donald RG, Dorso K, Genilloud O, Gill C, Goetz M, Hairston NN, Murgolo N (2015) Elucidation of DnaE as the antibacterial target of the natural product, nargenicin. Chem Biol 22:1362–1373. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2015.08.015
Park JW, Jung WS, Park SR, Park BC, Yoon YJ (2007) Analysis of intracellular short organic acid-coenzyme A esters from actinomycetes using liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom 42:1136–1147
Pokhrel AR, Dhakal D, Jha AK, Sohng JK (2015) Herboxidiene biosynthesis, production, and structural modifications: prospect for hybrids with related polyketide. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:8351–8362. doi:10.1007/s00253-015-6860-2
Prather KL, Martin CH (2008) De novo biosynthetic pathways: rational design of microbial chemical factories. Curr Opin Biotechnol 19:468–474. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2008.07.009
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Laboratory Press, New York
Shao Z, Zhao H (2012) Exploring DNA assembler, a synthetic biology tool for characterizing and engineering natural product gene clusters. Methods Enzymol 517:203–224. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-404634-4.00010-3
Siedler S, Bringer S, Blank LM, Bott M (2012) Engineering yield and rate of reductive biotransformation in Escherichia coli by partial cyclization of the pentose phosphate pathway and PTS-independent glucose transport. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:1459–1467. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3626-3
Sohng JK, Yamaguchi T, Seong CN, Baik KS, Park SC, Lee H, Jang J, Simkhada J, Yoo JC (2008) Production, isolation and biological activity of nargenicin from Nocardia sp. CS682. Arch Pharm Res 31:1339–1345. doi:10.1007/s12272-001-2115-0
Wang Y, Fang X, F A, Wang G, Zhang X (2011) Improvement of antibiotic activity of Xenorhabdus bovienii by medium optimization using response surface methodology. Microb Cell Factories 10:98. doi:10.1186/1475-2859-10-98
Weisser P, Krämer RE, Sahm H, Sprenger GA (1995) Functional expression of the glucose transporter of Zymomonas mobilis leads to restoration of glucose and fructose uptake in Escherichia coli mutants and provides evidence for its facilitator action. J Bacteriol 177:3351–3354
Xu P, Vansiri A, Bhan N, Koffas MA (2012) ePathBrick: a synthetic biology platform for engineering metabolic pathways in E. coli. ACS Synth Biol 1:256–266. doi:10.1021/sb300016b
Yoo JC, Cho HS, Park E, Park JA, Kim S, Kim DK, Kim CS, Chun HS (2009) Nargenicin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in BV-2 cells. Neuroreport 20:1007–1012. doi:10.1097/WNR.0b013e32832d2239
Zabala D, Braña AF, Salas JA, Méndez C (2016) Increasing antibiotic production yields by favoring the biosynthesis of precursor metabolites glucose-1-phosphate and/or malonyl-CoA in Streptomyces producer strains. J Antibiot 69:179–182. doi:10.1038/ja.2015.104
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) (NRF-2014R1A2A2A01002875).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1248 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhakal, D., Chaudhary, A.K., Yi, J.S. et al. Enhanced production of nargenicin A1 and creation of a novel derivative using a synthetic biology platform. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 9917–9931 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7705-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7705-3