Abstract
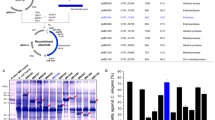
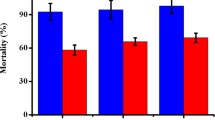
Due to their ability to degrade the proteins in nematode cuticle, serine proteases play an important role in the pathogenicity of nematophagous fungi against nematodes. The serine protease Ver112 was identified from the nematophagous fungus Lecanicillium psalliotae capable of degrading the nematode cuticle and killing nematodes effectively. In this study, the gene ver112 was introduced into the commercial biocontrol fungal agent Paecilomyces lilacinus by the restriction enzyme-mediated integration transformation. Compared to the wild strain, the transformant P. lilacinus 112 showed significantly greater protease activity, with nematicidal activities increased by 79% and 96% to Panagrellus redivivus and Caenorhabditis elegans at the second day, respectively. The crude protein extract isolated from the culture filtrate of P. lilacinus 112 also showed 20–25% higher nematicidal activity than that of the wild-type strain. Reverse transcription PCR results showed that the expression of gene ver112 in P. lilacinus 112 was correlated to protease activity of the culture filtrate. Our results demonstrated the first successful transfer of a virulence gene from one nematophagous fungus to another nematophagous fungus, and improved the pathogenicity of the recipient fungus against pest nematodes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åhman J, Johanson T, Olsson M, Punt PJ, van den Hondel CAMJJ, Tunlid AS (2002) Improving the pathogenicity of a nematode-trap** fungus by genetic engineering of a subtilisin with nematotoxic activity. Appl Environ Microbiol 689:3408–3415
Basualdo J, Ciarmela M, Sarmiento P, Minvielle M (2000) Biological activity of Paecilomyces genus against Toxocara canis eggs. Parasitol Res 86:854–859
Bonants PJM, Fitters PFL, Thijs H, den Belder E, Waalwijk C, Henfling JWDM (1995) A basic serine protease from Paecilomyces lilacinus with biological activity against Meloidogyne hapla eggs. Microbiology 141:775–784
Brand D, Roussos S, Pandey A, Zilioli P, Pohl J, Soccol C (2004) Development of a bionematicide with Paecilomyces lilacinus to control Meloidogyne incognita. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 118:81–88
Cox G, Kusch M, Edgar R (1981) Cuticle of Caenorhabditis elegans: its isolation and partial characterization. J Cell Biol 90:7–17
Dong LQ, Mo MH, Yang JK, Zhang KQ (2007) A method for obtaining quantities of Caenorhabditis elegans eggs. Nematology 9:743–744
Jiang Q, Ying SH, Feng MG (2007) Enhanced frequency of Beauveria bassiana blastospore transformation by restriction enzyme-mediated integration and electroporation. J Microbiol Methods 69:512–517
Kalele DN, Affokpon A, Coosemans J (2007) Efficacy of Paecilomyces lilacinus strain 251 against root knot nematodes in tomato under greenhouse conditions. Commun Agric Appl Biol Sci 72:209–213
Khan A, Williams K, Molloy MP, Nevalainen H (2003) Purification and characterization of a serine protease and chitinases from Paecilomyces lilacinus and detection of chitinase activity on 2D gels. Prot Expr Purif 32:210–220
Khan A, Willianms K, Nevalainen H (2004) Effects of Paecilomyces lilacinus protease and chitinase on the eggeshell structures and hatching of Meloidogyne javanica juveniles. Biol Control 31:346–352
Li J, Yu L, Yang JK, Dong LQ, Tian BY, Yu ZF, Liang LM, Zhang Y, Wang X, Zhang KQ (2010) New insights into the evolution of subtilisin-like serine protease genes in Pezizomycotina. BMC Evol Biol 10:68
Liang LM, Meng ZH, Ye FP, Yang JK, Liu SQ, Sun YN, Guo Y, Mi QL, Huang XW, Zou CG, Rao ZH, Lou ZY, Zhang KQ (2010) The crystal structures of two cuticle-degrading proteases from nematophagous fungi and their contribution to infection against nematodes. FASEB J 24:1391–1400
Lopez-Llorca LV, Robertson WM (1992) Immunocytochemical localization of a 32-kDa protease from the nematophagous fungus Verticillium suchlasporium in infected nematode eggs. Exp Mycol 16:261–267
Maizels RM, Blaxter ML, Selkirk ME (1993) Forms and functions of nematode surfaces. Exp Parasitol 77:380–384
Morton CO, Hirsch PR, Kerry BR (2004) Infection of plant-parasitic nematodes by nematophagous fungi: a review of the application of molecular biology to understand infection processes and to improve biological control. Nematology 62:161–170
Nordbring-Hertz B, Jansson HB, Tunlid A (2006) Nematophagous fungi. In: Encyclopedia of life sciences. Wiley, Chichester
Punt PJ, Dingemanse MA, Kuyvenhoven A, Soede RD, Pouwels PH, van den Hondel CA (1990) Functional elements in the promoter region of the Aspergillus nidulans gpdA gene encoding glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Gene 93:101–109
Qin Y, Ying SH, Chen Y, Shen ZC, Feng MG (2010) Integration of insecticidal protein Vip3Aa1 into Beauveria bassiana enhances fungal virulence to Spodoptera litura larvae by cuticle and per os infection. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:4611–4618
Riggle PJ, Kumamoto CA (1998) Genetic analysis in fungi using restriction-enzyme-mediated integration. Curr Opin Microbiol 1:395–399
Siddiqui ZA, Mahmood I (1996) Biological control of plant parasitic nematodes by fungi: a review. Bioresour Technol 58:229–239
St Leger RJ, Wang C (2010) Genetic engineering of fungal biocontrol agents to achieve greater efficacy against insect pests. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:901–907
Tunlid A, Rosen S, Ek B, Rask L (1994) Purification and characterization of an extracellular serine protease from the nematode-trap** fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Microbiology 140:1687–1695
Tunlid A, Åhman J, Oliver RP (1999) Transformation of the nematode-trap** fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. FEMS Microbiol Lett 173:111–116
Wang C, St Leger RJ (2007) A scorpion neurotoxin increases the potency of a fungal insecticide. Nat Biotechnol 25:1455–1456
Wang M, Yang JK, Zhang KQ (2006) Characterization of an extracellular protease and its cDNA from the nematode-trap** fungus Monacrosporium microscaphoides. Can J Microbiol 52:130–139
Xu J, Mo MH, Wei Z, Huang XW, Zhang KQ (2005) Transformation and mutagenesis of the nematode-trap** fungus Monacrosporium sphaeroides by restriction enzyme-mediated integration (REMI). J Microbiol 43:417–423
Yang JK, Huang XW, Tian BY, Wang M, Nui QH, Zhang KQ (2005a) Isolation and characterization of a serine protease from the nematophagous fungus, Lecanicillium psalliotae, displaying nematicidal activity. Biotechnol Lett 27:1123–1128
Yang JK, Huang XW, Tian BY, Sun H, Duan JX, Wu WP, Zhang KQ (2005b) Characterization of an extracellular serine protease gene from the nematophagous fungus Lecanicillium psalliotae. Biotechnol Lett 27:1329–1334
Yang JK, Tian BY, Liang LM, Zhang KQ (2007) Extracellular enzymes and the pathogenesis of nematophagous fungi. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75:21–31
Yang JK, Gan ZW, Lou ZY, Tao N, Mi QL, Liang LM, Sun YN, Guo Y, Huang XW, Zou CG, Rao ZH, Meng ZH, Zhang KQ (2010) Crystal structure and mutagenesis analysis of a chitinase CrChi1 from the nematophagous fungus Clonostachys rosea in complex with the inhibitor caffeine. Microbiology 156:3566–3574
Ying SH, Feng MG (2006) Novel blastospore-based transformation system for integration of phosphinothricin resistance and green fluorescence protein genes into Beauveria bassiana. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:206–210
Zare R, Gams W, Culham A (2000) A revision of Verticillium sect. Prostrata I. Phylogenetic studies using ITS sequences. Nova Hedwig 71:465–480
Zhang D, Yang Y, Castlebury LA, Cerniglia CE (1996) A method for the large scale isolation of high transformation efficiency fungal genomic DNA. FEMS Microbiol Lett 145:216–265
Zhang L, Yang JK, Niu QH, Zhao XN, Ye FP, Liang LM, Zhang KQ (2008) Investigation on the infection mechanism of the fungus Clonostachys rosea against nematodes using the green fluorescent protein. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:983–990
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Prof. Jian** Xu of the Department of Biology, McMaster University, for the valuable comments and critical discussions. This work was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (approved no. 2007CB411600), by projects from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (approved nos. 30630003, 30960229, and 30660107), by project from the Major State Basic Research Development Program (2009CB125905), the Department of Science and Technology of Yunnan Province (approved nos. 2007C007Z and 2009CI052), and the Yunnan Branch of China Tobacco Industrial Corporation (grant no. 2010yn17).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
**kui Yang and Xuna Zhao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Zhao, X., Liang, L. et al. Overexpression of a cuticle-degrading protease Ver112 increases the nematicidal activity of Paecilomyces lilacinus . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89, 1895–1903 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-3012-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-3012-6