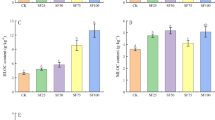
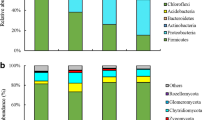
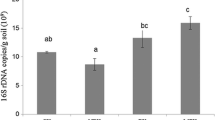
Abstract
The decline in soil nutrients is becoming a major concern of soil degradation. The possibility of using organic waste as a soil additive to increase nutrients and essential components is significant in soil quality protection and waste management. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of composted spent mushroom substrate (MS), giant panda feces (PF), and cattle manure (CM) as organic fertilizers in soil microbial communities and metabolites in blueberry orchard in China, which were measured by using high-throughput sequencing and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS)-based metabolomics. Altogether, 45.66% of the bacterial operational taxonomic units (OTUs) and 9.08% of the fungal OTUs were detected in all treatments. Principal coordinates analysis demonstrated that the bacterial and fungal communities in MS and PF treatments were similar, whereas the communities in the not-organic fertilized control (CK) were significantly different from those in the organic fertilizer treatments. Proteobacteria, Acidobacteria, and Bacteroidetes were the dominant bacterial phyla, and Basidiomycota, Ascomycota, and Mortierellomycota the dominant fungal phyla. Redundancy analysis indicated that pH and available potassium were the main factors determining the composition of microbial communities. The fungal genera Postia, Cephalotrichum, and Thermomyces increased in organic fertilizer treatments, and likely promoted the degradation of organic fertilizers into low molecular-weight metabolites (e.g., amino acids). PCA and PLS-DA models showed that the metabolites in CK were different from those in the other three treatments, and those in CM were clearly different from those in MS and PF. Co-occurrence network analysis showed that several taxa correlated positively with amino acid contents. The results of this study provide new insights into organic waste reutilization and new directions for further studies.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Penakalapati G, Swarthout J, Delahoy MJ, McAliley L, Wodnik B, Levy K, Freeman MC (2017) Exposure to animal feces and human health: a systematic review and proposed research priorities. Environ Sci Technol 51:11537–11552. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b02811
Zhuang M, Lam SK, Zhang J, Li H, Shan N, Yuan Y, Wang L (2019) Effect of full substituting compound fertilizer with different organic manure on reactive nitrogen losses and crop productivity in intensive vegetable production system of China. J Environ Manage 243:381–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.05.026
Gómez-Brandón M, Juárez MF-D, Zangerle M, Insam H (2016) Effects of digestate on soil chemical and microbiological properties: a comparative study with compost and vermicompost. J Hazard Mater 302:267–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.09.067
Yang X, Li G, Jia X, Zhao X, Lin Q (2020) Net nitrogen mineralization delay due to microbial regulation following the addition of granular organic fertilizer. Geoderma 359:113994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.113994
Cavagnaro TR (2014) Impacts of compost application on the formation and functioning of arbuscular mycorrhizas. Soil Biol Biochem 78:38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.07.007
Mu HY, Zhuang Z, Li YM, Qiao YH, Chen Q, **ong J, Guo LL, Jiang RF, Li HF (2020) Heavy metal contents in animal manure in China and the related soil accumulation risks. Huan **g ke xue= Huan**g kexue 41:986–996 https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.201903078
Gunkel-Grillon P, Roth E, Laporte-Magoni C, Le Mestre M (2015) Effects of long term raw pig slurry inputs on nutrient and metal contamination of tropical volcanogenic soils, Uvéa Island (South Pacific). Sci Total Environ 533:339–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.06.110
He MY, Dong TX, Ru SH, Su DC (2017) Accumulation and migration characteristics in soil profiles and bioavailability of heavy metals from livestock manure. Huan **g ke xue= Huan**g kexue 38:1576–1586 https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.201609227
Mazzola M, Manici LM (2012) Apple replant disease: role of microbial ecology in cause and control. Annu Rev Phytopathol 50:45–65. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-081211-173005
Ling N, Sun Y, Ma J, Guo J, Zhu P, Peng C, Yu G, Ran W, Guo S, Shen Q (2014) Response of the bacterial diversity and soil enzyme activity in particle-size fractions of Mollisol after different fertilization in a long-term experiment. Biol Fertil Soils 50:901–911. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-014-0911-1
Murase J, Hida A, Ogawa K, Nonoyama T, Yoshikawa N, Imai K (2015) Impact of long-term fertilizer treatment on the microeukaryotic community structure of a rice field soil. Soil Biol Biochem 80:237–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.10.015
Zou C, Li Y, Huang W, Zhao G, Pu G, Su J, Coyne MS, Chen Y, Wang L, Hu X, ** Y (2018) Rotation and manure amendment increase soil macro-aggregates and associated carbon and nitrogen stocks in flue-cured tobacco production. Geoderma 325:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.03.017
Li F, Kong Q, Zhang Q, Wang H, Wang L, Luo T (2020) Spent mushroom substrates affect soil humus composition, microbial biomass and functional diversity in paddy fields. Appl Soil Ecol 149:103489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.103489
Sun J, Zou L, Li W, Yang J, Wang Y, **a Q, Peng M (2018) Rhizosphere soil properties and banana Fusarium wilt suppression influenced by combined chemical and organic fertilizations. Agric Ecosyst Environ 254:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2017.10.010
Lin Y, Ye Y, Wu C, Hu Y, Shi H (2020) Changes in microbial community structure under land consolidation in paddy soils: a case study in eastern China. Ecol Eng 145:105696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.105696
Cai A, Zhang W, Xu M, Wang B, Wen S, Shah SAA (2018) Soil fertility and crop yield after manure addition to acidic soils in South China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 111:61–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-018-9918-6
Lal B, Sharma SC, Meena RL, Sarkar S, Sahoo A, Balai RC, Gautam P, Meena BP (2020) Utilization of byproducts of sheep farming as organic fertilizer for improving soil health and productivity of barley forage. J Environ Manage 269:110765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110765
Louca S, Polz MF, Mazel F, Albright MBN, Huber JA, O’Connor MI, Ackermann M, Hahn AS, Srivastava DS, Crowe SA, Doebeli M, Parfrey LW (2018) Function and functional redundancy in microbial systems. Nat Ecol Evol 2:936–943. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-018-0519-1
Graham EB, Crump AR, Kennedy DW, Arntzen E, Fansler S, Purvine SO, Nicora CD, Nelson W, Tfaily MM, Stegen JC (2018) Multi ’omics comparison reveals metabolome biochemistry, not microbiome composition or gene expression, corresponds to elevated biogeochemical function in the hyporheic zone. Sci Total Environ 642:742–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.256
Zhang H, Huang M, Zhang W, Gardea-Torresdey JL, White JC, Ji R, Zhao L (2020) Silver nanoparticles alter soil microbial community compositions and metabolite profiles in unplanted and cucumber-planted soils. Environ Sci Technol 54:3334–3342. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b07562
Lin Y, Huang G, Zhang Q, Wang Y, Dia VP, Meng X (2020) Ripening affects the physicochemical properties, phytochemicals and antioxidant capacities of two blueberry cultivars. Postharvest Biol Technol 162:111097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2019.111097
Chen S, Zhu Y, Shao T, Long X, Gao X, Zhou Z (2019) Relationship between rhizosphere soil properties and disease severity in highbush blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum). Appl Soil Ecol 137:187–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.02.015
Zhang Y, Wang X, Liu B, Liu Q, Zheng H, You X, Sun K, Luo X, Li F (2020) Comparative study of individual and co-application of biochar and wood vinegar on blueberry fruit yield and nutritional quality. Chemosphere 246:125699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125699
Marcos MS, Bertiller MB, Olivera NL (2019) Microbial community composition and network analyses in arid soils of the Patagonian Monte under grazing disturbance reveal an important response of the community to soil particle size. Appl Soil Ecol 138:223–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.03.001
Liu C, Gong X, Dang K, Li J, Yang P, Gao X, Deng X, Feng B (2020) Linkages between nutrient ratio and the microbial community in rhizosphere soil following fertilizer management. Environ Res 184:109261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109261
Ren C, Zhao F, Kang D, Yang G, Han X, Tong X, Feng Y, Ren G (2016) Linkages of C:N: P stoichiometry and bacterial community in soil following afforestation of former farmland. For Ecol Manag 376:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2016.06.004
Liu J, Sui Y, Yu Z, Shi Y, Chu H, ** J, Liu X, Wang G (2014) High throughput sequencing analysis of biogeographical distribution of bacterial communities in the black soils of northeast China. Soil Biol Biochem 70:113–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.12.014
Guo Z, Wan S, Hua K, Yin Y, Chu H, Wang D, Guo X (2020) Fertilization regime has a greater effect on soil microbial community structure than crop rotation and growth stage in an agroecosystem. Appl Soil Ecol 149:103510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2020.103510
Jiao S, Yang Y, Xu Y, Zhang J, Lu Y (2020) Balance between community assembly processes mediates species coexistence in agricultural soil microbiomes across eastern China. ISME J 14:202–216. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-019-0522-9
Li C, Wang L, Ji S, Chang M, Wang L, Gan Y, Liu J (2021) The ecology of the plastisphere: microbial composition, function, assembly, and network in the freshwater and seawater ecosystems. Water Res 202:117428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.117428
Mukhtar H, Lin C-M, Wunderlich RF, Cheng L-C, Ko M-C, Lin Y-P (2021) Climate and land cover shape the fungal community structure in topsoil. Sci Total Environ 751:141721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141721
Kakumanu M, Cantrell C, Williams M (2013) Microbial community response to varying magnitudes of desiccation in soil: a test of the osmolyte accumulation hypothesis. Soil Biol Biochem 57:644–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.08.014
Lin Y, Ye G, Kuzyakov Y, Liu D, Fan J, Ding W (2019) Long-term manure application increases soil organic matter and aggregation, and alters microbial community structure and keystone taxa. Soil Biol Biochem 134:187–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.03.030
Magoc T, Salzberg SL (2011) FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27:2957–2963. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr507
Zhang S, Sun L, Wang Y, Fan K, Xu Q, Li Y, Ma Q, Wang J, Ren W, Ding Z (2020) Cow manure application effectively regulates the soil bacterial community in tea plantation. BMC Microbiol 20:190. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-020-01871-y
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27:2194–2200. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr381
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10:996–998. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2604
Deng W, Zhang A, Chen S, He X, ** L, Yu X, Yang S, Li B, Fan L, Ji L, Pan X, Zou L (2020) Heavy metals, antibiotics and nutrients affect the bacterial community and resistance genes in chicken manure composting and fertilized soil. J Environ Manage 257:109980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109980
Langfelder P, Horvath S (2008) WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 9:559. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-9-559
Mazhar SH, Li X, Rashid A, Su J, Xu J, Brejnrod AD, Su J-Q, Wu Y, Zhu Y-G, Zhou SG, Feng R, Rensing C (2021) Co-selection of antibiotic resistance genes, and mobile genetic elements in the presence of heavy metals in poultry farm environments. Sci Total Environ 755:142702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142702
Bongiorno G, Bünemann EK, Brussaard L, Mäder P, Oguejiofor CU, de Goede RGM (2020) Soil management intensity shifts microbial catabolic profiles across a range of European long-term field experiments. Appl Soil Ecol 154:103596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2020.103596
Segata N, Izard J, Waldron L, Gevers D, Miropolsky L, Garrett WS, Huttenhower C (2011) Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol 12:R60. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2011-12-6-r60
Nguyen NH, Song Z, Bates ST, Branco S, Tedersoo L, Menke J, Schilling JS, Kennedy PG (2016) FUNGuild: an open annotation tool for parsing fungal community datasets by ecological guild. Fungal Ecol 20:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funeco.2015.06.006
Yang S, Li X, Yao S, Yang X, Jiang X (2020) Correlations between soil metabolomics and bacterial community structures in the pepper rhizosphere under plastic greenhouse cultivation. Sci Total Environ 728:138439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138439
Xu Y, Du A, Wang Z, Zhu W, Li C, Wu L (2020) Effects of different rotation periods of Eucalyptus plantations on soil physiochemical properties, enzyme activities, microbial biomass and microbial community structure and diversity. For Ecol Manag 456:117683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2019.117683
Cui X, Zhang Y, Gao J, Peng F, Gao P (2018) Long-term combined application of manure and chemical fertilizer sustained higher nutrient status and rhizospheric bacterial diversity in reddish paddy soil of Central South China. Sci Rep 8:16554. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-34685-0
Zhu L, Wu Q, Dai J, Zhang S, Wei F (2011) Evidence of cellulose metabolism by the giant panda gut microbiome. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:17714. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1017956108
Zhong Z, Bian F, Zhang X (2018) Testing composted bamboo residues with and without added effective microorganisms as a renewable alternative to peat in horticultural production. Ind Crops Prod 112:602–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.12.043
Tao J, Liu X, Liang Y, Niu J, **ao Y, Gu Y, Ma L, Meng D, Zhang Y, Huang W, Peng D, Yin H (2017) Maize growth responses to soil microbes and soil properties after fertilization with different green manures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:1289–1299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7938-1
Jami E, Mizrahi I (2012) Composition and similarity of bovine rumen microbiota across individual animals. PLoS ONE 7:e33306. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0033306
Bei S, Zhang Y, Li T, Christie P, Li X, Zhang J (2018) Response of the soil microbial community to different fertilizer inputs in a wheat-maize rotation on a calcareous soil. Agric Ecosyst Environ 260:58–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2018.03.014
Rousk J, Baath E, Brookes PC, Lauber CL, Lozupone C, Caporaso JG, Knight R, Fierer N (2010) Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J 4:1340–1351. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2010.58
Tupinambá DD, Cantão ME, Costa OYA, Bergmann JC, Kruger RH, Kyaw CM, Barreto CC, Quirino BF (2016) Archaeal community changes associated with cultivation of Amazon forest soil with oil palm. Archaea 2016:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3762159
Lehtovirta-Morley LE, Ge C, Ross J, Yao H, Nicol GW, Prosser JI (2014) Characterisation of terrestrial acidophilic archaeal ammonia oxidisers and their inhibition and stimulation by organic compounds. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 89:542–552. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6941.12353
Vo N, Tsai TC, Maxwell C, Carbonero F (2017) Early exposure to agricultural soil accelerates the maturation of the early-life pig gut microbiota. Anaerobe 45:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anaerobe.2017.02.022
Suzuki Y, Ida M, Kubota H, Ariyoshi T, Murakami K, Kobayashi M, Kato R, Hirai A, Suzuki J, Sadamasu K (2019) Multiple beta-lactam resistance gene-carrying plasmid harbored by Klebsiella quasipneumoniae isolated from urban sewage in Japan. mSphere 4:1132–1141 https://doi.org/10.1128/mSphere.00391-19
Zhang Y, Hou L, Li Z, Zhao D, Song L, Shao G, Ai J, Sun Q (2020) Leguminous supplementation increases the resilience of soil microbial community and nutrients in Chinese fir plantations. Sci Total Environ 703:134917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134917
Ågren GI, Hyvönen R, Baskaran P (2019) Ectomycorrhiza, friend or foe? Ecosystems 22:1561–1572. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-019-00356-y
Hebbar KP, AGDaPJA (1992) Rhizobacteria of maize antagonistic to fusarium monilii;orme, a soil-borne fungal pathogen: isolation and identification. Soil Biol Biochem 24(10):979–981https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(92)90026-T
Evueh GAaO, N. O.* (2008) Use of phylloplane fungi as biocontrol agent against Colletotrichum leaf disease of rubber (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.). Afr J Biotechnol 7(15):2569–2572 https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB07.757
VandenWymelenberg A, Gaskell J, Mozuch M, Splinter BonDurant S, Sabat G, Ralph J, Skyba O, Mansfield SD, Blanchette RA, Grigoriev IV, Kersten PJ, Cullen D (2011) Significant alteration of gene expression in wood decay fungi Postia placenta and Phanerochaete chrysosporium by plant species. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:4499–4507. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.00508-11
Williams CL, Willard S, Kouba A, Sparks D, Holmes W, Falcone J, Williams CH, Brown A (2013) Dietary shifts affect the gastrointestinal microflora of the giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca). J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl) 97:577–585. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0396.2012.01299.x
Schilling JS, Ai J, Blanchette RA, Duncan SM, Filley TR, Tschirner UW (2012) Lignocellulose modifications by brown rot fungi and their effects, as pretreatments, on cellulolysis. Bioresour Technol 116:147–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.04.018
Singh S, Madlala AM, Prior BA (2003) Thermomyces lanuginosus: properties of strains and their hemicellulases. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:3–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-6445(03)00018-4
Escoriaza G, García Lampasona S, Gomez Talquenca S, Piccoli P (2019) In vitro plants of Vitis vinifera respond to infection with the fungus Phaeoacremonium parasiticum by synthesizing the phytoalexin nerolidol. Plant Cell. Tissue Organ Cult (PCTOC) 138:459–466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-019-01641-3
Spies CFJ, Moyo P, Halleen F, Mostert L (2018) Phaeoacremonium species diversity on woody hosts in the Western Cape Province of South Africa. Persoonia 40:26–62. https://doi.org/10.3767/persoonia.2018.40.02
Ikoyi I, Fowler A, Schmalenberger A (2018) One-time phosphate fertilizer application to grassland columns modifies the soil microbiota and limits its role in ecosystem services. Sci Total Environ 630:849–858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.263
Hamer U, Marschner B (2005) Priming effects in different soil types induced by fructose, alanine, oxalic acid and catechol additions. Soil Biol Biochem 37:445–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.07.037
Kuzyakov Y (2002) Review: Factors affecting rhizosphere priming effects. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 22:66–70. https://doi.org/10.1002/1522-2624(200208)165:4382::AID-JPLN3823.0.CO;2-#
Wu K, Chaparro JM, Badri DV, Bakker MG, Sugiyama A, Manter DK, Vivanco JM (2013) Root exudation of phytochemicals in Arabidopsis follows specific patterns that are developmentally programmed and correlate with soil microbial functions. PLoS ONE 8:e55731. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0055731
Fekete A, Malik AK, Kumar A, Schmitt-Kopplin P (2010) Amines in the environment. Crit Rev Anal Chem 40:102–121. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408340903517495
Huang Y-S, Shen F-T (2016) Bioprospecting of facultatively oligotrophic bacteria from non-rhizospheric soils. Appl Soil Ecol 108:315–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2016.09.004
Cheng Q, Liu Z, Huang Y, Li F, Nengzi L, Zhang J (2020) Influence of temperature on CODMn and Mn2+ removal and microbial community structure in pilot-scale biofilter. Bioresour Technol 316:123968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123968
** Y, Shuling N, Kunyuan T, Qiuyang Z, Hewen D, ChenCheng G, Tianhe Y, Liancheng L, **n F (2019) Characteristics of the intestinal flora of specific pathogen free chickens with age. Microb Pathog 132:325–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2019.05.014
Muleta D, Assefa F, Börjesson E, Granhall U (2013) Phosphate-solubilising rhizobacteria associated with Coffea arabica L. in natural coffee forests of southwestern Ethiopia. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 12:73–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2012.07.002
Sreelatha B, Koteswara Rao V, Ranjith Kumar R, Girisham S, Reddy SM (2017) Culture conditions for the production of thermostable lipase by Thermomyces lanuginosus. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci 6:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjbas.2016.11.010
Withers E, Hill PW, Chadwick DR, Jones DL (2020) Use of untargeted metabolomics for assessing soil quality and microbial function. Soil Biol Biochem 143:107758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2020.107758
Luo X, Yuan X, Wang S, Sun F, Hou Z, Hu Q, Zhai L, Cui Z, Zou Y (2017) Methane production and characteristics of the microbial community in the co-digestion of spent mushroom substrate with dairy manure. Bioresour Technol 32:611–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.11.088
Ganesh C, Kumar, and, Hiroshi, Takagi (1999) Microbial alkaline proteases: from a bioindustrial viewpoint. Biotechnol Adv https://doi.org/10.1016/s0734-9750(99)00027-0
Ma Z, Guo D, Xu X, Lu M, Bardgett RD, Eissenstat DM, McCormack ML, Hedin LO (2018) Evolutionary history resolves global organization of root functional traits. Nature 555:94–97. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25783
Yao L, Wang D, Kang L, Wang D, Zhang Y, Hou X, Guo Y (2018) Effects of fertilizations on soil bacteria and fungi communities in a degraded arid steppe revealed by high through-put sequencing. PeerJ 6:e4623. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.4623
Alfredsen G, Fossdal CG, Nagy NE, Jellison J, Goodell B (2016) Furfurylated wood: impact on Postia placenta gene expression and oxalate crystal formation. Holzforschung 70:947–962. https://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2015-0203
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key Laboratory of State Forestry and Grassland Administration on Conservation Biology of Rare Animals in the Giant Panda National Park, the China Conservation and Research Center for the Giant Panda (KLSFGAGP2020.003), and the Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province (2020YJ0338, 2020ZHCG0044, 21GJHZ0113).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Investigation, methodology, visualization, and writing-original draft: YT. Software, formal analysis, and project administration: JW. Conceptualization: YH. Investigation and project administration: KZ. Methodology: XY. Data curation and software: SC. Investigation and data curation: PP. Investigation and project administration: SL. Investigation and data curation: YY. Conceptualization, supervision, writing-review and editing and project administration: LZ. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Yulan Tan and **g Wang are contributed equally
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, Y., Wang, J., He, Y. et al. Organic Fertilizers Shape Soil Microbial Communities and Increase Soil Amino Acid Metabolites Content in a Blueberry Orchard. Microb Ecol 85, 232–246 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-022-01960-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-022-01960-7